【AI-For-Everyone】03 Build AI In Company
0 Reference
| Description | url |
|---|---|
| coursera: ai-for-everyone (2021-10) | https://www.coursera.org/learn/ai-for-everyone/home/week/3 |
1. building complex AI product
building complex AI products, where isn’t just using a single machine-learning algorithm to map from A to B, but that learning algorithm is part of a bigger more complex project or product.
1.1 Smart speakers and voice-activated devices
Smart speakers and voice-activated devices like these are taking the world by storm and if you don’t already have one in your home, maybe you’ll buy one someday.
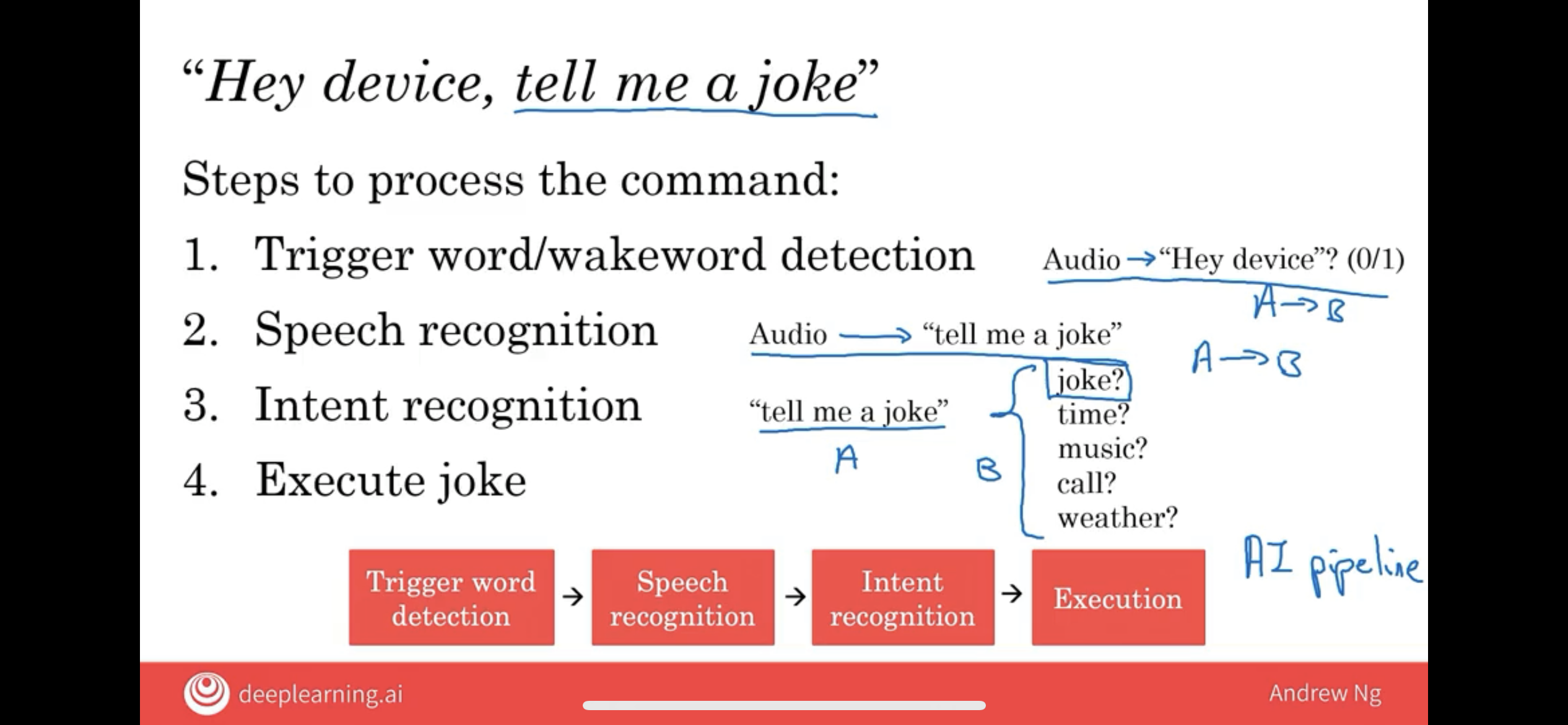
I’d like to go through a case study of how you would write AI software to get a smart speaker to respond to a verbal command such as “Hey device, tell me a joke.”
1.1.1 demo step
1.1.1.1 trigger word detection
Step one is the trigger word or the wake word detection.
Did they just hear the wake word or the trigger word “Hey, Device,” so outputs 0 or one and once it hears the trigger word or wake word,
1.1.1.2 speech recognition
once it hears “Hey device,” it then has to perform step two, which is speech recognition. So what the software has to do is take the audio of what came after “Hey device” and map that to “Tell me a joke.”
1.1.1.3 intent recognition
And so the third step is intent recognition. That means to take whatever you said and to figure out what you actually wanted to do.
Now, the algorithm has to figure out what you actually want by saying these four words.
what intent recognition does is take the four words, the speech recognition’s output, and use another piece of AI software, another A to B mapping, that inputs those four words and outputs which of these five or other intents do you have.
there are lot of ways for you to ask a smart speaker for a joke and a well-designed intent recognition system should recognize most of them.
1.1.1.4 execution
execution of what are the command the user asked the smart speaker to execute.
now that your smart speaker has figured out that you really, really want to hear a joke, the last step is that there will be a software engineer that has written a piece of code to randomly select a joke and to play the joke back through the speaker. In other words, they’ll execute a joke.
1.1.2 another demo: set timer for 10 minutes.
1,2,3: is same 4: execution
- One is extract the duration
- start the timer. preconditon: a specialized software component in the smart speaker that can start a timer with a set duration.
1.1.3 summary
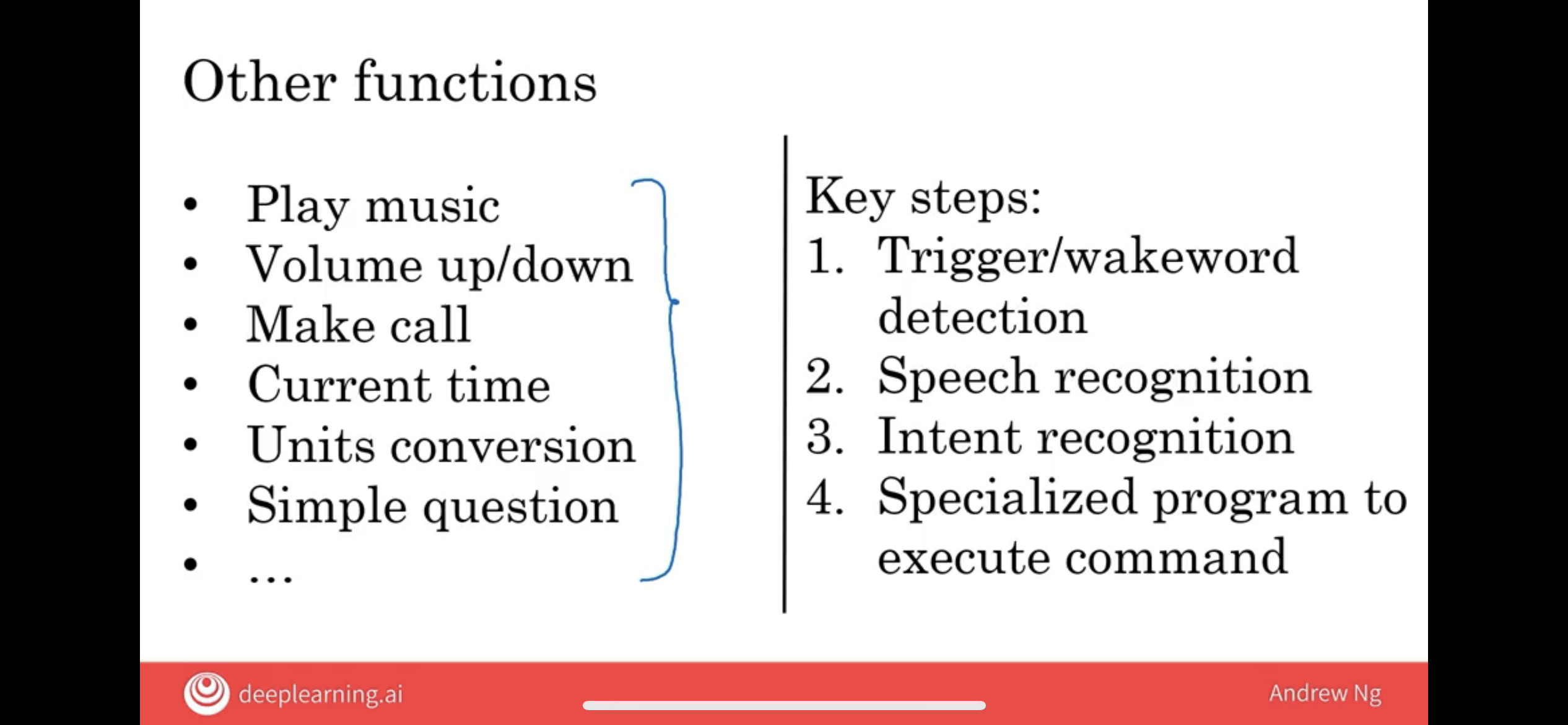
Today’s smart speakers have many functions.
One of the challenges of the smart speaker world is that, if you want your smart speaker to have this many different functions, say, 20 different functions, then you do need software engineering teams to write 20 specialized pieces of software.
So, there are as many software teams as there are functions.
Because on one hand, they can’t do everything. There are lot of things you can’t ask smarts speakers to do such as please call all of my three friends and see when all of them are able to meet for dinner.
Nonetheless, with what they can do using voice to command, these speakers is making life much more convenient for many people.
1.2 self-driving car
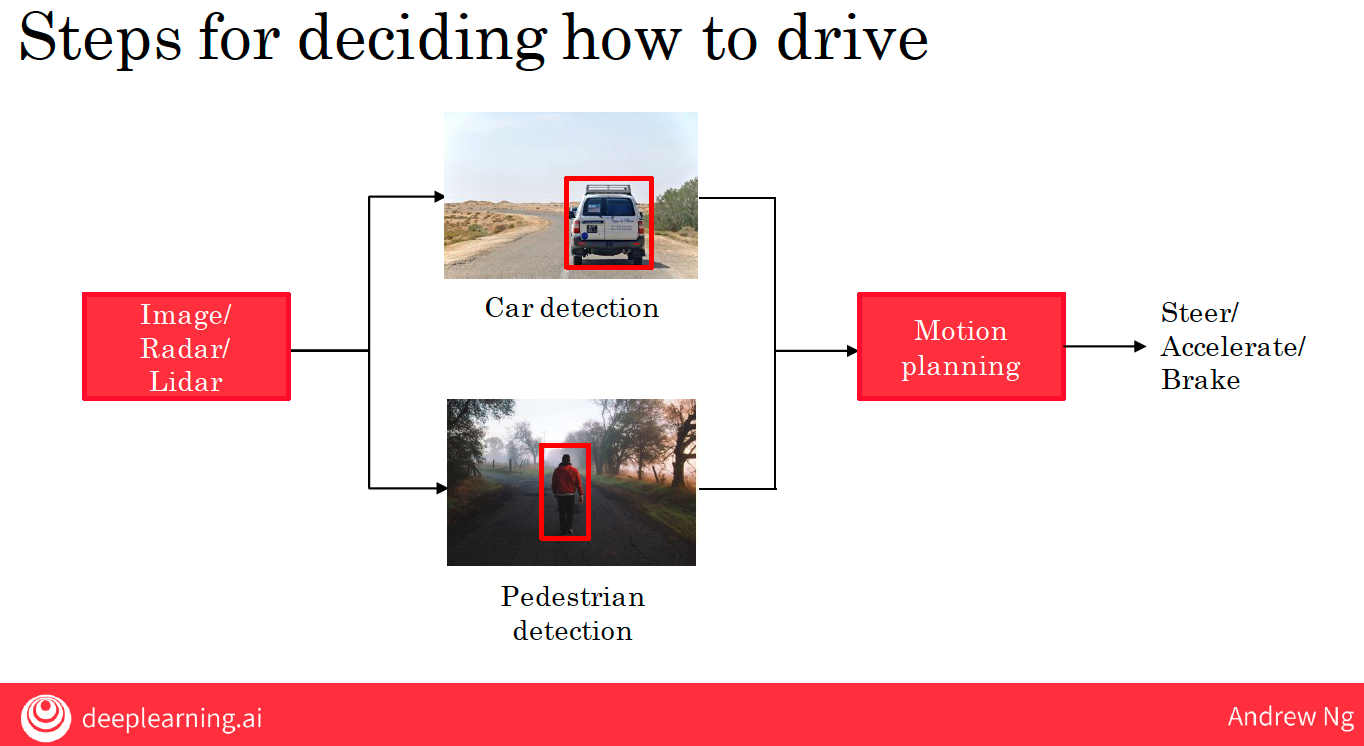
1.2.1 three steps
car detection -> pedestrian detection -> motion planning
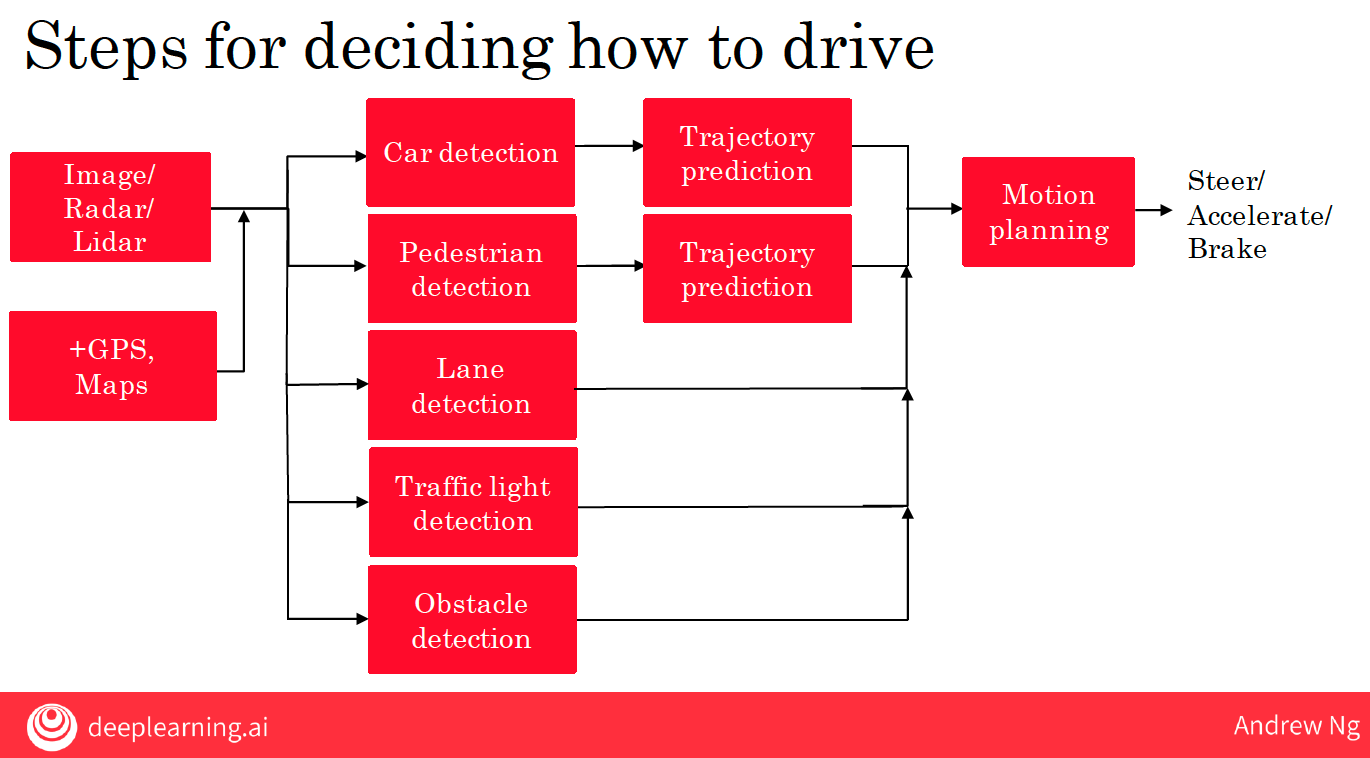
1.2.2 more factors about self-driving car
On a large self-driving car team, it would not be that unexpected to have a team or maybe a few people working on each of the boxes shown here in red, and it’s by building all of these components and putting them together that you can build a self-driving car.
So the process of having four steps in an AI system like this or multiple steps, this is sometimes called an AI pipeline, where you have multiple AI components.
2 Example roles of AI team
One caveat, because AI is evolving so fast, the job titles and various responsibilities are ot yet a 100 percent defined, and they are a little bit different across different companies.
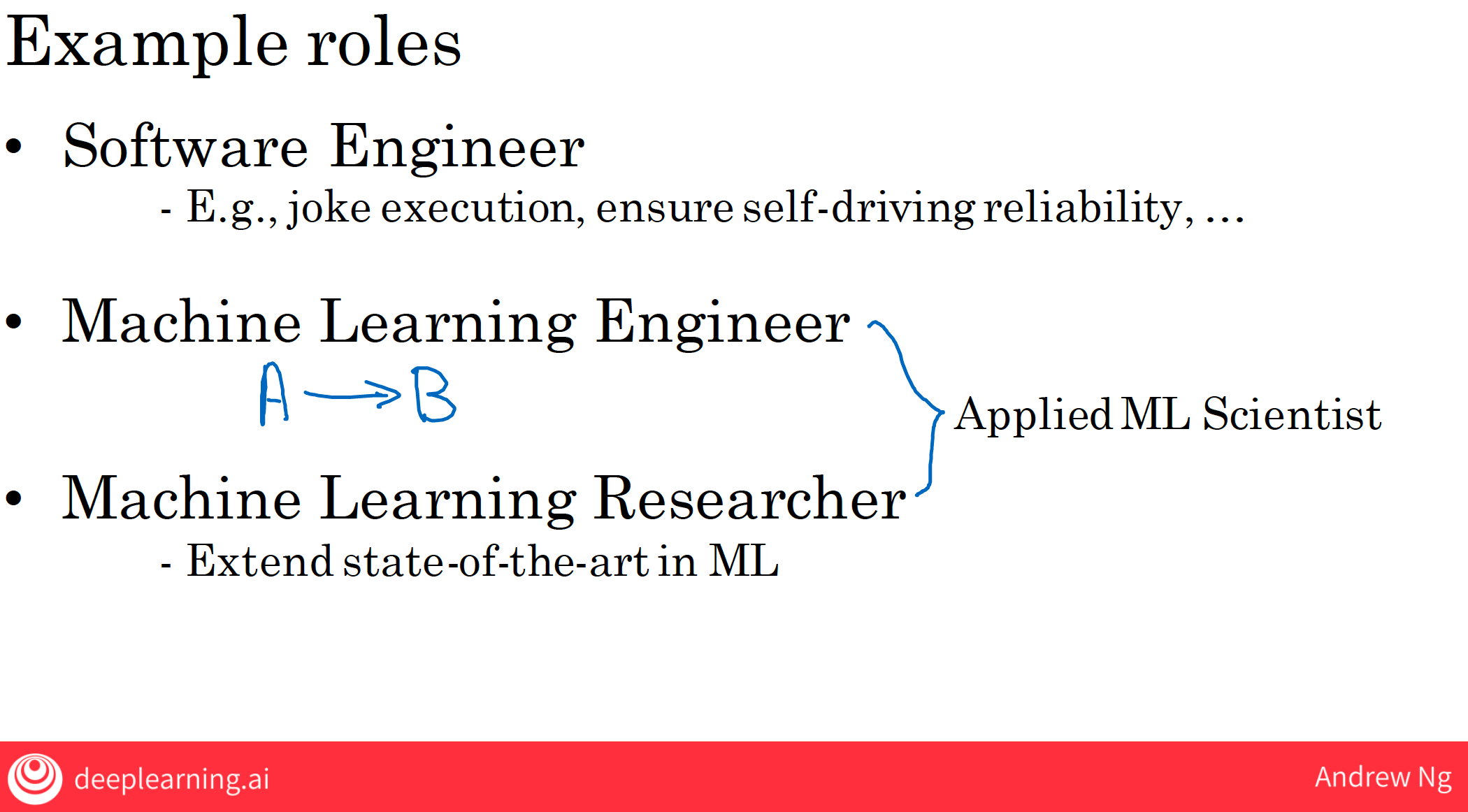
2.1 Software Engineers
- smart speaker: we needed to write specialized software to execute on the joke or to set a timer or to answer questions about today’s weather
- self-driving car: make sure that your self-driving car software is reliable and doesn’t crash.
2.2 Machine Learning Engineer
- write the software responsible for generating the A to B mapping or for building other machine-learning algorithms needed for your product.
- train a neural network or train a deep learning algorithm and work iteratively to make sure that the learning algorithm is giving accurate outputs.
2.3 Machine Learning Researcher
- extend the state of the art in machine-learning
- publish papers or do research
2.4 Applied Machine Learning Scientists
- They are often responsible for going to the academic literature or the research literature and finding the steady VR techniques and finding ways to adapt them to the problem they are facing
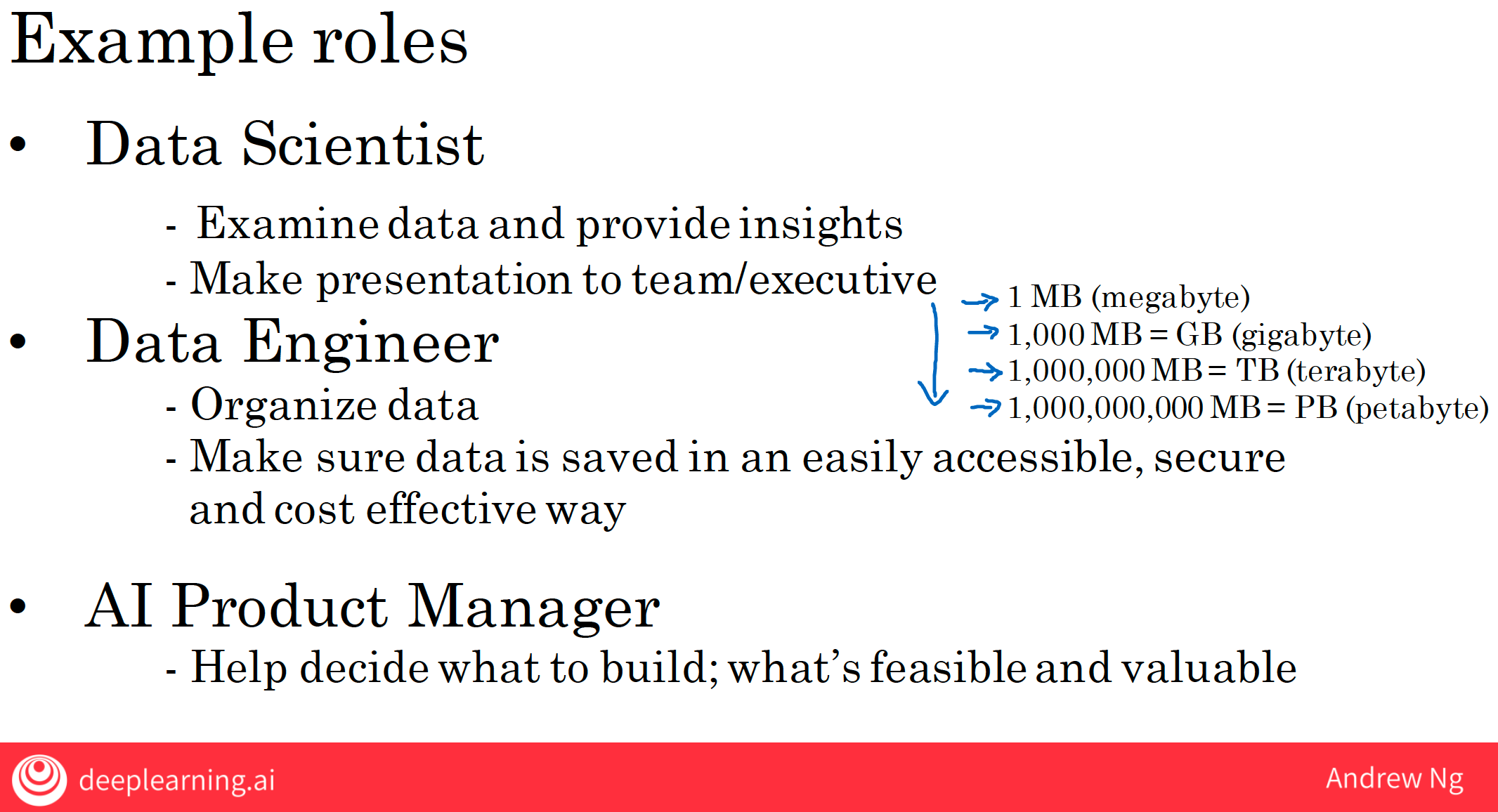
2.5 Data Scientists
- examine data and provide insights, as well as to make presentations to teams or the executives in order to help drive business decision-making.
2.6 Data Engineers
- help you organize your data, meaning, to make sure that your data is saved and is easily accessible, secure and cost-effective way.
2.7 AI Product Managers
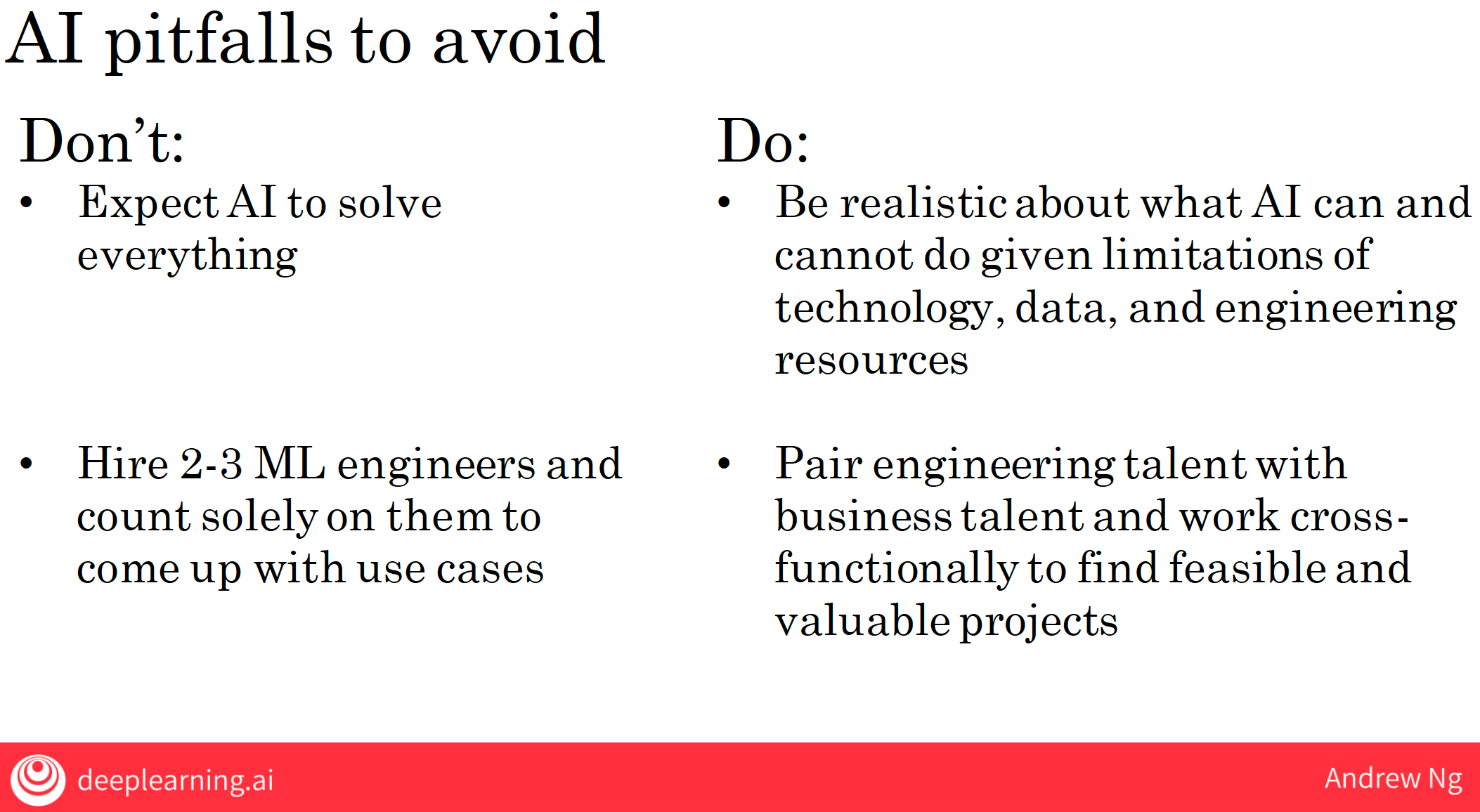
2.8 most important thing is to start with something small
maybe nobody, but yourself, if either you or an engineer working with you has taken some online courses on machine-learning or deep learning or data science, that’s often enough for you by yourself or for you and an engineer to start looking at some smaller volumes of data, start drawing some conclusions or start trading some machine learning models to get going.
3 AI transformation playbook
3.1 execute pilot projects to gain momentum
If you want your company to gain momentum with AI, the most important consideration for the initial project or projects, is for them to be successful rather than necessarily be the most valuable.
Andrew Ng: Google’s speech recognition team -> Google Maps Team -> online advertising team
So, when selecting your initial project, try to pick something that you think has a good chance of success. They can start to fly wheel turning even if it may not be the most valuable project that you could eventually do for the company.
Because the goal of the first few projects is just to gain momentum is also now you see if you can pick something that can show traction within 6 to 12 months.
So you can start to fly wheel turning quickly.
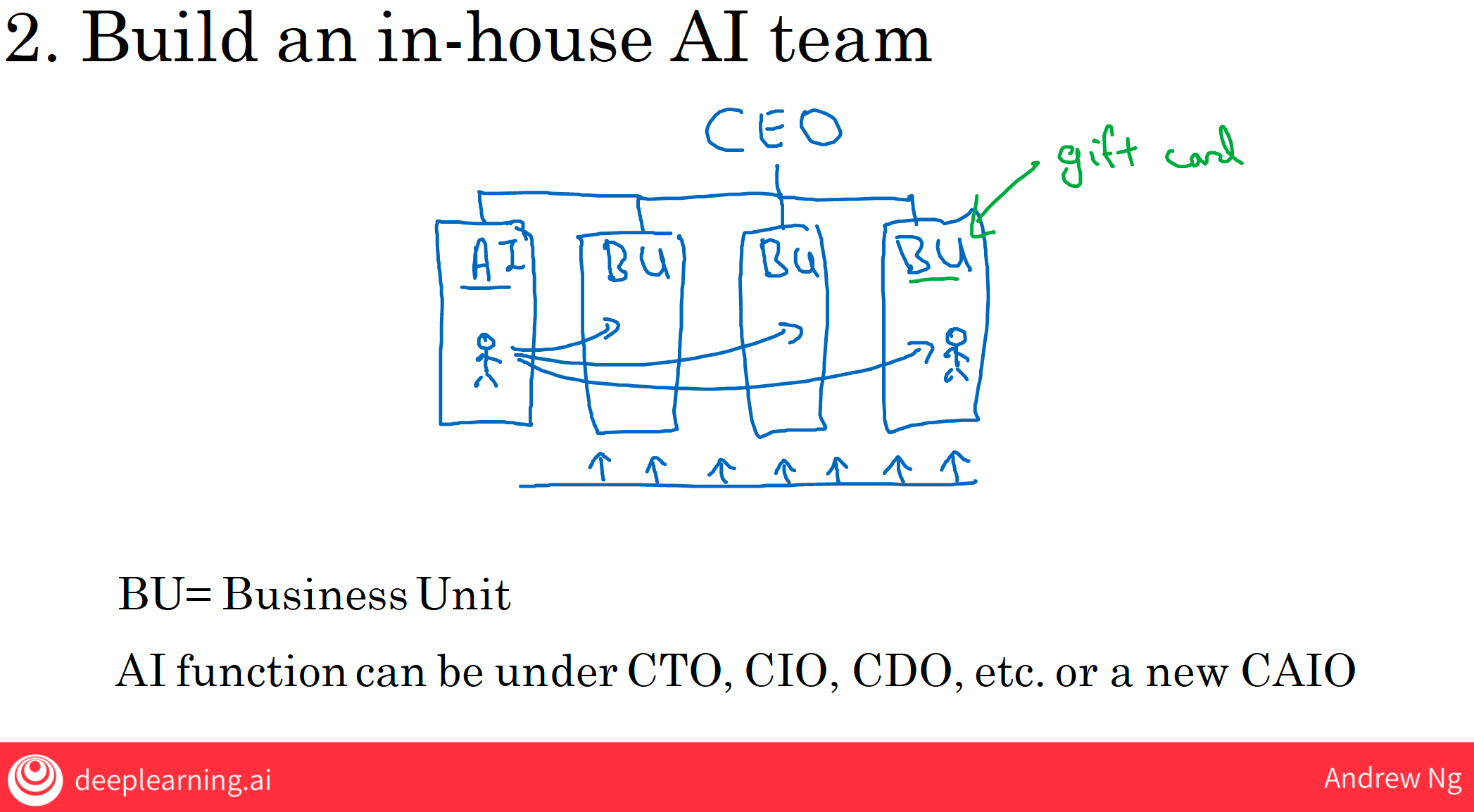
3.2 build an in-house AI team
Now, beyond a certain point, you will need your own in-house AI team to execute a long-term sequence of maybe many dozens of AI projects.
So, what I recommend for most companies is to build a centralized AI team and then to take the talent in the matrix organization and two matrix them into these different business units(BU, reports up to the CEO) to support their work.
3.2.1 Why essentialize the AI?
recruiting, retention of all AI talent:
- it may be very difficult for that business unit leader to hire and retain an appropriately manage their own AI talent.
- I think you also successfully much higher if you find that AI team leader that can be responsible for consistent company wise standards for recruiting, retention.
give the AI team the community
- Have essentialized AI team to give the team the community to talk to each other about how AI applies to your business radical.
build a company wide platforms
- If there are software platforms or other tools or data infrastructure that could be useful for the whole company
- then a single business unit may not have the resources or the incentive to build these company-wide platforms and resources that can support the whole company
3.2.2 organization of AI teams
this new AI business unit can be under the:
- CTO: chief technology officer
- CIO: chief information officer
- CDO: chief data officer or Chief Digital Officer
- CAIO: chief AI officer
if some other senior executive has the right skill set, they could also manage the AI unit.
3.2.3 About ROI of AI team
I think it is hopeful if to get the AI units started the company or the CEO provides funding to build at the AI unit rather than required AI unit to get funding from the business units. Eventually, after the initial investment and after the initial ramp-up, the AI unit will have to show his value that is creating for the business units
but having CEO inject funding at the outset so they can get going, will often help you get that initial momentum much faster.
3.3 provide broad AI training
Now, for a company that become good at AI, is not just that you need engineers to know AI, you need multiple people at multiple levels of the company to understand how AI interacts with their roles. 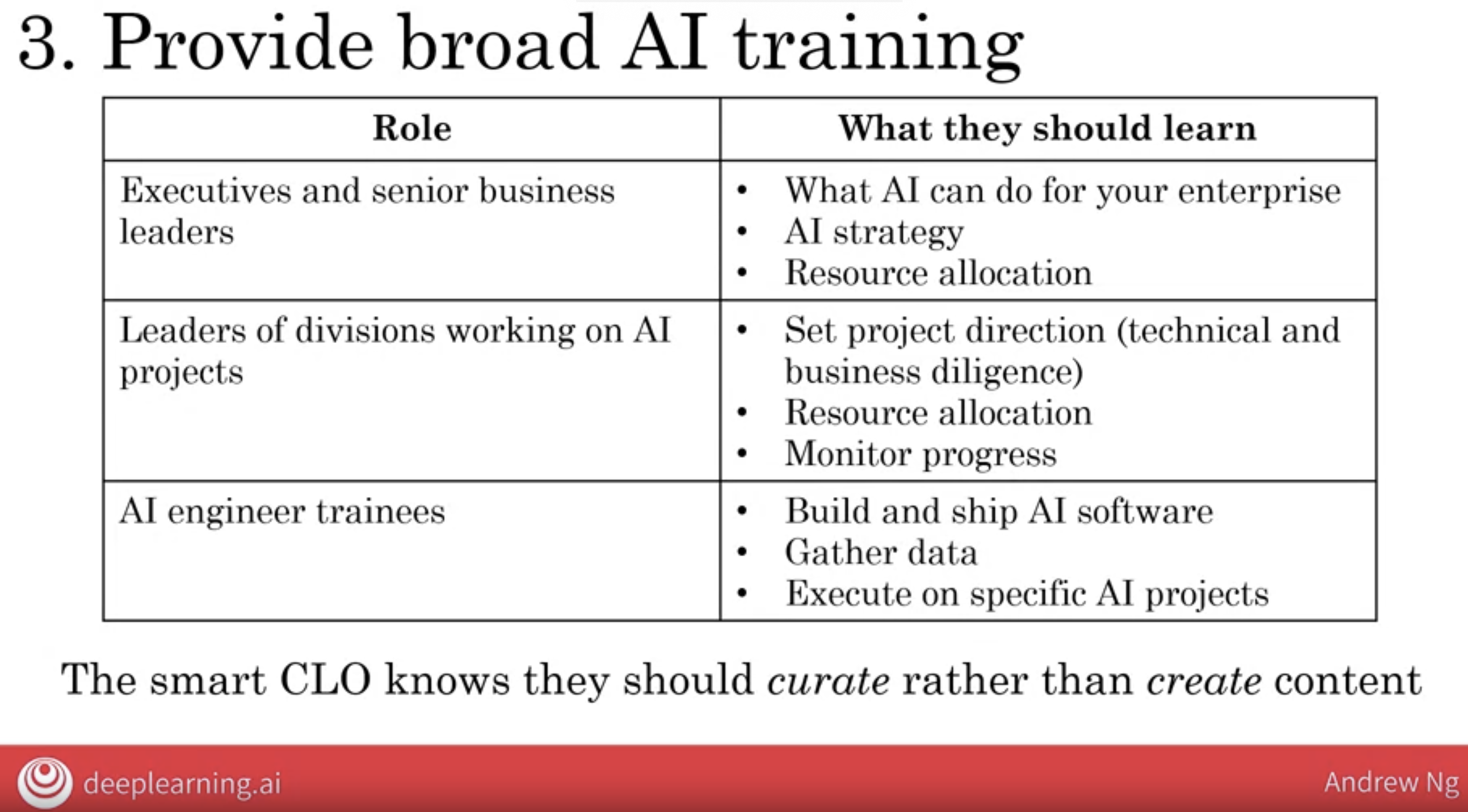
3.3.1 for executives and senior business leaders
I recommend that they learn what AI can do for your enterprise, that they learned the basics of these of AI strategy and they learned enough about AI to make resource allocation decisions.
maybe at least 4 hours of training is enough.
3.3.2 Leaders of divisions work on AI projects
I think these leaders would need to understand how to set project directions.
So how the conduct technical and business diligence how to make resource allocation decisions at the division level as well as how to track and monitor progress of AI projects.
maybe at least 12 hours of training is enough.
3.3.3 for existing engineering workforce
but I will also not underestimate the importance and the impact of training of your existing engineering workforce with AI skills for a software engineer to become proficient at AI .
I’m seeing many companies provide training to help engineers learn to build and ship AI software to gather and managed data as was helped them become effective at executing on specific AI projects.
maybe at least a 100 hours of training is enough.
3.3.4 for continuous learning organization
Thanks to the rise of online digital content, ranging from of course, online courses to also books and YouTube videos and blog posts.
There is a lot of great content online about all of these subjects.
a good CLO should work of experts to curate this type of content and motivated teams to complete these learning activities rather than necessarily create contents which is much more expensive thing to do.
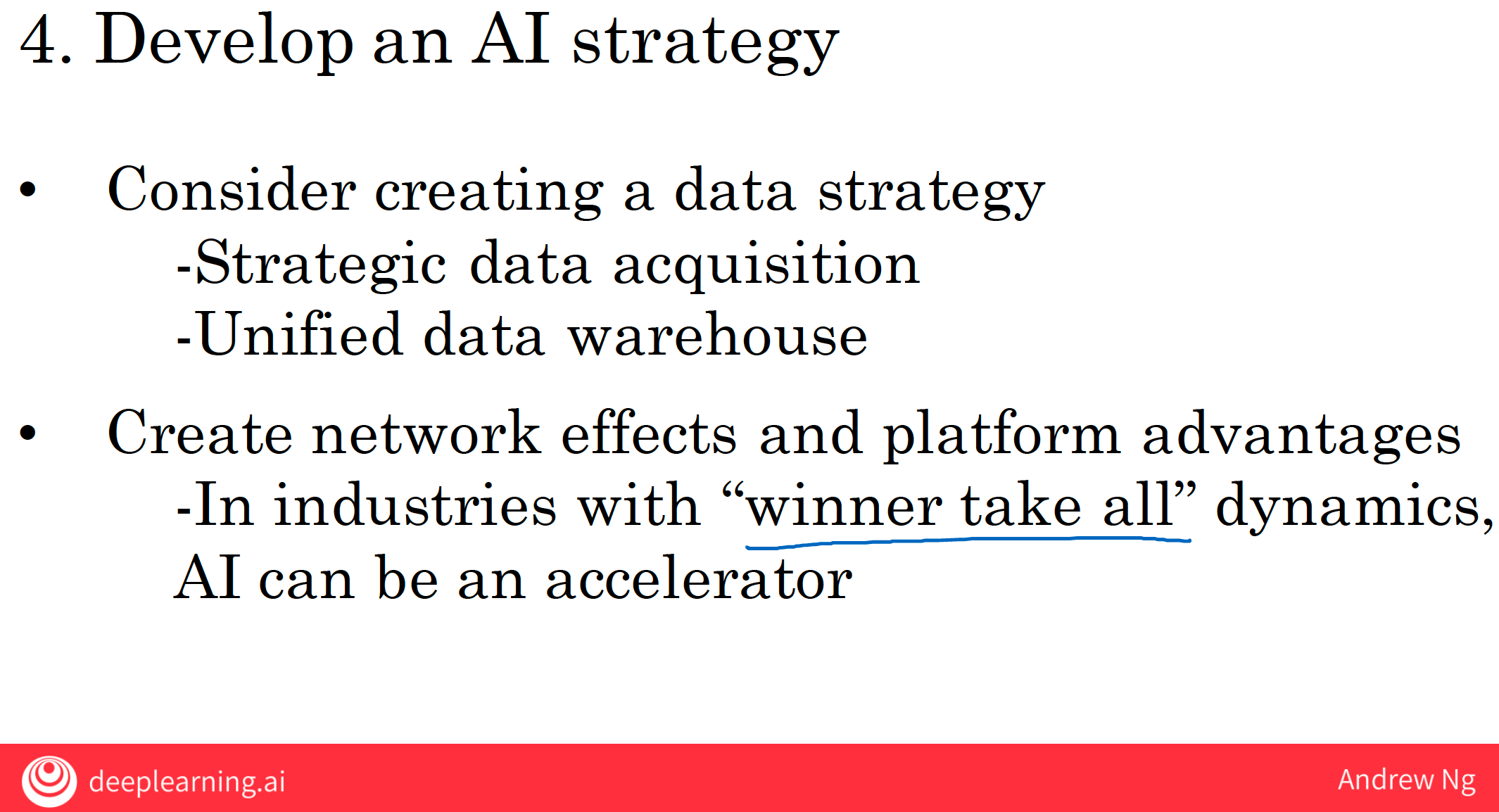
3.4 developing the AI strategy
- Difficult Assets
- create advantage to industry vertical
- virtuous cycle of AI
- strategic data acquisition
- unified data warehouse
- recognize what data is valuable, what is not
- create network effect and platform advantages
3.4.1 Why AI strategy is step four?
One unusual part of this playbook is that developing the AI strategy is step four, not step one.
But I found that companies that try to define the strategy as step one before getting your feet wet, before trying out AI and knowing what it feels like to build an AI project.
Companies like that tend to end up with sometimes very academic strategies that are sometimes not true to life.
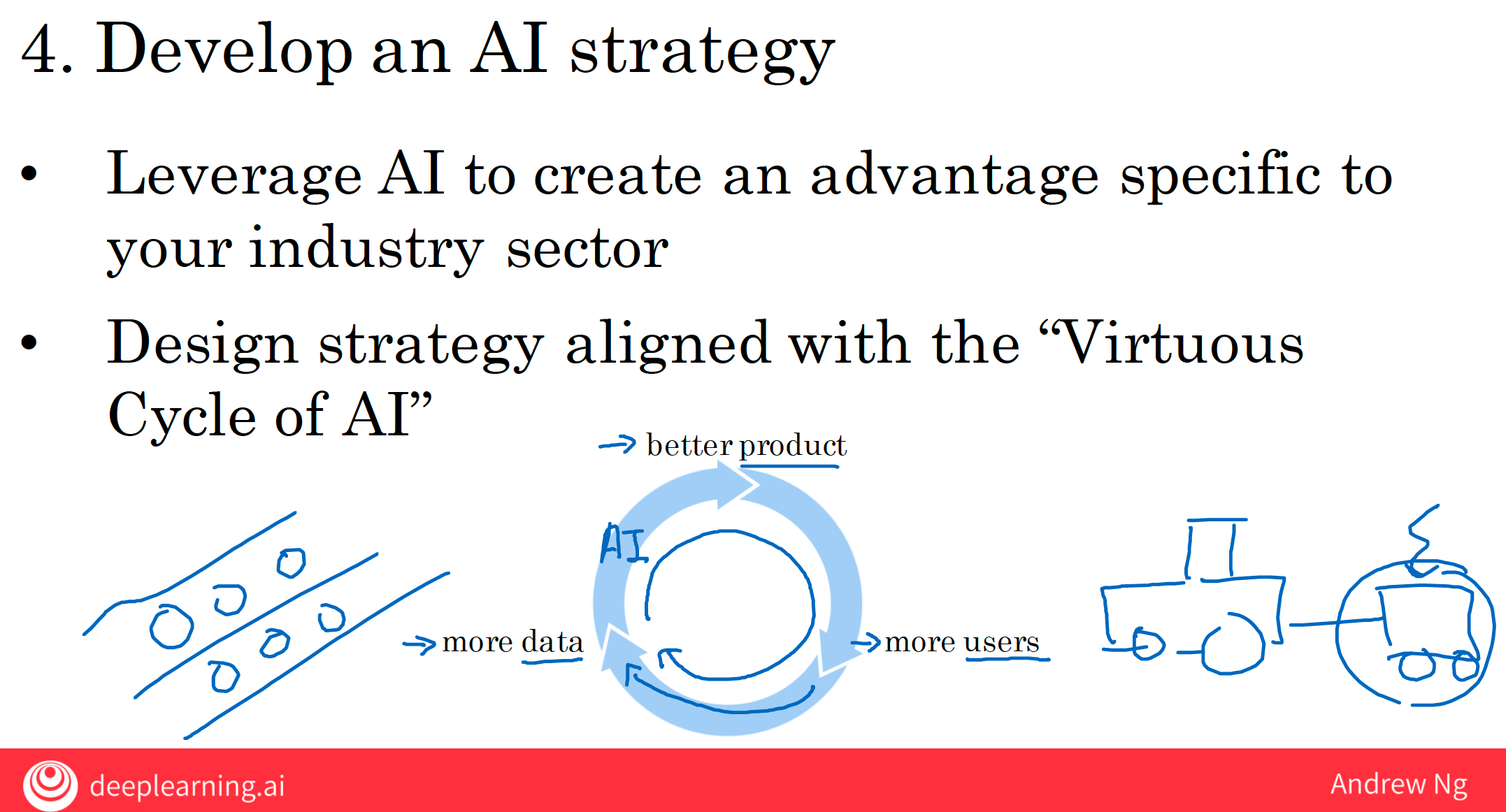
3.4.2 the Virtuous Cycle of AI
If a company has a better product, maybe a slightly better product, then that web search engine can acquire more users. And having more users means that you collect more data, because you get to observe what different users click on when they search for different terms. And that data can be fed into an AI engine to produce an even better product.
So this means that, the company with a somewhat better product ends up with even more users, ends up with even more data, and does an even better product with this link being created by modern AI technology.
And it makes it very difficult for a new entrant to break into this self reinforcing positive feedback loop called the Virtuous Cycle of AI.
Fortunately though, this Virtuous Cycle of AI can be used by smaller teams entering new verticals as well. So I think today it’s very difficult to build a new web search engine to compete with Google, or Baidu, or Bing, or Yandex. But if you are entering a new vertical, a new application area where there isn’t an entrenched incumbent.
Then you might be able to develop a strategy that lets you be the one to take advantage of this virtuous cycle.
3.4.3 Demo: Blue River
So they started to collect pictures of heads of cabbage and weeds around the cabbage. Once they had enough data, start off with a small data set, they could train a basic product.
And the first product, frankly, wasn’t that great, it was trained on a small data set. But it kind of worked well enough to start to convince some users to start to use their product. To tow this machine behind a tractor in order to start cooling weeds for the farmers. And once this thing was running around the farms, through the process of taking pictures of heads of cabbage and killing off weeds, they naturally acquired more and more data.
And over the next few years, what they did was, they were able to enter this positive feedback loop where having more data allows you to have a better product, have a better product allows you to convince more farmers to use it, and having farmers use it, allows you to collect more data. And over several years entering a virtuous cycle like this, can allow you to collect a huge data asset that then makes your business quite defensible.
3.4.4 About large tech companies are very good at AI
One more piece of advice, a lot of people think that some of the large tech companies are great at AI, and I think that’s true. Some of the large tech companies are very good at AI. But this doesn’t mean you need to or should try to compete with these large tech companies on AI in general. Because a lot of AI needs to be specialized or verticalized for your industry sector.
And so for most companies, it’ll be in your best interest to build AI specialized for your industry, and to do great work on AI for your application areas. Rather than try to compete or feel like you need to compete left and right with the large tech companies on AI over the place, which just isn’t true for most companies.
3.4.5 About faith and confidence
if AI can be used to help you with growing faster, for example, with accelerating user acquisition. Then that can perhaps translate into a much bigger chance that your company will be the one to succeed in this business vertical.
3.4.6 About data acquisition
Leading AI companies are very good at strategic data acquisition.
For example, some of the large consumer facing AI companies will launch services like a free email service, or a free photo sharing service, or many other free services that do not monetize.
But allows them to collect data in all sorts of ways that lets them learn more about you, so they can serve you more relevant ads and thereby monetize the data in a way that is quite different than direct monetization of that product.
The way you acquire data is very different depending on your industry vertical.
But I have been involved in what feels like these multi-year chess games, where other corporate competitors and I play multi-year games to see who can acquire the most strategic data assets.
3.4.7 About building a unified data warehouse
Because this increases the odds that an engineer or a piece of software can connect the dots and spot the patterns
3.4.8 About your already existing process
between how an elevated temperature in manufacturing today, may result in a faulty device that leads to a customer complaint two months in the future.
Thus letting you go back to improve your manufacturing processes, there are many examples of this in multiple industries.
3.4.9 About your already existing corporate strategy.
AI capabilities can also help augment existing elements of a broader corporate strategy.
About AI for an entrenched incumbent
In industries with winner take all dynamics, AI can be a huge accelerator.
3.5 develop internal and external communications
AI can change a company and its products, and it’s important to communicate appropriately with the relevant stakeholders about this.
4 AI pitfalls
5 AI initial steps
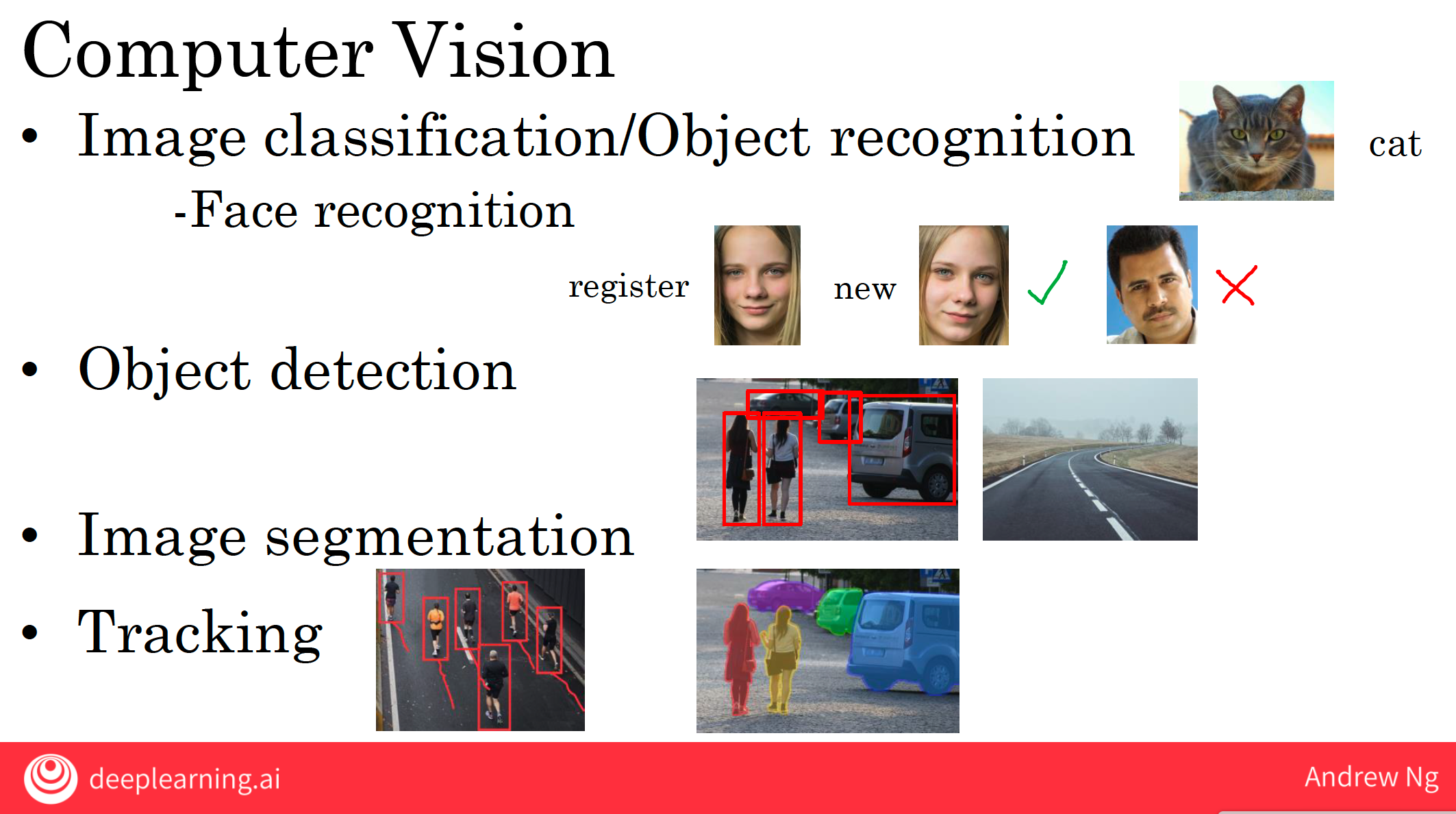
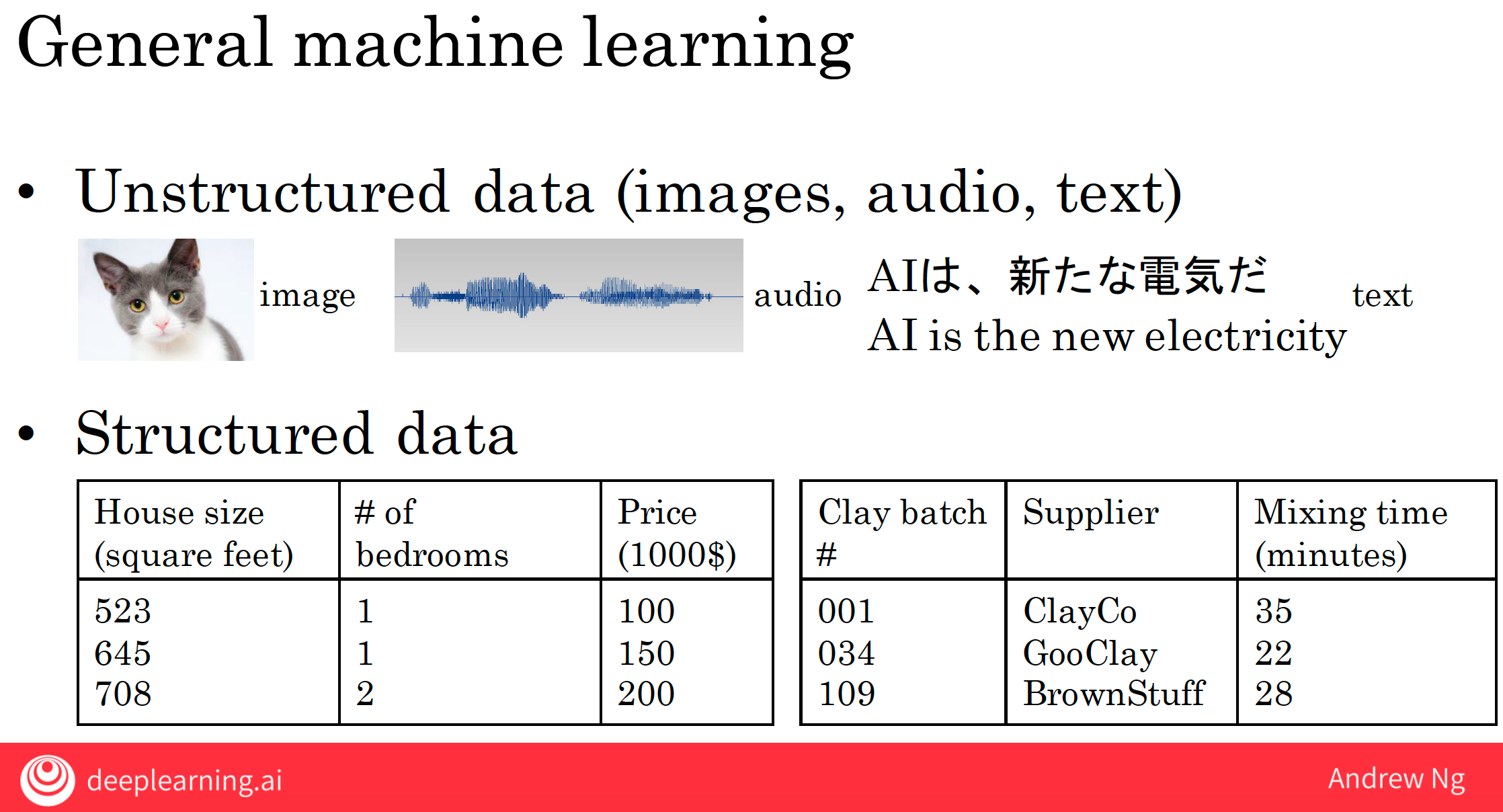
6 AI application areas
7 Major AI techniques
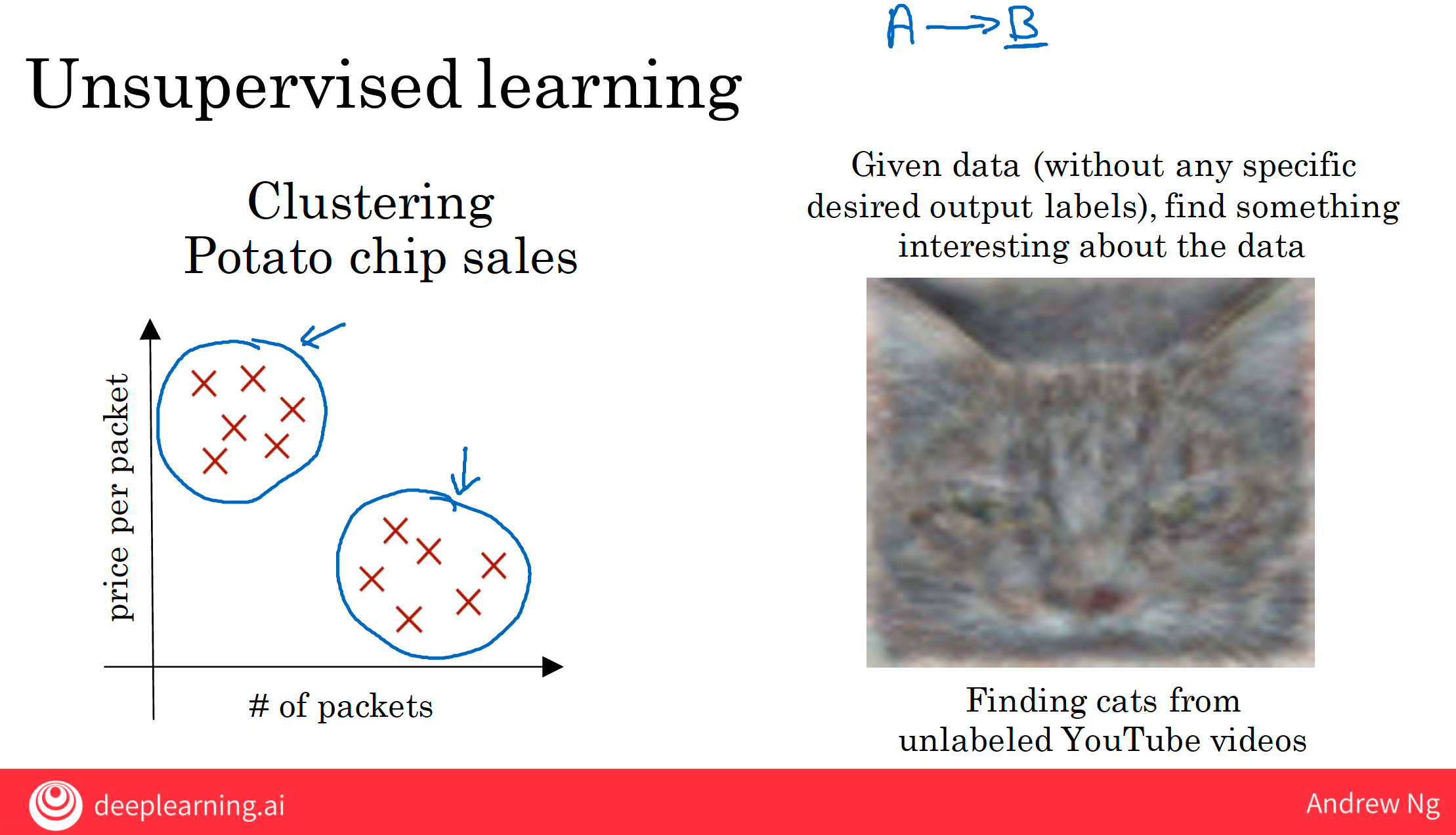
7.1 unsupervised learning
Given data like this, a clustering algorithm will say that it looks like you have two clusters in your data. Some of your customers tend to buy relatively inexpensive potato chips, but buy a lot of packets.
A clustering algorithm looks at data like this, and automatically groups the data into two clusters or more clusters, and is commonly used for market segmentation. And will help you discover things
It’s hard to visualize exactly what an AI algorithm is thinking sometimes,
Now, we have pretty much no idea how the biological brain works, and so to realize this vision, we’ll take major breakthroughs in AI than none of us know yet today how to realize. But many of us hold a lot of hope for the future of unsupervised learning.
But the value today of unsupervised learning is so a lot smaller than the value created through supervised learning.
7.2 Transfer Learning
Where transfer learning really shines is if having learn from a very large dataset of car detection, task A, you can now do pretty well on golf cart detection, even though you have a much smaller golf cart dataset. Because some of the knowledge it has learned from the first task, of what the vehicles look like, what the wheels look like, how the vehicles move. Maybe that will be useful also for golf cart detection.
Transfer learning doesn’t get a lot of press, but it is one of the very valuable techniques in AI today. And for example, many computer vision systems are built using transfer learning, and this makes a big difference to their performance.
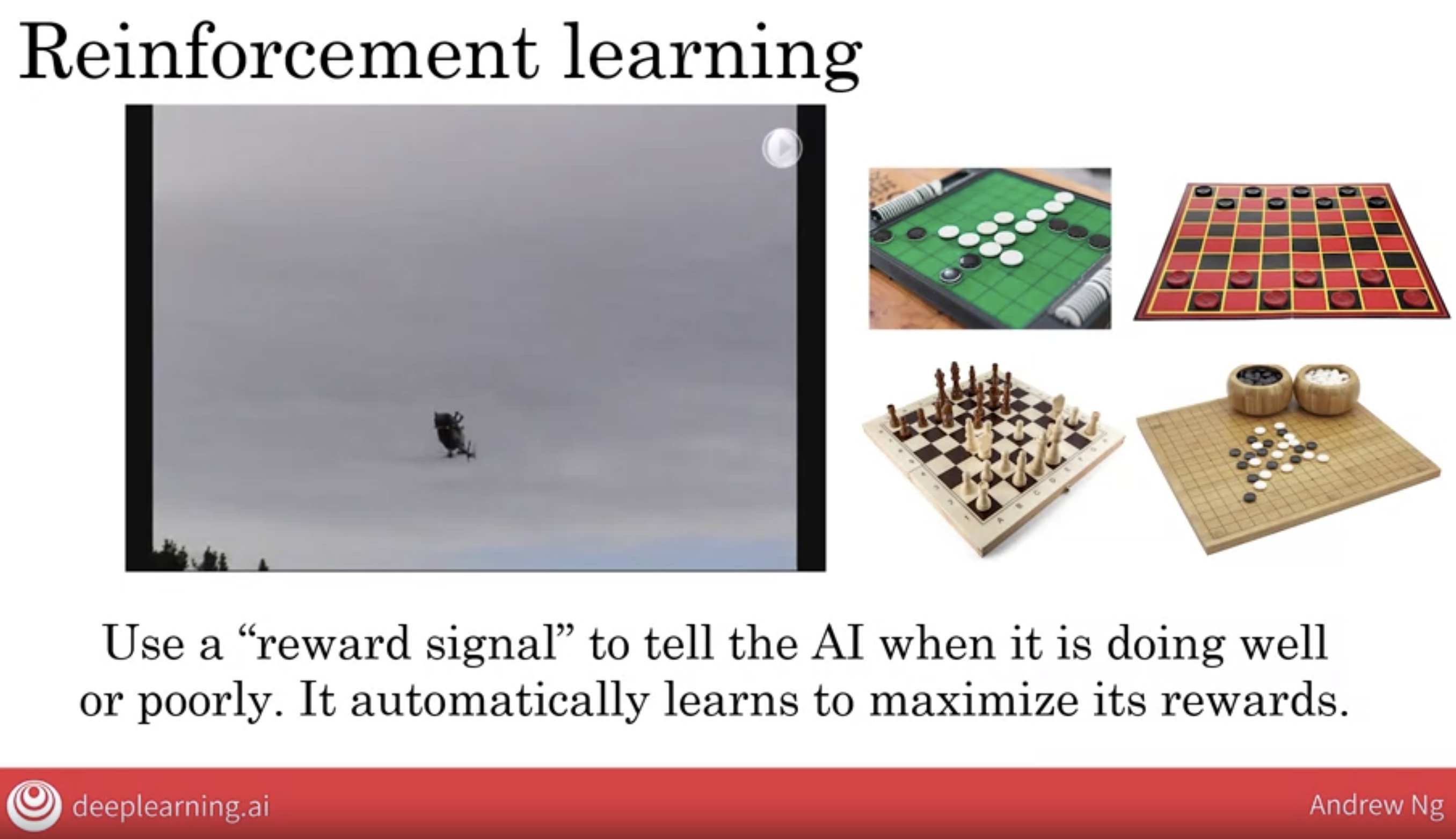
7.3 Reinforcement Learning
And let’s say you want to write a program to make it fly by itself. It’s hard to used supervised learning, input/output, A to B mappings, because it’s very difficult to specify what is the optimal way.
What is the best way to fly the helicopter when it is in a certain, given position. Reinforcement learning offers a different solution.
I think of reinforcement learning as similar to how you might train a pet dog to behave. My family, when I was growing up, had a pet dog. So, how do you train a dog to behave itself? Well, we let the dog do whatever it wanted to do, and then whenever it behaved well we would praise it. You go, good dog, and whenever it does something bad you would go, bad dog.
More formally, a reinforcement learning algorithm uses a reward signal, to tell the AI when it’s doing well or poorly. This means that whenever it’s doing well, you give it a large positive number to give it a large positive reward. And whenever it’s doing really bad job, you send it a negative number to give it a negative reward.
And it’s the AI’s job to then automatically learn to behave so as to maximize the rewards.
In addition to robotic control, reinforcement learning has also had a lot of traction in playing games, games such as Othello or checkers or chess or Go.
One of the weaknesses of reinforcement learning algorithms is that they can require a huge amount of data.
7.4 GANs
The role of GANs:
- Generate data sets
- Face generation
- Item generation
- Image conversion
- Image repair
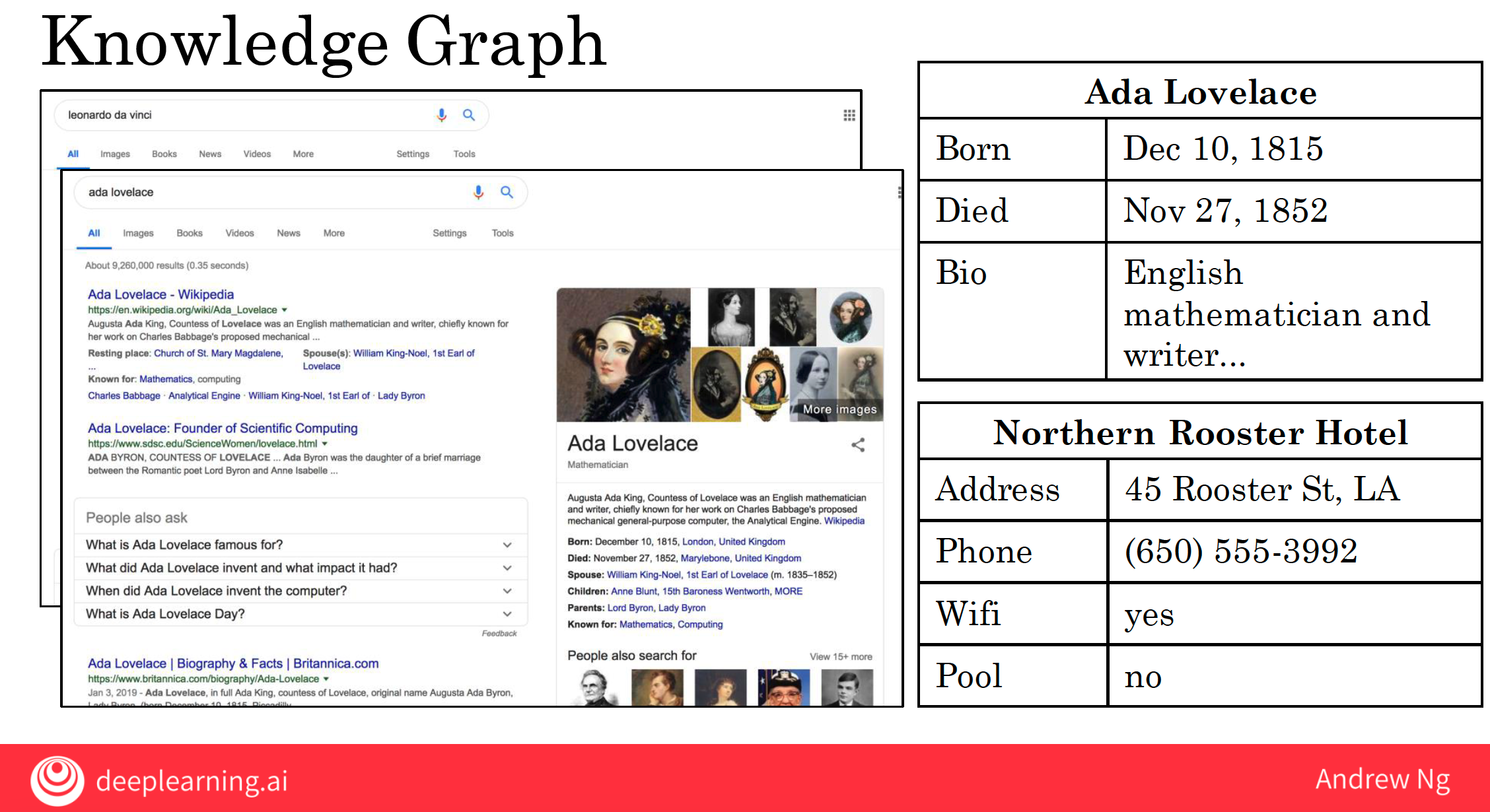
7.5 knowledge graph
In simple terms, KG is the representation of human knowledge in graph theory, so that computers can understand their semantics.
In other words, KG is a way of representing knowledge through graphs that allow a computer to answer questions by reasoning and reference.
But, depending on what industry vertical you work in, perhaps some of the techniques for building Knowledge Graphs will also be useful for building a big database of information about something relevant to your company.