【AI-For-Everyone】02 Build AI Project
0 Reference
| Description | url |
|---|---|
| coursera: ai-for-everyone (2021-10) | https://www.coursera.org/learn/ai-for-everyone/home/week/2 |
1. Workflow for Meachine Learning Project
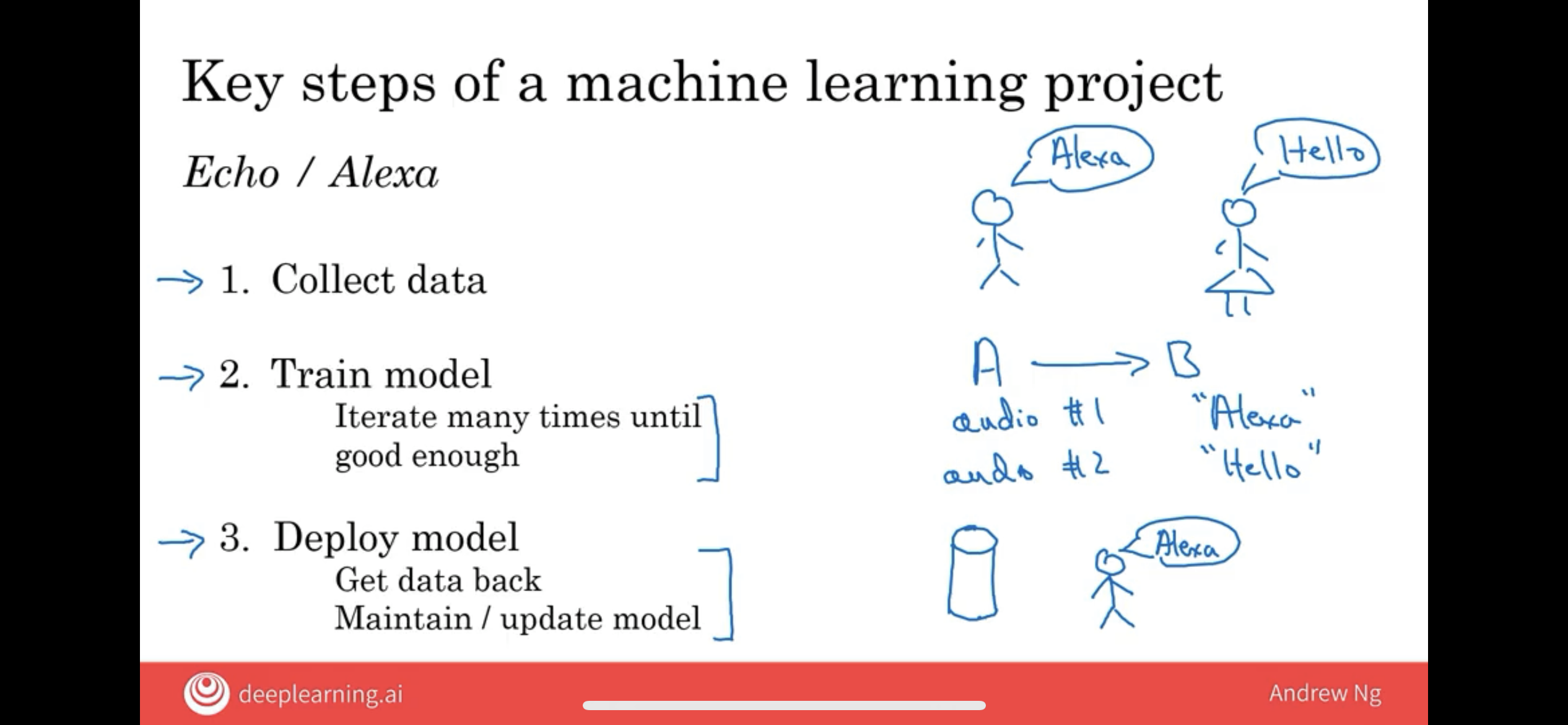
Just for simplicity, I’m going to use Amazon Echo or detecting the Alexa keywords as this running example.
1.1 collect data
If you want to build an AI system or build a machine learning system to figure out when a user has said the word Alexa, the first step is to collect data.
So, that means, you would go around and get some people to say the word “Alexa” for you and you record the audio of that.
1.2 train the model
Having collected a lot of audio data, a lot of these audio clips of people saying either “Alexa” or saying other things, step two is to then train the model.
This means you will use a machine-learning algorithm to learn an input to output or A to B mapping, where the input A would be an audio clip.
So invariably, the team will need to try many times or in AI, we call this iterate many times.
You have to iterate many times until, hopefully, the model looks like is good enough.
1.3 deploy the model
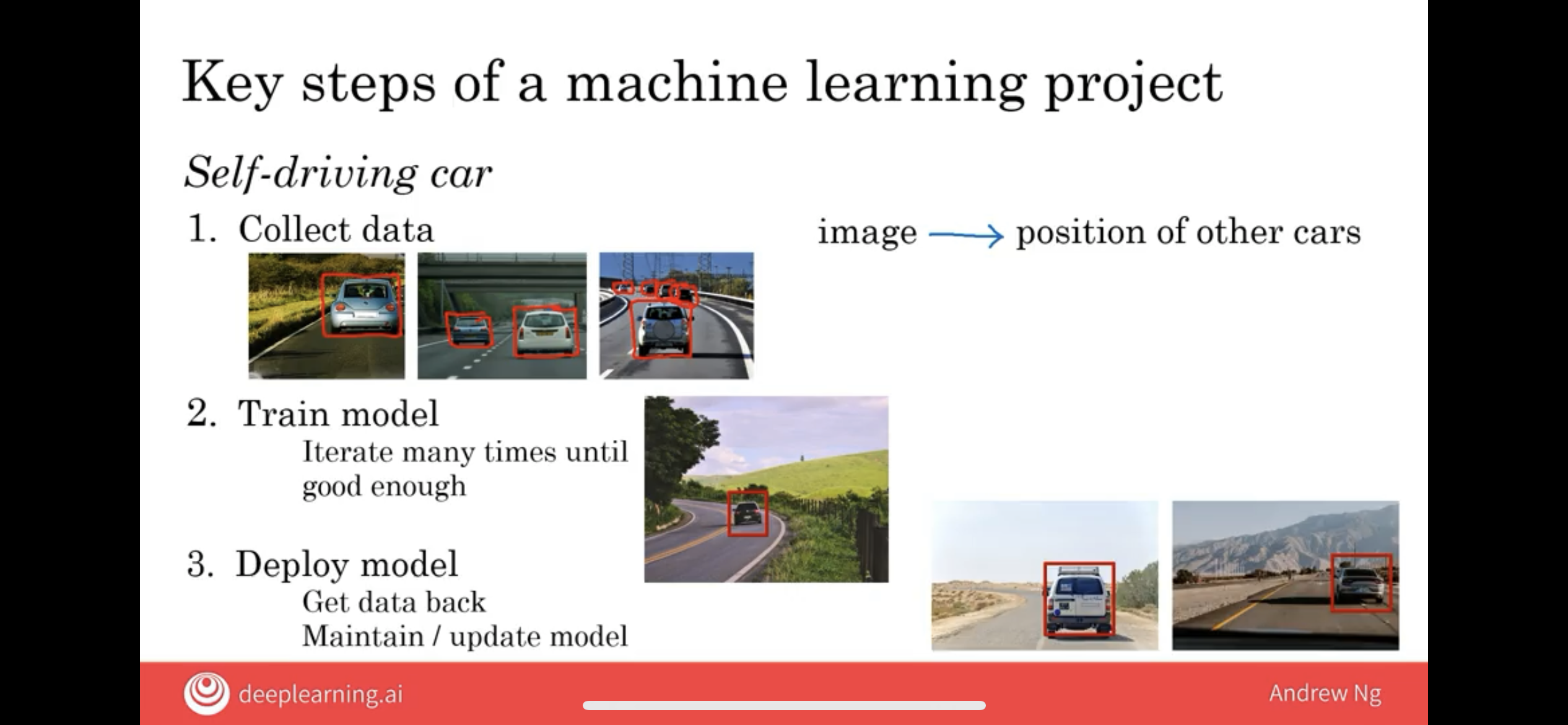
The third step is to then actually deploy the model.
What that means is you put this AI software into an actual smart speaker and ship it to either a small group of test users or to a large group of users.
What happens in a lot of AI products is that when you ship it, you see that it starts getting new data and it may not work as well as you had initially hoped.
So, for example, I am from the UK. So, I’m going to pick on the British. They may find that it doesn’t recognize the speech as well as you had hoped.
you can get data back of cases such as maybe British-accented speakers was not working as well as you’re hoping, and then use this data to maintain and to update the model.
2. Workflow for Data Science Project
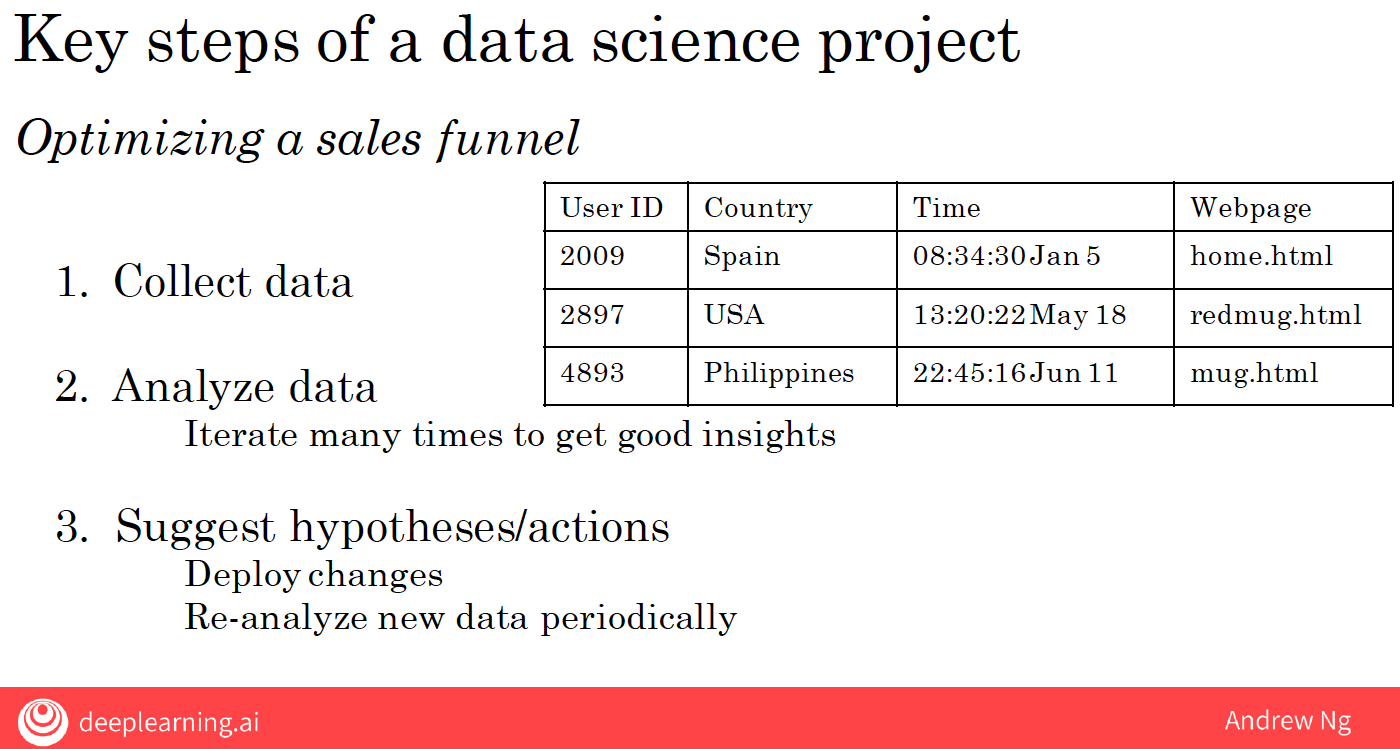
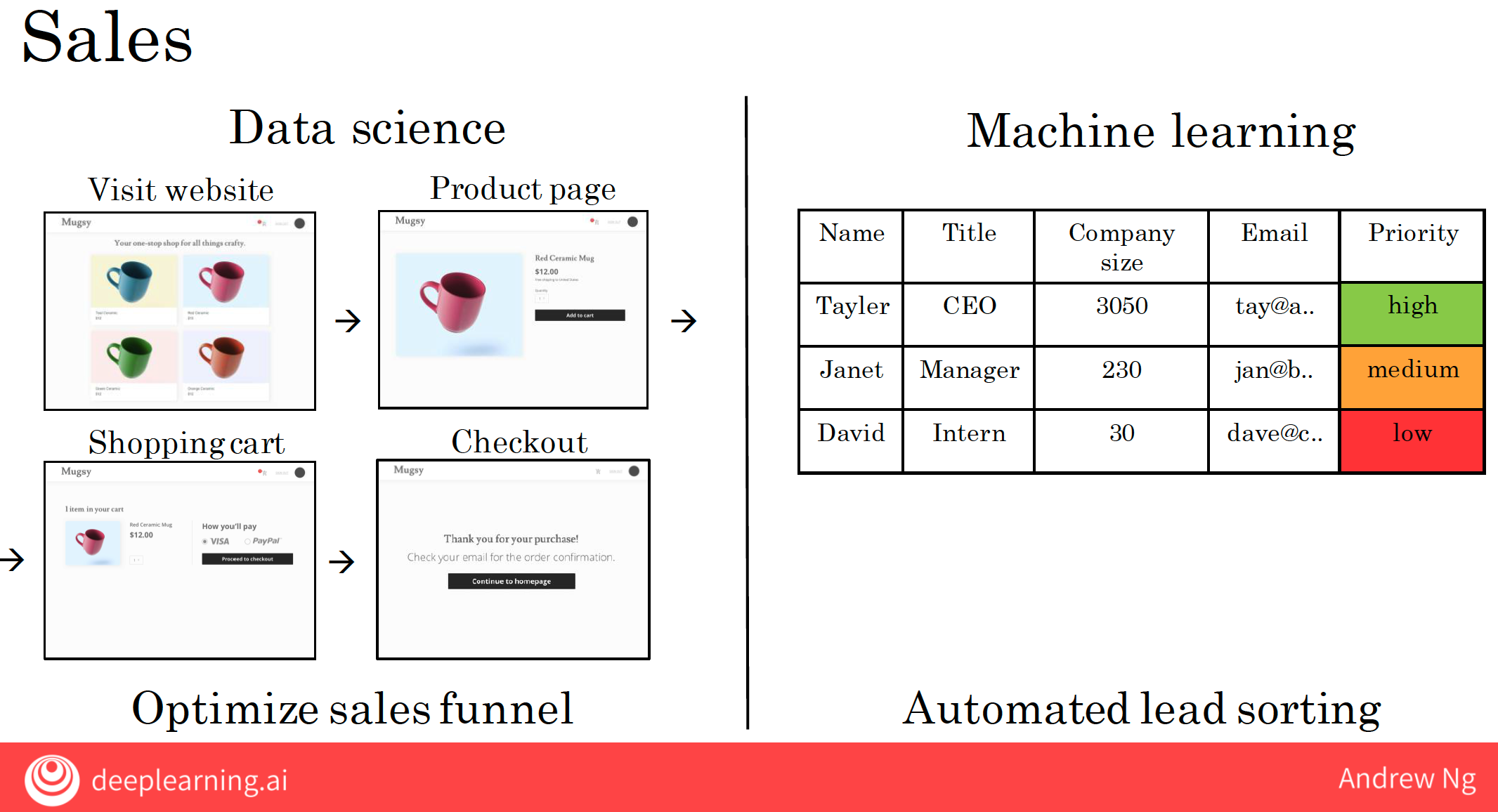
Let’s take a look at one of the steps of a data science project. As our running example, let’s say you want to optimize a sales funnel.
2.1 collect data
So, on a website like the one we saw, you may have a data set that stores when different users go to different web pages.
2.2 analyze the data
Your data science team may have a lot of ideas about what is affecting the performance of your sales funnel.
| possible ideas |
|---|
| international shipping costs |
| there are blips in the data whenever there’s a holiday |
| time-of-day blips wherein countries that observe a siesta |
So, a good data science team may have many ideas and so they try many ideas or will say iterate many times to get good insights.
Finally, the data science team will distill these insights down to a smaller number of hypotheses about ideas
2.3 suggest hypotheses and actions
When you take some of these suggested actions and deploy these changes to your website, you then start to get new data back as users behave differently now that you advertise differently at the time of siesta or have a different check-out policy.
Then your data science team can continue to collect data and we analyze the new data periodically to see if they can come up with even better hypotheses or even better actions over time.
3. how to use data
What’s happened in the last few decades is the digitization of our society.
This availability of data means that there’s a good chance that your job function could be helped with tools like data science or machine learning.
3.1 About Data Science
With the increase in data, we can conduct comprehensive research across multiple factors (such as time, space, business sectors, departments, fields, and even countries). This approach may reveal hypotheses or conclusions that we never previously imagined or realized, allowing us to take actions that enhance efficiency and profit margins.
Overall, data science is an interdisciplinary field aimed at extracting valuable insights from vast amounts of data.
3.2 About Machine Learning
As data increases,
First, for decisions that humans can easily make—such as autonomous driving, defect detection, resume screening, personalized recommendations, and precision agriculture—machine learning can be employed. By training reliable models with extensive specialized data, we can let machines handle these tasks, thereby improving efficiency, accuracy, consistency, and adaptability.
Secondly, due to advancements in computational power and infrastructure, when the volume of learning data is sufficiently large (like with ChatGPT), the breadth and scalability of machine learning models significantly improve. For example, ChatGPT:
- First, it can answer any question posed by anyone.
- Secondly, its breadth of knowledge surpasses that of any individual in history, making the comprehensiveness of its responses unmatched by any human.
3.3 some demo
sales
manufacture
recruite
market
agriculture
summary
| Industry | Data Science | Machine Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Sales | Data science optimizes the sales funnel by analyzing customer interactions and conversion rates. | Machine learning prioritizes leads, helping salespeople focus on high-potential customers, improving efficiency. |
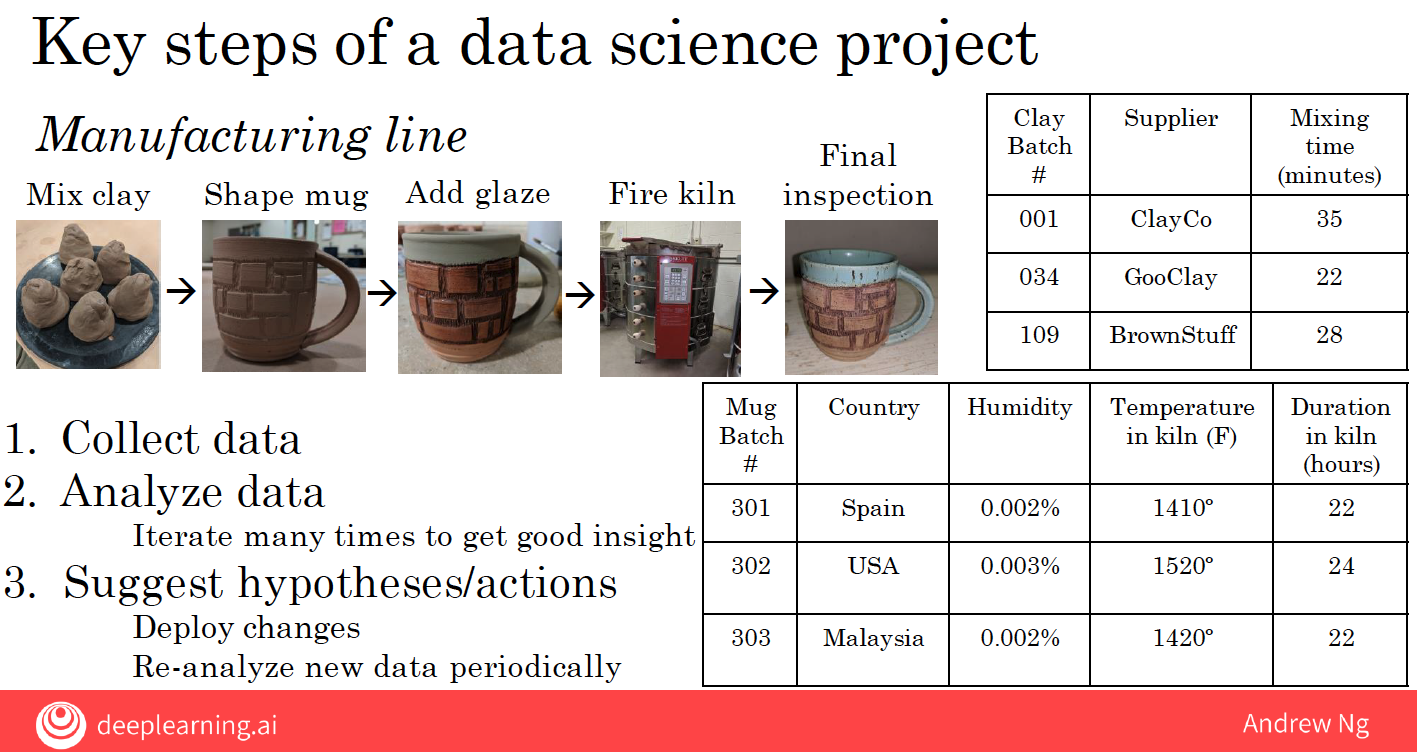
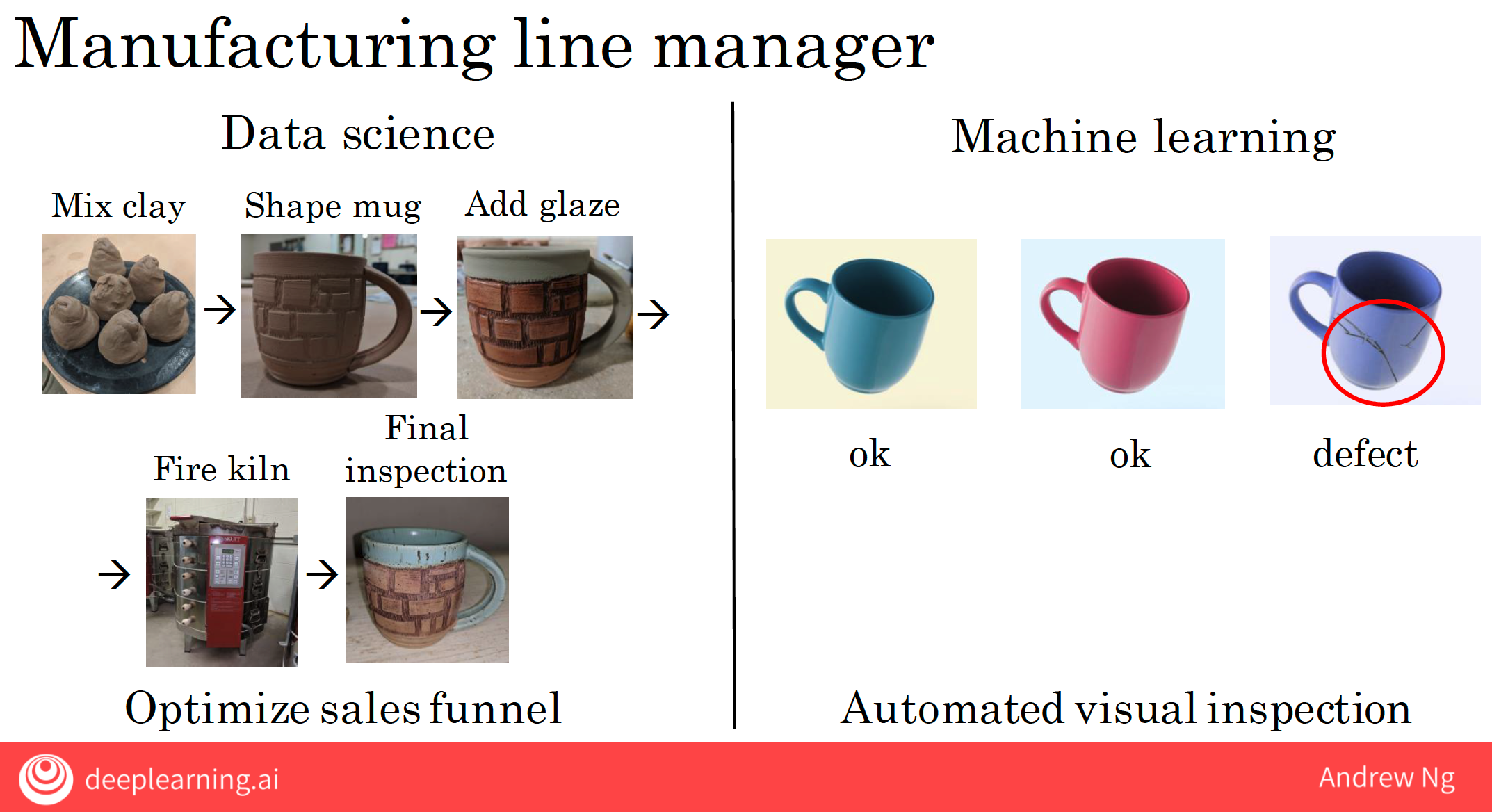
| Manufacturing | Data science helps optimize manufacturing lines by analyzing production data to improve efficiency and reduce waste. | Machine learning automates visual inspection to detect defects in products, reducing labor costs and improving quality. |
| Recruiting | Data science optimizes the recruiting funnel by identifying stages where candidates drop out and suggesting improvements. | Machine learning automates resume screening, making ethical considerations to ensure fairness and avoid bias. |
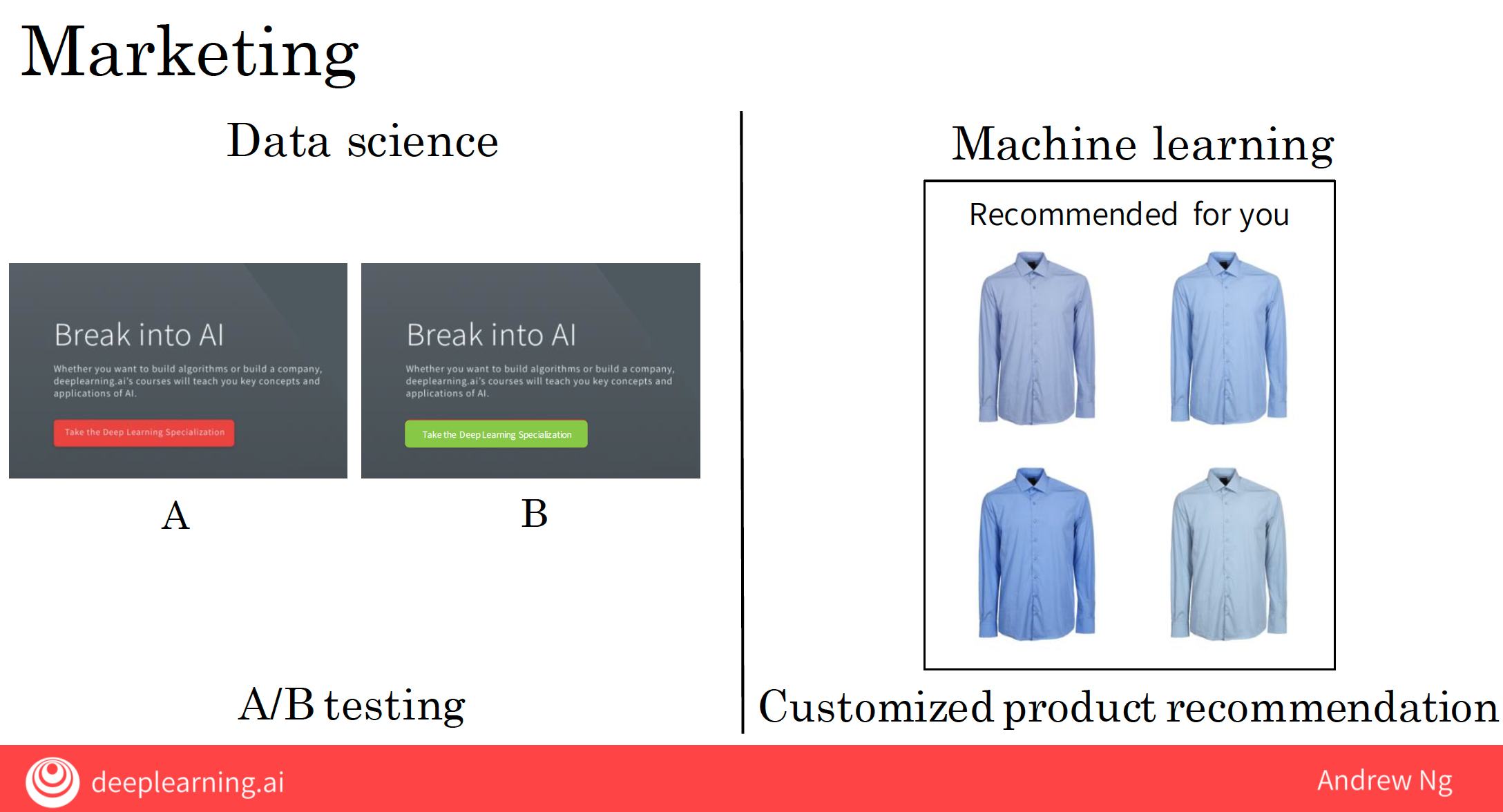
| Marketing | Data science utilizes A/B testing to optimize website performance by comparing different versions to see which performs better. | Machine learning provides customized product recommendations based on user behavior, significantly increasing online sales. |
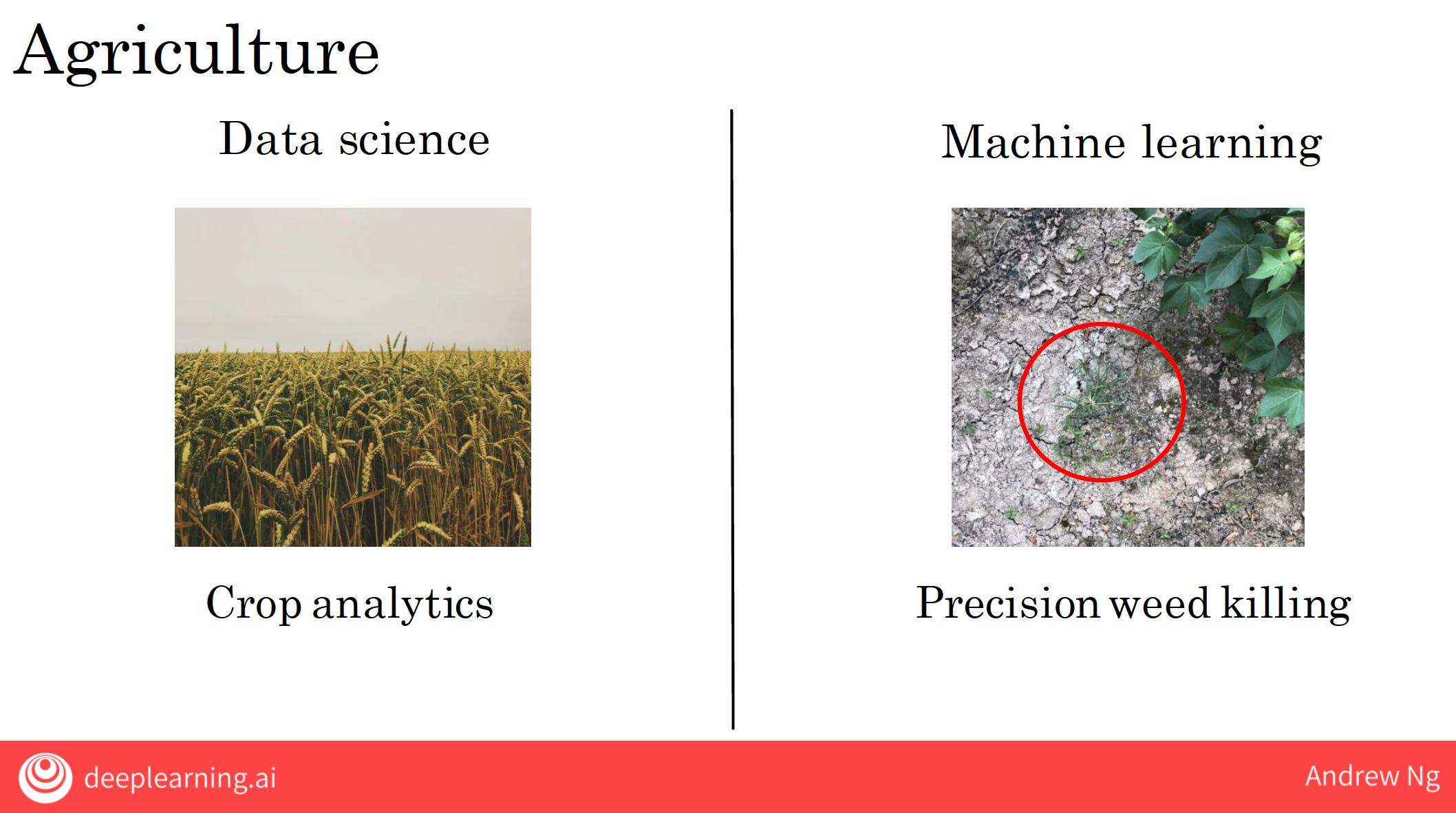
| Agriculture | Data science teams make planting recommendations based on soil conditions, weather, and market data. | Machine learning enables precision agriculture by training models to identify weeds and control them with targeted spraying, reducing the use of weed killers. |
4. select a AI project
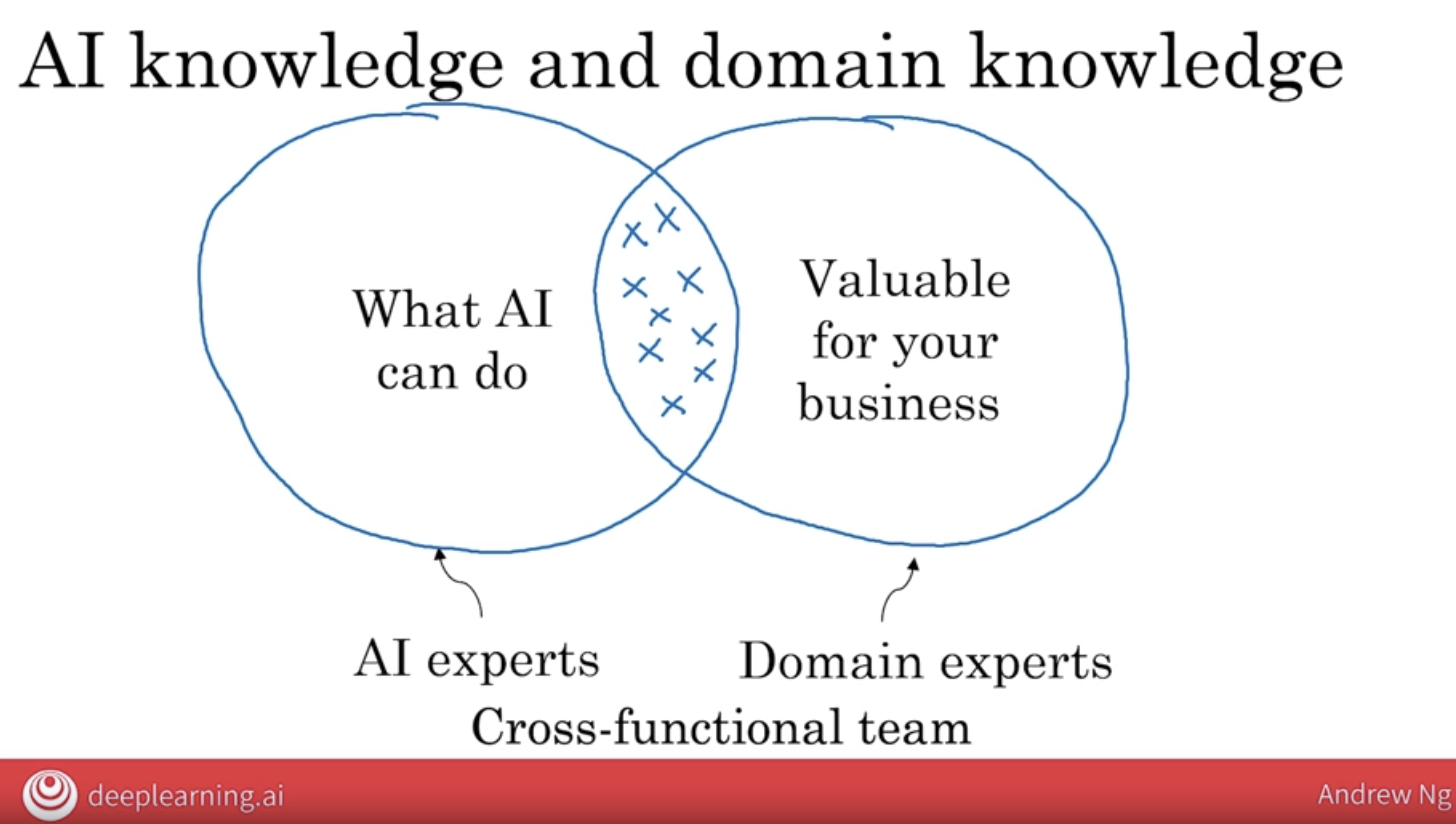
4.1 cross-functional teams brainstorming
I will often bring together a team comprising both people, knowledgeable of AI, as well as experts in your business area to brainstorm together, so that together they can try to identify projects at the intersection of both of these two sets.
Sometimes we also call these cross-functional teams, and that just means a team that includes both AI experts as well as domain experts, meaning experts in your area of business.
4.2 brainstorming framework
think about automating tasks rather than automating jobs. if you look at your business, think about the tasks that people do to see if you can identify just one of them or just a couple of them that may be automatable using machine learning.
what are the main drivers of business value? Sometimes finding AI solutions or data science solutions to augment this can be very valuable.
you can make progress even without big data, even without tons of data.
The amount of data you need is very problem-dependent and speaking with a AI engineer or an AI expert would help you get a better sense.

4.3 three diligences
4.3.1 technical diligence
Technical diligence is the process of making sure that the AI system you hope to build really is doable, really is feasible.
So, you might talk to AI experts about whether or not the AI system can actually meet the desired level of performance.
- is this actually doable with today’s technology?
- how much data is needed to get to this desired level of performance, and do you have a way to get that much data.
- how long it will take and how many people it will take to build a system that you would like to have built.
4.3.2 business diligence
When conducting business diligence, I’ll often end up building spreadsheet financial models to estimate the value quantitatively such as estimate how many dollars are actually saved or what do we think is a reasonable assumption in terms of entries revenue, and to model out the economics associated with a project before committing to many months of effort on a project.
4.3.3 ethical diligence
So, in addition to technical diligence and business diligence, I hope you also conduct ethical diligence and make sure that whatever you’re doing is actually making humanity and making society better off.
4.4 in-house or outsourced
4.4.1 data science and meachine learning
It is nice if eventually you build your own in-house AI team and can also do these projects in-house. Unlike machine learning projects though, data science projects are more commonly done in-house. They’re not impossible to outsource,
4.4.2 Don’t sprint in front of a train,
build the things that are going to be quite specialized to you or completely specialized to you or they’ll allow you to build a unique defensible advantage, but the things that will be industry standard probably some other company will build and it’ll be more efficient for you to just buy it rather than build it in-house.
The train is the industry standard solution, and so, if there’s a company, maybe a startup, maybe a big company or maybe an open-source effort that is building an industry-standard solution, then you may want to avoid trying to run faster and faster to keep ahead of the train.
Because even though you could sprint faster in the short term, eventually, the train will catch up and crash someone trying to sprint in front of a train.
So, when there’s a massive force of an industry-standard solution that is been built, you might be better off just embracing an industry-standard or embracing someone else’s platform rather than trying to do everything in-house.
We all live in a world of limited resources, limited time, limited data, limited engineering resources, and so, I hope you can focus those resources on the projects with our most unique and will make the biggest difference to your company.
5. how you can work with an AI team.
5.1 acceptance criteria
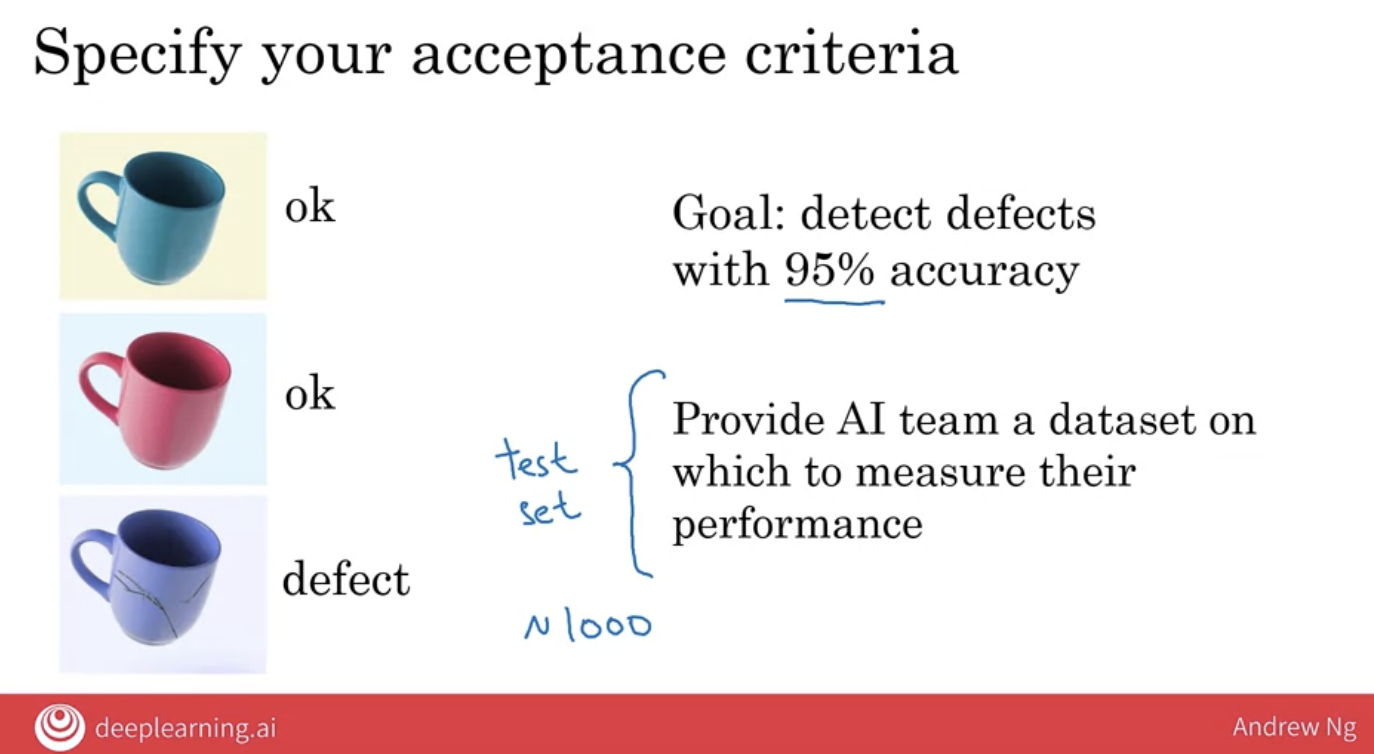
First, it really helps your AI team if you can specify an acceptance criterion for the project.
how do you measure accuracy?
One of the things that an AI team would need is a dataset on which to measure the accuracy.
test set
test set, is a dataset is just a set of pictures like these together with the labels, with the design output B that the first two coffee mugs are okay and the third one is defective.
So, as part of your specification for the acceptance criteria you should make sure that the AI team has a dataset on which to measure the performance so that they can know if they’ve achieved 95% accuracy.
The test set may not need to be too big, maybe a 1,000 pictures will be just fine for this example.
But, if you consult with an AI expert they can give you a better sense of how big the test set needs to be for them to be able to evaluate whether or not they’re getting to 95% accuracy.
AI systems, their performance is usually specified in a statistical way.
So, when specifying your acceptance criteria think of whether your acceptance criteria needs to be specified in a statistical way where you specify on average hour does or what percent of time it has to get the right answer.
5.2 two main datasets
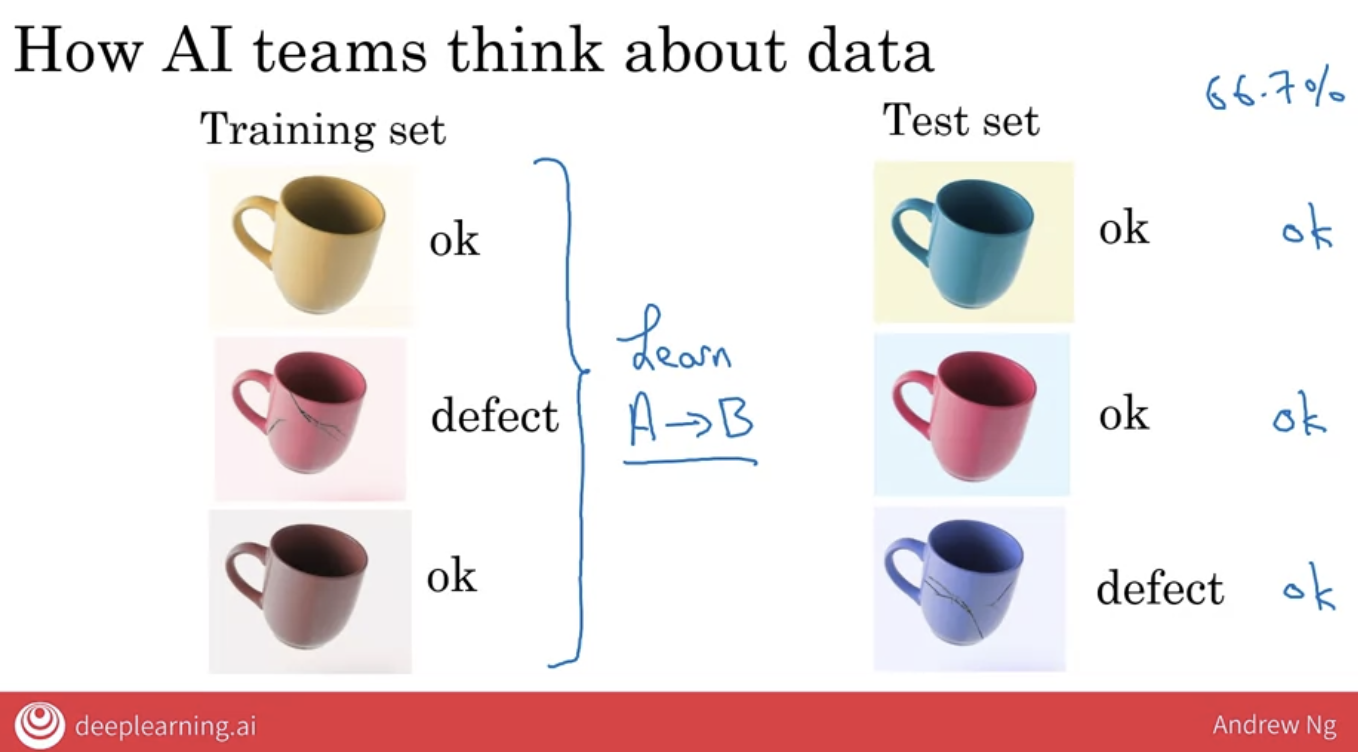
AI teams group data into two main datasets:
5.2.1 train set
the training set is the input to the machine learning software that lets it figure out what is this A to B mapping.
5.2.2 test set:
- this is just another set of images that’s different from the training sets also with the labels provided.
- The way an AI team will evaluate their learning algorithms performance is to give the images into the test set to the AI software and see what the AI software outputs.
third set: development or dev or validation tests
for technical reasons some AI teams will need not just one but two different test sets.
if an AI team asks you for two different test sets it’s quite reasonable to try to provide that to them.
5.3 pitfall: expecting a 100% accuracy from your AI software.
- limitations of ML: So, you may be working on a problem that it’s just very difficult even for today’s machine learning technology.
- ambiguous: someone think is ok, but expert think is not ok.
- So, there are ways to try to make these things better, but, a lot of AI systems are incredibly valuable even without achieving a 100% accuracy.
- So, I will urge you to discuss with your AI engineers what is a reasonable level of accuracy to try to accomplish?
- Then try to find something that passes both technical diligence as well as business diligence without necessarily needing a 100% accuracy.
6. AI tools
We’re fortunate that the AI world today is very open and many teams will openly share idea years with each other. There are great machine learning, open-source tools and frameworks that many teams will use to build their systems.
6.1 open-source AI frameworks
6.2 CPUs and GPUs
CPU stands for central processing unit, and CPUs are made by intel and AMD and a few other companies, this does a lot of the computation in your computer.
GPU stands for graphics processing unit. Historically, the GPU was made to process pictures.
The AI community has had this insatiable hunger for more and more computational power to train bigger and bigger neural networks. And GPUs have proved to be a fantastic fit to this type of computation that we need to have done to train very large neural networks.
So that’s why gpus are playing a big role in the rise of deep learning.
6.3 cloud deployments versus on-perm deployments versus edge deployments
cloud versus on-premises or, for short, on-prem deployments, versus edge deployments.