【AI-For-Everyone】01 What's AI
0 Reference
| Description | url |
|---|---|
| coursera: ai-for-everyone (2021-10) | https://www.coursera.org/learn/ai-for-everyone/home/week/1 |
2 Introduction To AI
2.1 Economic Impact of AI
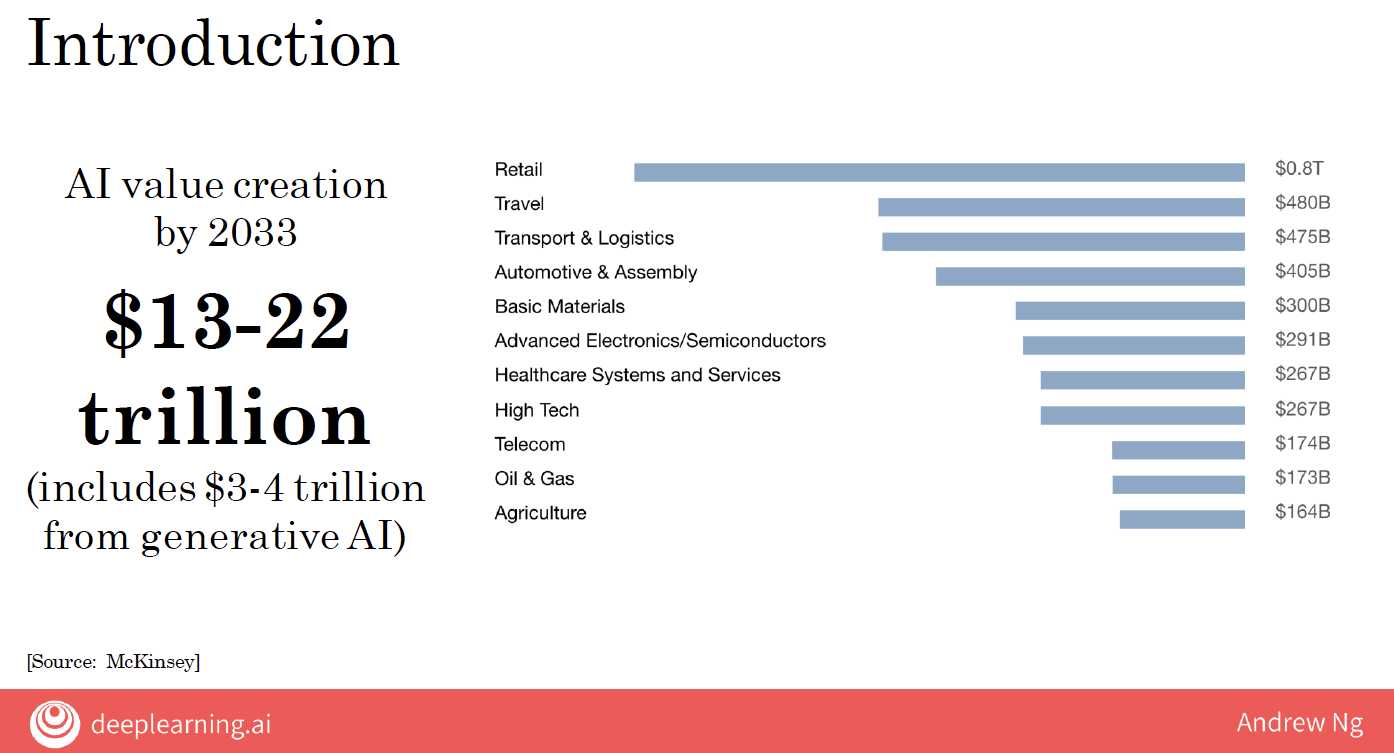
According to the McKinsey Global Institute, AI is expected to generate an additional $13 to $22 trillion of value annually by 2033.
Specifically, generative AI is projected to contribute $4 trillion to this economic impact.
A significant portion of the value AI is expected to generate will be outside the traditional software industry. Key sectors poised to benefit include:
- Retail
- Travel
- Transportation
- Automotive
- Materials manufacturing
- …
2.3 Current Status of AI
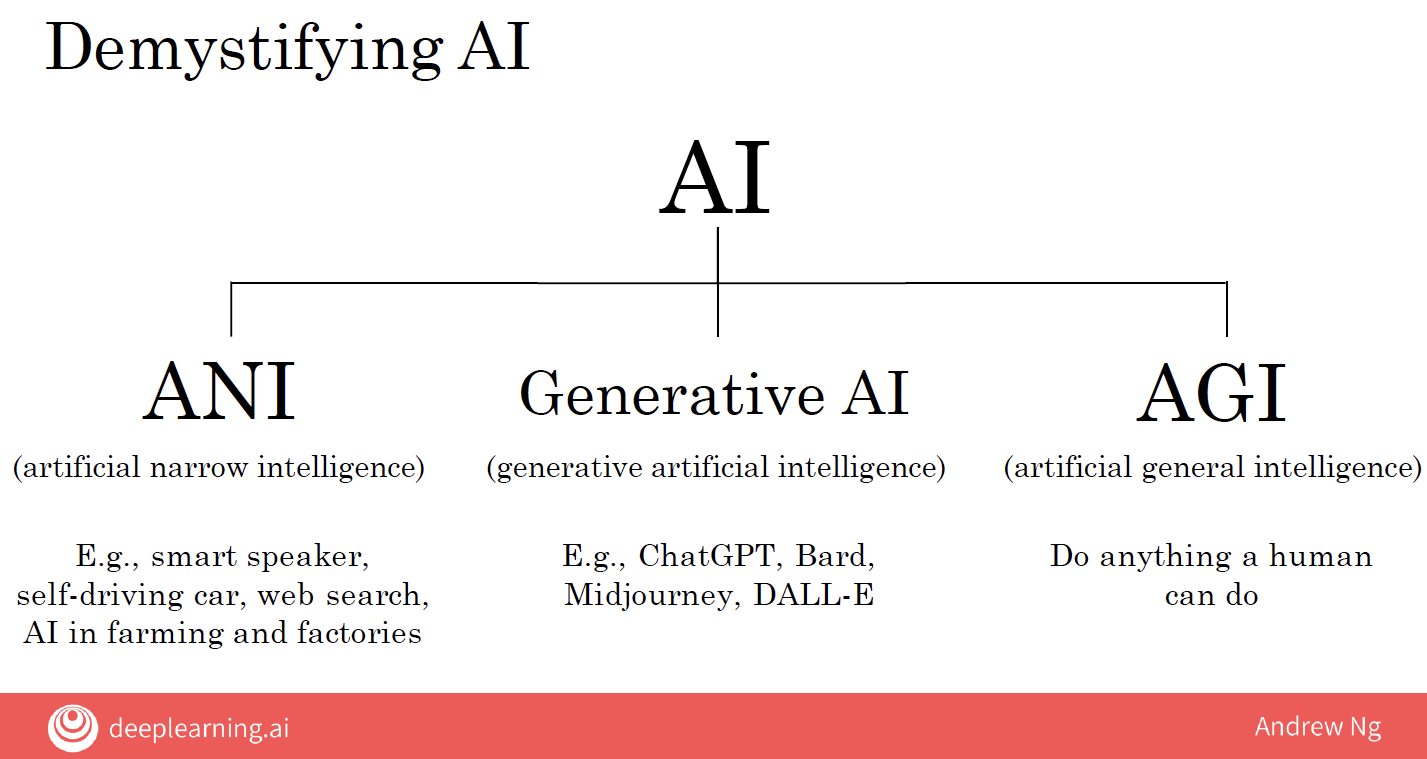
Rapid Progress in ANI and Generative AI: There has been remarkable advancement in Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) and generative AI, both of which are proving to be extremely valuable.
Slow Steps Towards AGI: While AI research is making incremental progress towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), we are still quite far from achieving it. AGI remains an exciting goal, but it will require numerous technological breakthroughs, potentially taking decades or even centuries to realize.
2.4 Conclusion
The potential of AI spans various industries, promising substantial economic impact. While ANI and generative AI are advancing rapidly, the journey to AGI is a long one, requiring sustained research and innovation.
3 Machine Learning
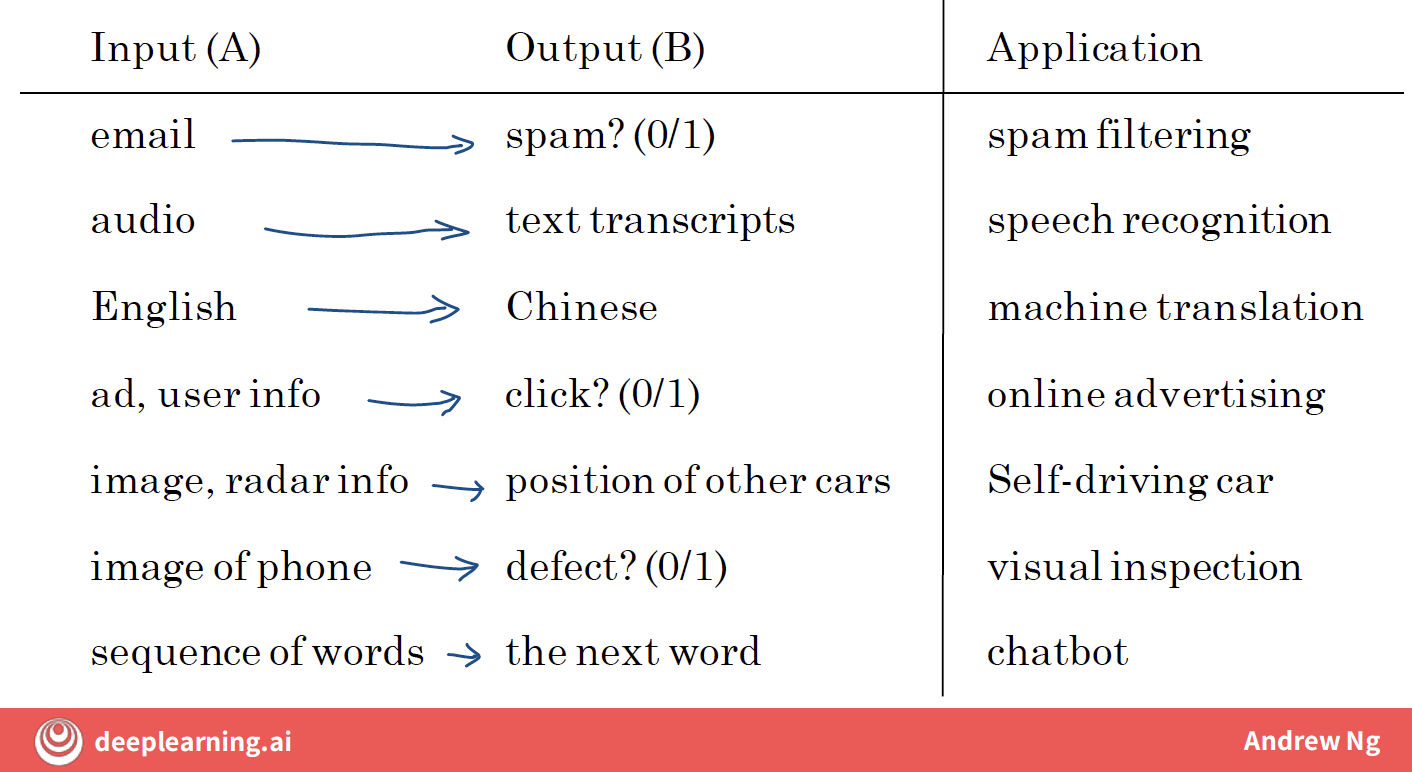
The most commonly used type of machine learning is a type of AI that learns A to B or input to output mappings, and this is called supervised learning.
3.1 Supervised Learning
3.1.1 Concept and Usage
Supervised Learning: learns A to B or input to output mappings.
On one hand, input, output A to B seems quite limiting. But when you find the right application scenario, this turns out to be incredibly valuable.
3.1.2 Large language models
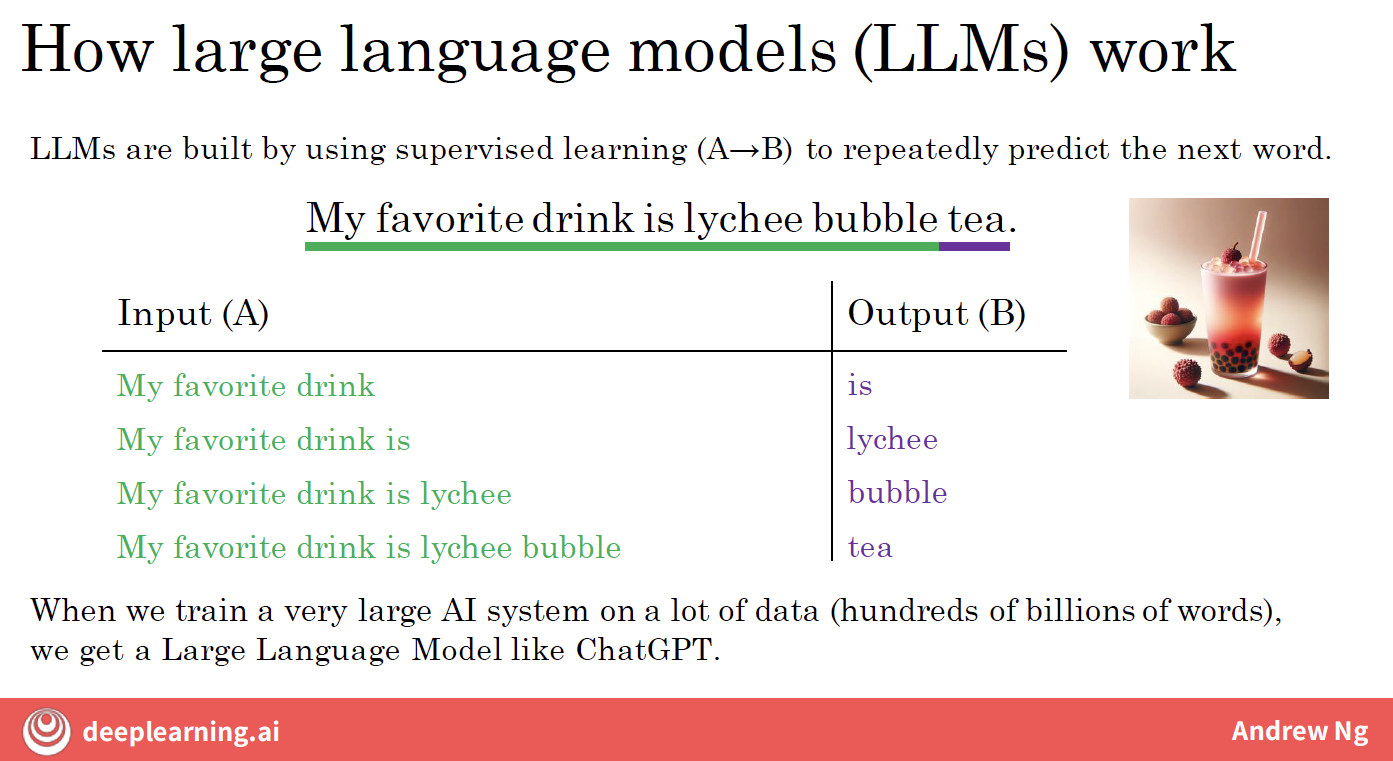
Large language models are built by using supervised learning to train a model to repeatedly predict the next word.
ChatGPT: given an initial piece of text called a prompt, is very good at generating some additional words in response to that prompt.
3.1.3 Why ai take off now
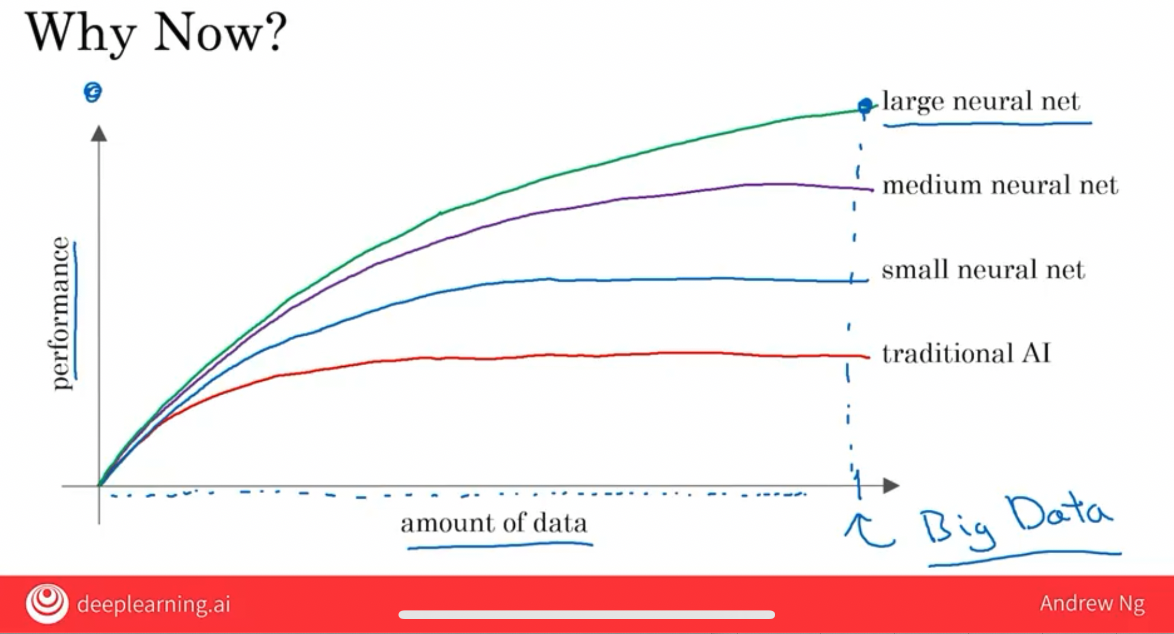
The idea of supervised learning has been around for many decades, but it’s really taken off in the last few years.
- Data Amount: In a lot of industries, the amount of data you have access to has really grown over the last couple of decades. Thanks to the rise of the Internet, the rise of computers.
- Machine Learning Tech: neural networks and deep learning.
In fact, it was also this type of scaling
increasing the amount of dataand thesize of the modelsthat was instrumental to the recent breakthroughs in training generative AI systems, including the large language models that we discussed just now.
4 data
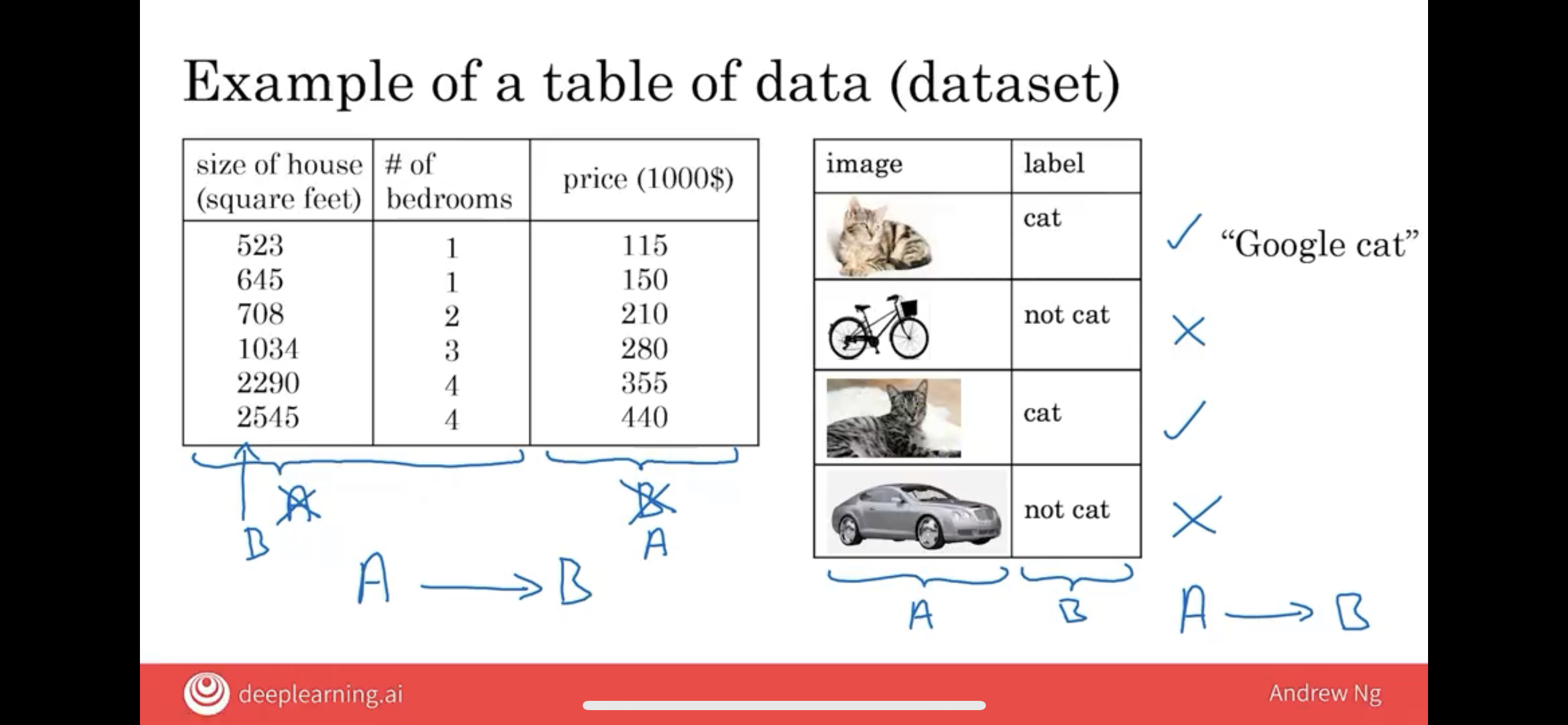
In AI, Data, also means DataSet.
4.1 DataSet
| A | B |
|---|---|
| the size of the house; | the price of the house. |
| both of these first two columns; | just the price of the house. |
| the price of the house; | the size of the house. |
Data is often unique to your business. And it’s up to you to decide, what is A and what is B, and how to choose these definitions of A and B to make it valuable for your business.
4.2 How to acquire data?
4.2.1 manual labeling
4.2.2 observing user behaviors or other types of behaviors
user behaviors an e-commerce website We can store the user ID, the time the user visit your website, the price you offer the product to the users, as well as whether or not they purchased it.
other types of behaviors There’s a machine ID, there’s the temperature of the machine, there’s a pressure within the machine, and then did the machine fail or not? And if your application prevents the maintenance, say you want to figure out if a machine is about to fail.
4.2.3 website/partner
- website
Thanks to the open Internet, there’s just so many data sets that you can download freely. If your application needs a type of data you just download off the web, keeping in mind licensing and copyright, then that could be a great way to get started on an application.
- partner if you work with a partner, say you’re working with a factory, then they may already have collected a big data set of machines and temperatures and pressure.
4.3 Misuses of Data
There are two of the most common misuses or the bad ways of thinking about data
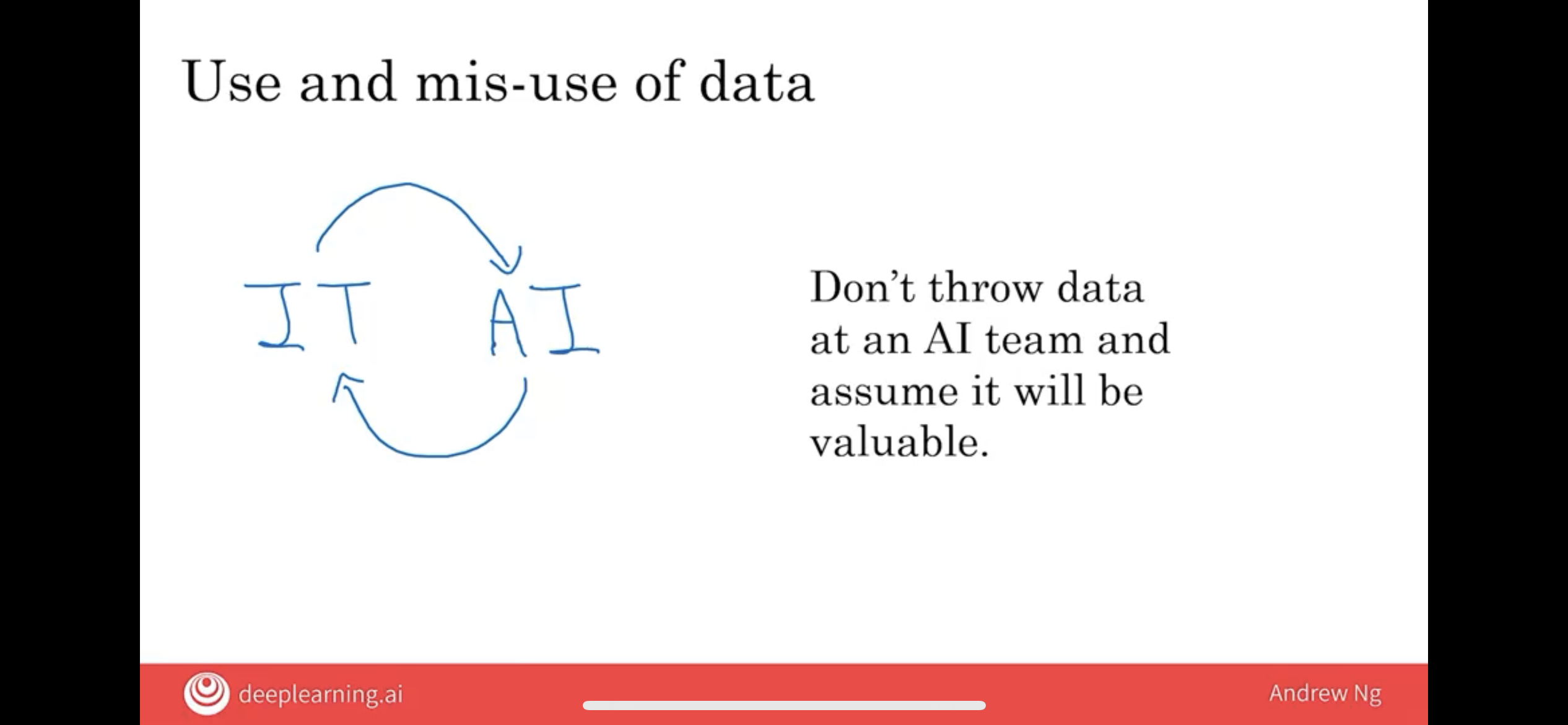
4.3.1 Interplay between AI and IT team
- the earlier and more frequently the AI team and IT team are connect, the less misdirection and resource waste in the IT infrastruture.
- on the contrary, if you throw a lot of data to AI team at once, and try to use it to provide valuable informat, it is impossible.
4.3.2 Not all data is useful
More data is usually better than less data, but I wouldn’t take it for granted just because you have many terabytes or gigabytes of data that an AI team can magically make that valuable. don’t throw data in AI team and assume it will be valuable.
I would not over invest in just acquiring data for the sake of data until unless you also get an AI team to take a look at it. Because they can help guide you to think through what is the data that is actually the most valuable.
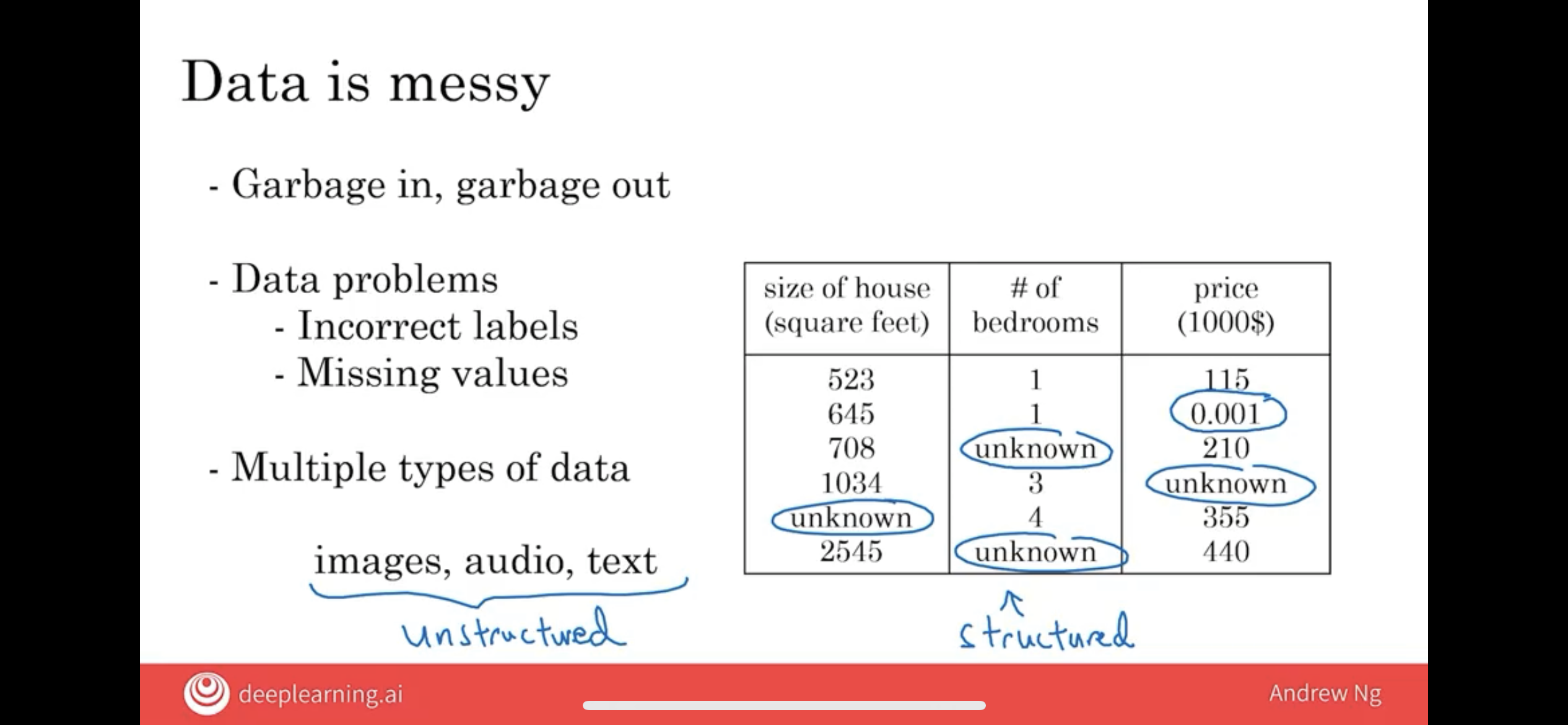
4.4 Data is messy
Data needs to be processed before it can be used by the AI team.
4.4.1 garbage in, garbage out
you may have heard the phrase garbage in, garbage out. And if you have bad data, then the AI will learn inaccurate things.
4.4.2 Multiple types of Data
- unstructured data: text, images, audio, and so on.
- structured data: basically means data that lives in a giant spreadsheet.
supervised learning can work very well for both of these types of data, unstructured data and structured data.
5 Terminologies
5.1 Machine Learning System vs Data Science Project
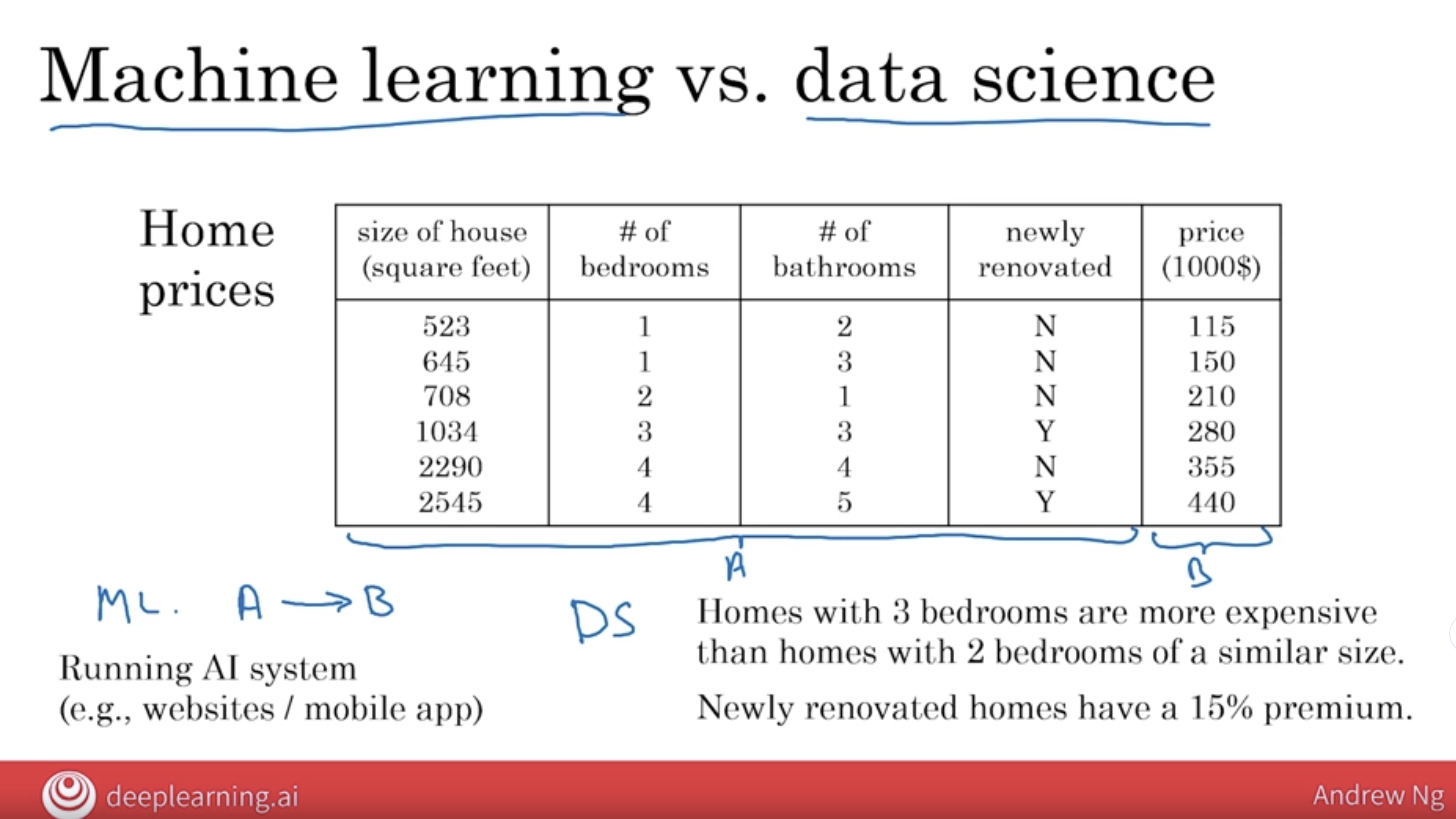
5.1.1 Machine Learning System: an AI system for A to B
if you have an AI system running serving dozens or hundreds of thousands of millions of users, any time of day, any time of night, can automatically input A these properties of a house and output B. , that’s usually a machine learning system.
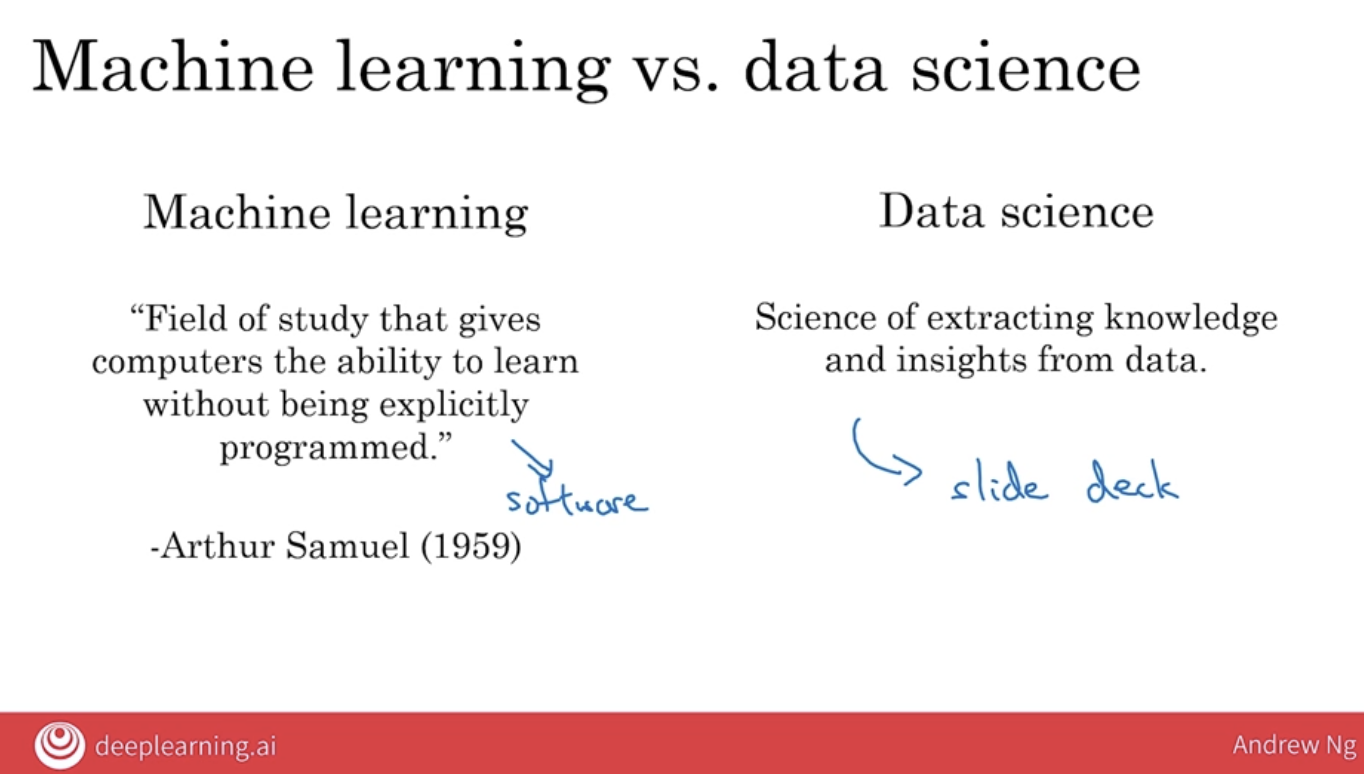
Arthur Samuel: Field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed。
5.1.2 Data Science Project: a project for get a set of insights
the output of data science project is a set of insights that can help you make business decisions, such as what type of house to build or whether to invest in renovation.
So even in one company, you may have different machine learning and data science projects, both of which can be incredibly valuable.
5.2 Neural Network vs Deep Learning
the terms neural network and deep learning are used almost interchangeably, they mean essentially the same thing. Many decades ago, this type of software was called a neural network. But in recent years, we found that deep learning was just a much better sounding brand.
a neural network is a very effective technique for learning A to B, or input to output mappings.
5.3 AI tools
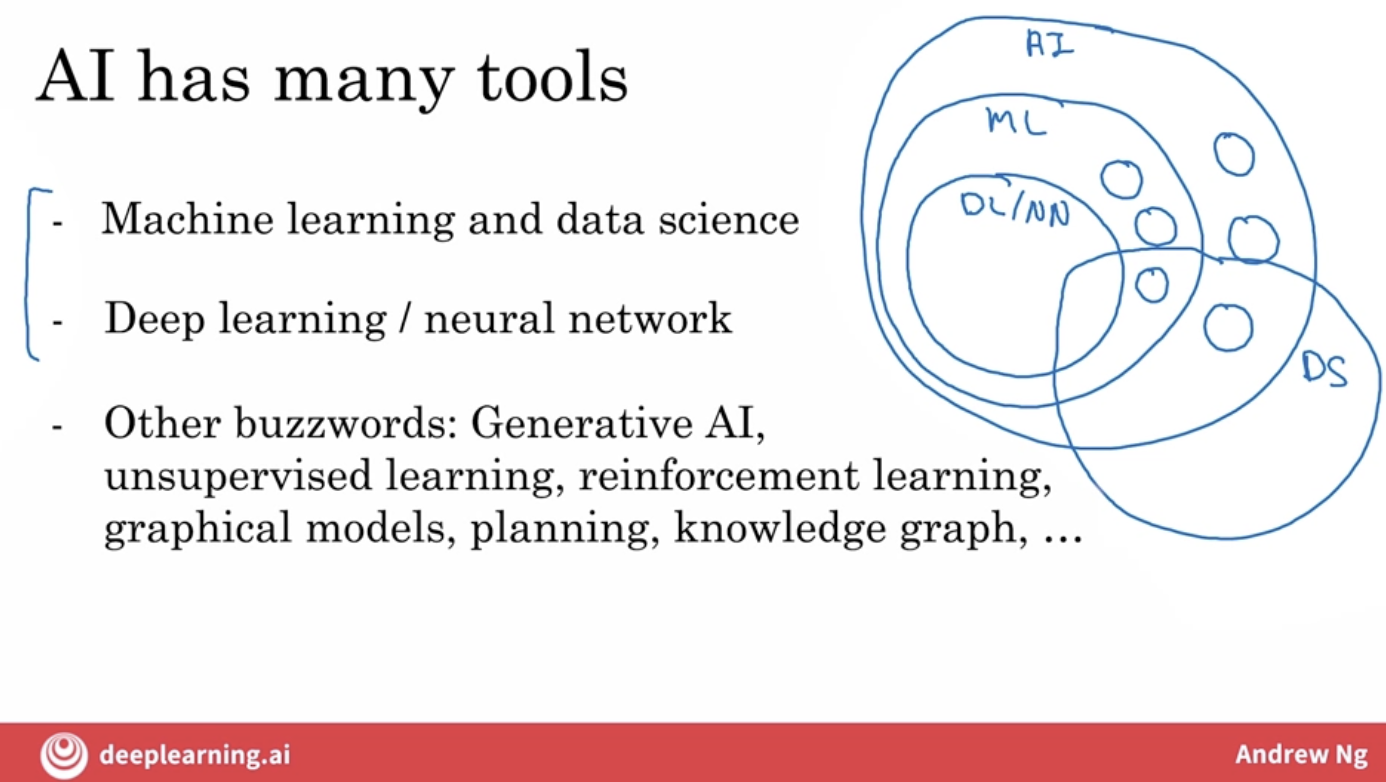
- AI: AI is this huge set of tools for making computers behave intelligently.
- Machine Learning: Of AI, the biggest subset is probably tools from machine learning, but AI does have other tools than machine learning, such as some of these buzzwords listed at the bottom.
- Deep Learning or Neural Network: is a very powerful set of tools for carrying out supervised learning, or A to B mappings, as well as some other things. But there are also other machine learning tools that are not just deep learning tools.
- Data Science: data science is maybe a cross cutting subset of all of these tools that uses many tools from AI, machine learning and deep learning. But has some other separate tools as well that solves a very set of important problems in driving business insights.
6 What makes an AI company
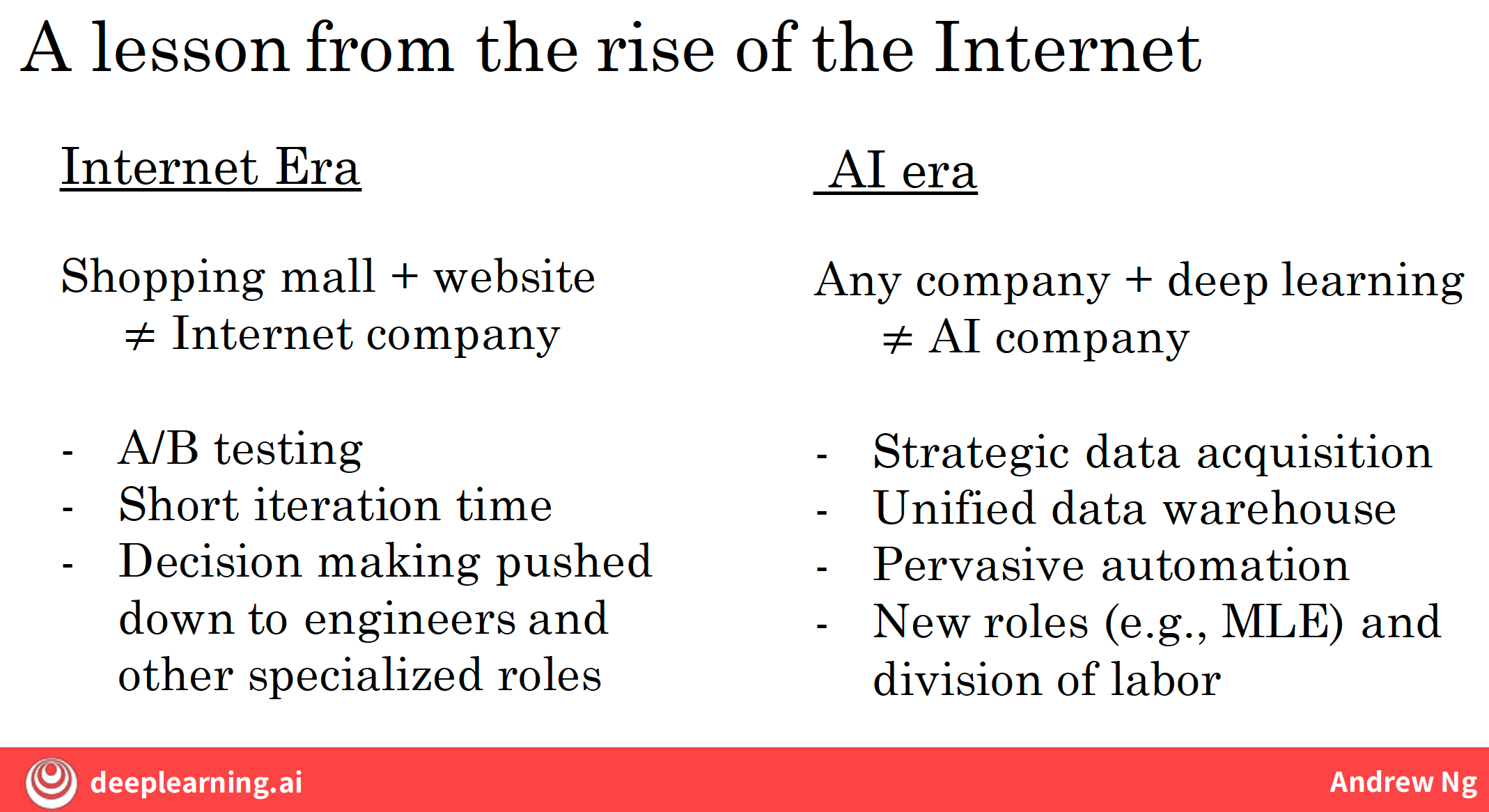
6.1 A lesson we learned from the rise of the Internet
Let’s study expirence from Internet era.
6.1.1 Internet Era
they do the things that the internet doesn’t do really well.
- iterative thinking
- Iterate quickly
- Decentralization of decision-making power, faster and more accurate decision-making (the advantages outweigh the disadvantages) and leaving professional matters to professionals
6.1.2 AI Era
are you doing the things that AI lets you do or it doesn’t do really well?
- help Internet do what it is good at
- help AI do what it is good at
6.2 Five-step AI transformation playbook
- pilot project
- in house AI team
- board AI training
- Develop an AI strategy
- strategic data acquisition
- bringing the data together into single data warehouse
- privasive automation
- architecting for company to do the things that AI makes it possible to do really well
- …
- Internal and external communication
7 What AI can and cannot do
7.1 some examples
7.1.1 a second of thought
pretty much anything you could do with a second of thought, we can probably now or soon automate using supervised learning using this input-output mapping.
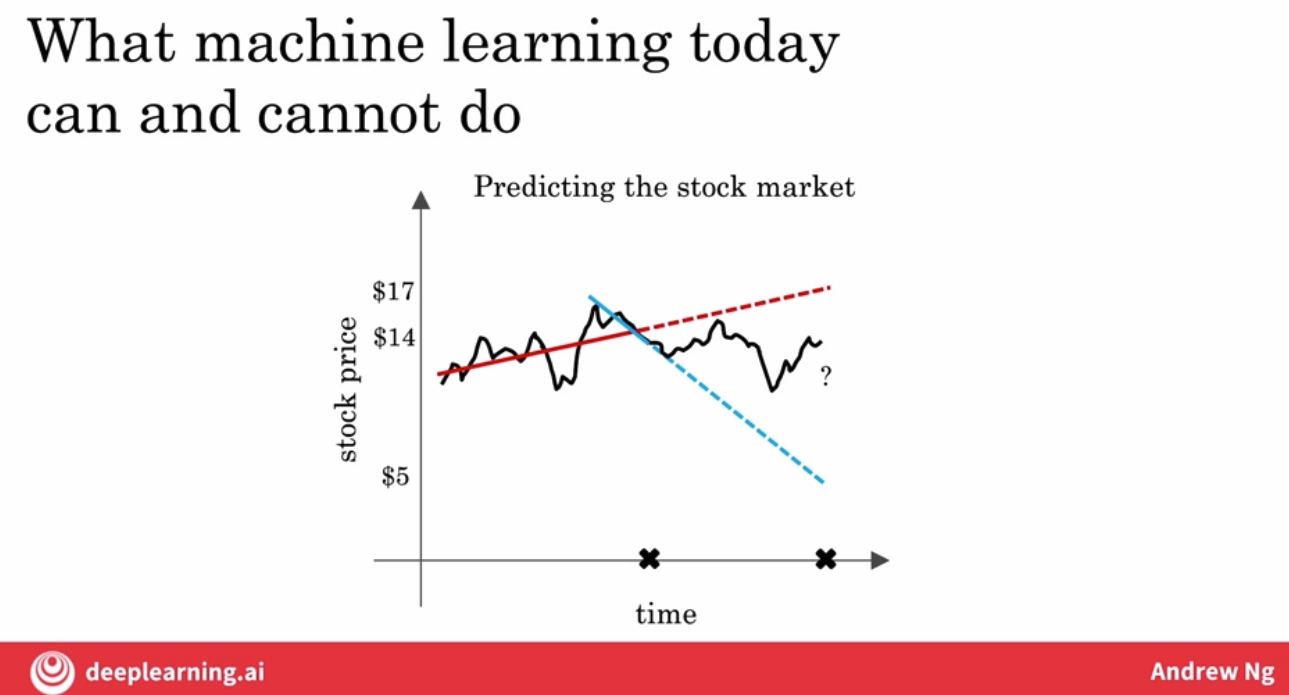
7.1.2 About stock market
predict the future price of some company stock, given only the historical price of that stock.
The main problem with this application, is that, the past history of a stock price is just not very predictive of the future stock price, which is why attempts to use machine learning this way haven’t been successful.
No matter how many inputs, these other inputs are typically complex or costly to acquire, and still can’t overcome the intrinsically, somewhat random nature of the stock market.
7.2 rules of thumb about what makes a machine learning problem easier or more likely to be feasible
| rule of thumb | good | bad |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Concept | looking outside the window of a self driving car to spot the other cars | come up with clever signals to predict a given company’s sales |
| lots of data available | 1. a lots of data; 2. both the input A and the output B. |
7.3 More examples about AI can and cannot do
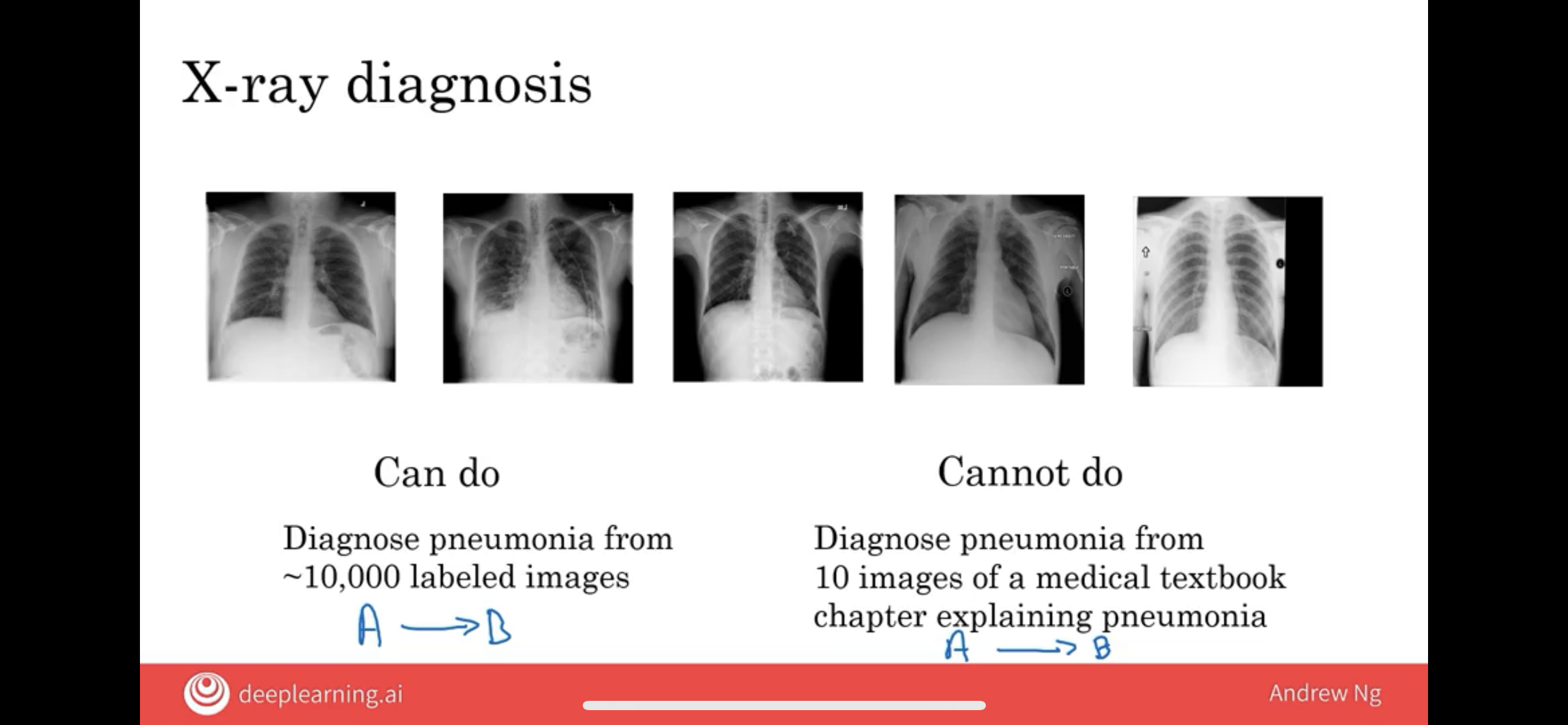
In fact, even people have a hard time figuring out sometimes what someone waving at your car wants.
Whereas a young medical doctor might learn quite well reading a medical textbook at just looking at maybe dozens of images.
In contrast, an AI system isn’t really able to do that today.
7.4 Summary of AI can and cannot do
More about different types from data set: A good AI team would be able to ameliorate, or to reduce some of these problems, but doing this is not that easy. This is one of the things that AI is actually much weaker than humans.
8 Deep Learning or Neural Network
Let’s start by an example.
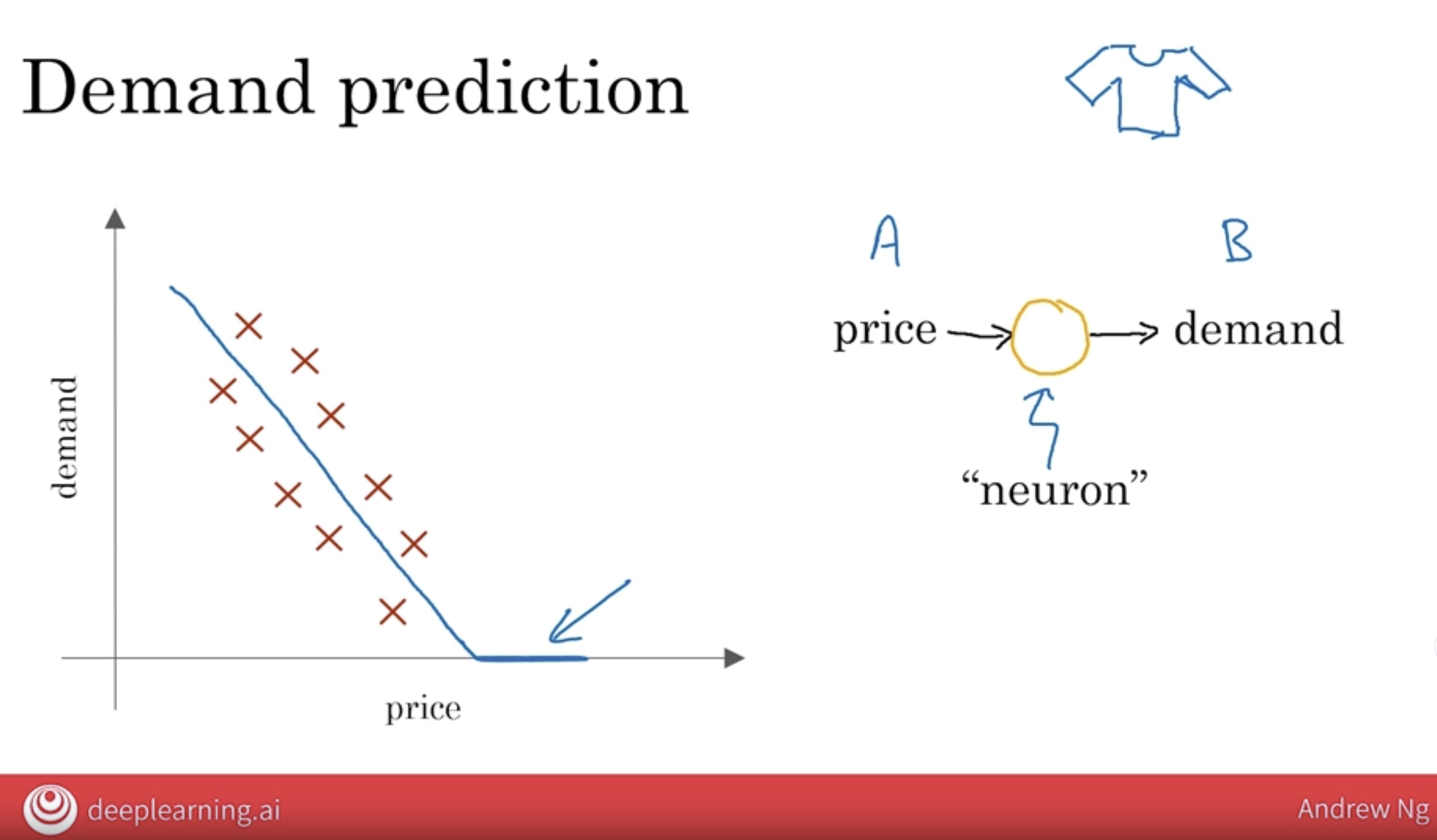
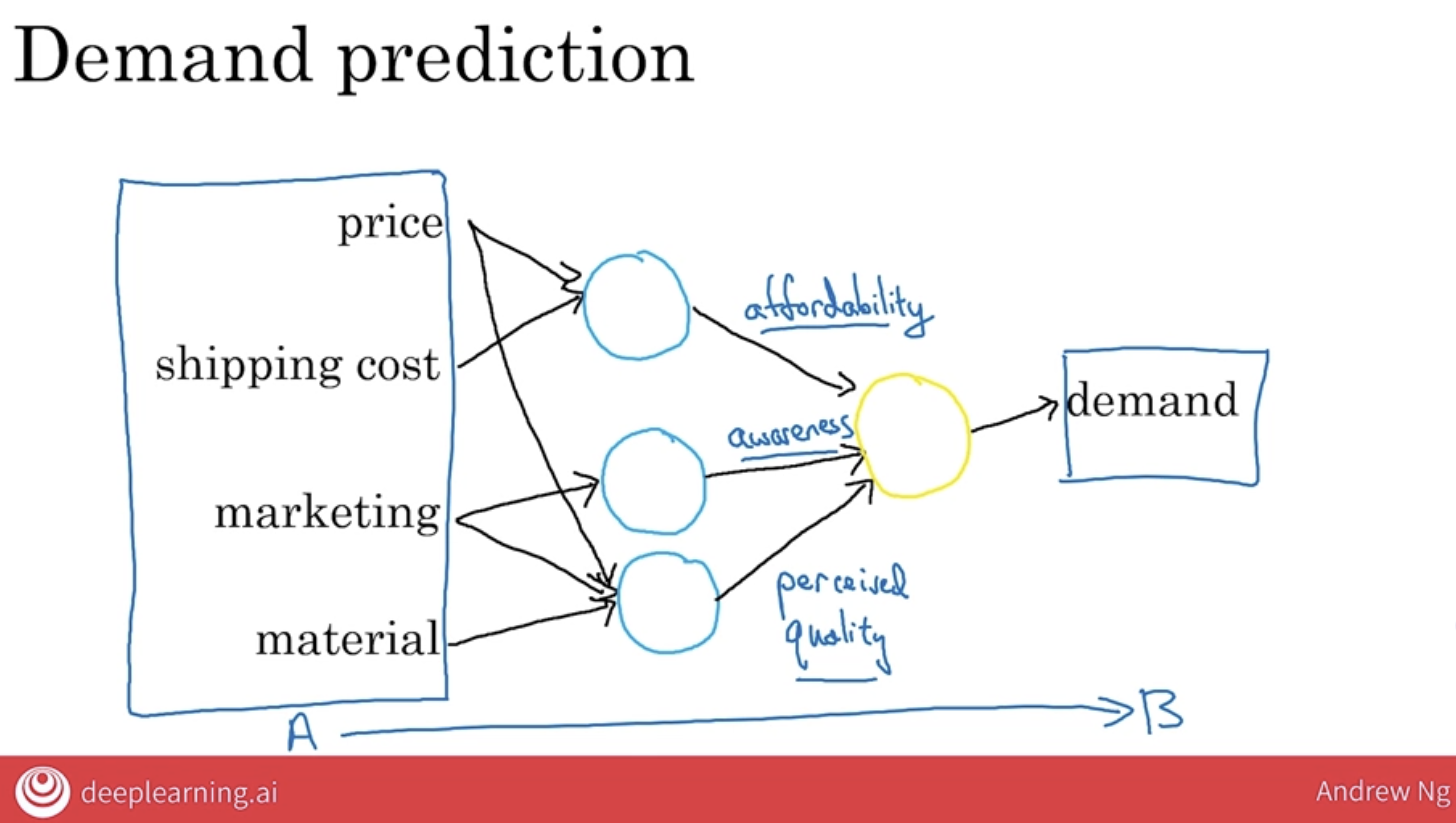
8.1 Demond Prediction v1
It turns out this blue line is maybe the simplest possible neural network.
- You have as input the price A, and you want it to output the estimated demand, B.
So the way you would draw this as a neural network is that the price would be input to this little round thing there, and this little round thing outputs the estimated demand.
- In the terminology of AI, this little round thing here is called a neuron, or sometimes it’s called an artificial neuron,
- and all it does is compute this blue curve that I’ve drawn here on the left.
This is maybe the simplest possible neural network with
a single artificial neuronthat just inputs the price and outputs the estimated demand.
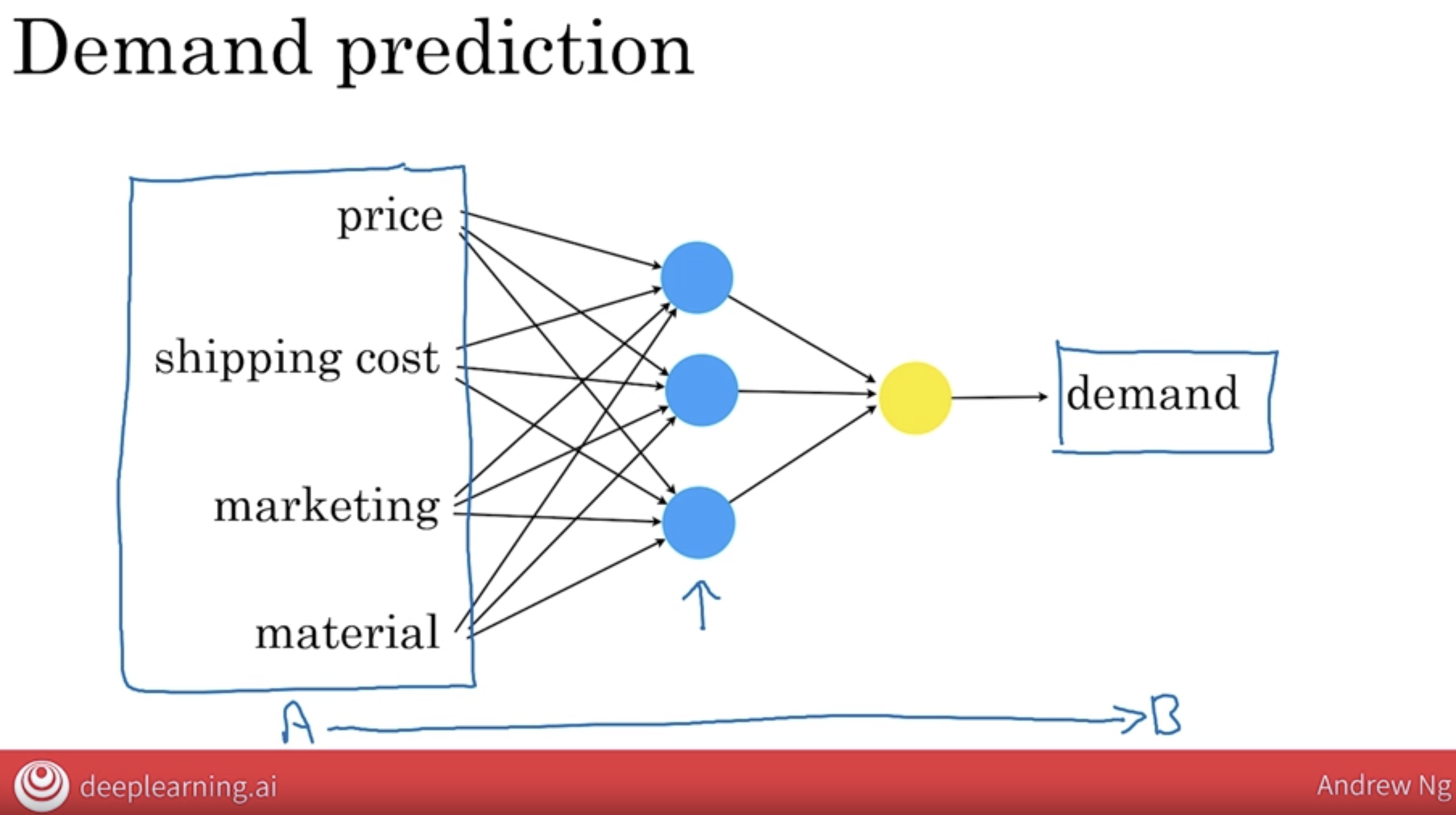
8.2 Demond Prediction v2
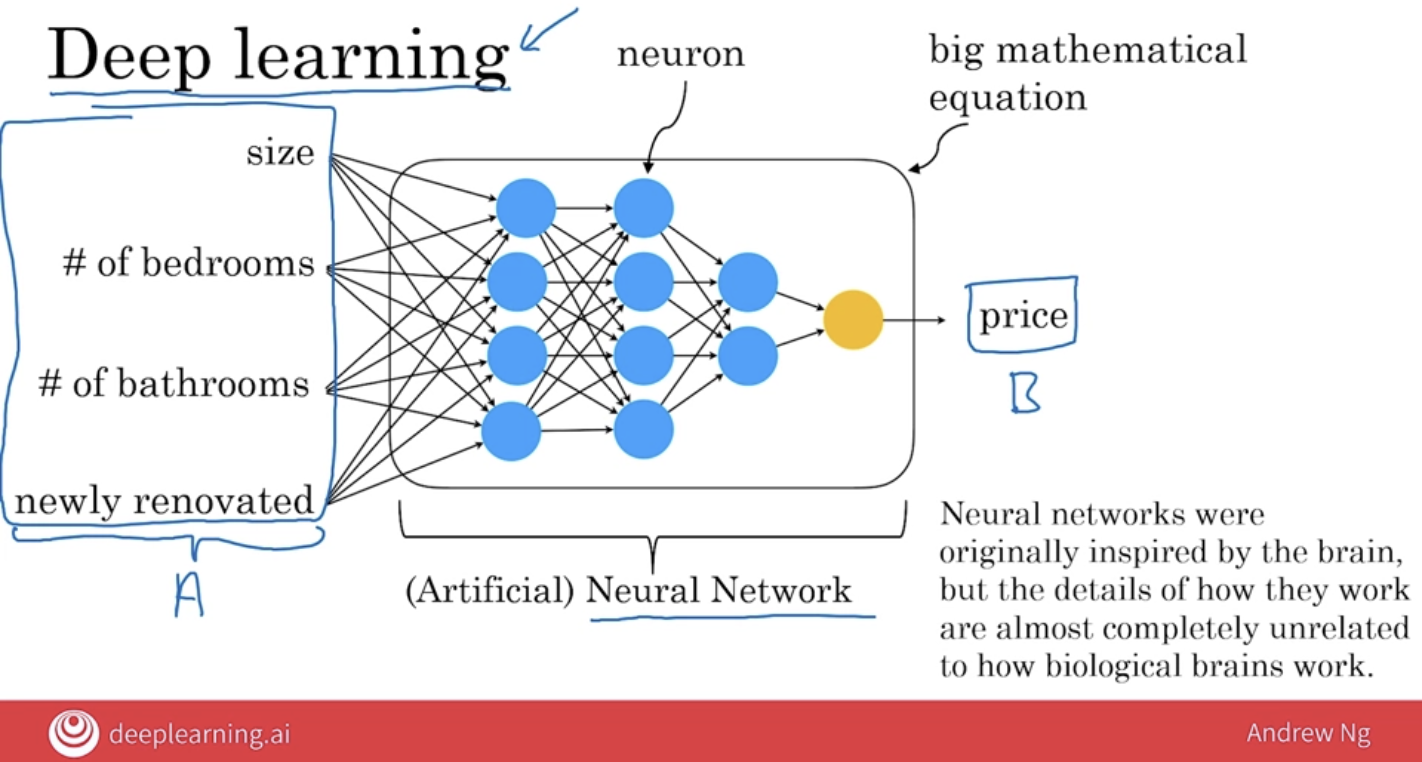
If you think of this orange circle, this artificial neuron, as a little lego break, all that a neural network is, is if you take a lot of these Lego breaks and stack them on top of each other until you get a big tower or a big network of these neurons.
One of the wonderful things about building a machine learning system using a neural network, all you have to do is give it the input A and the output B, and it figures out all of the things in the middle by itself.
And it turns out that if you give this enough data and train a neural network that is big enough, this can do an incredibly good job mapping from inputs A to outputs B.
This is a fairly small neural network with just four artificial neurons. In practice, neural networks used today are much larger, with easily thousands, tens of thousands, or even much larger than that numbers of neurons.
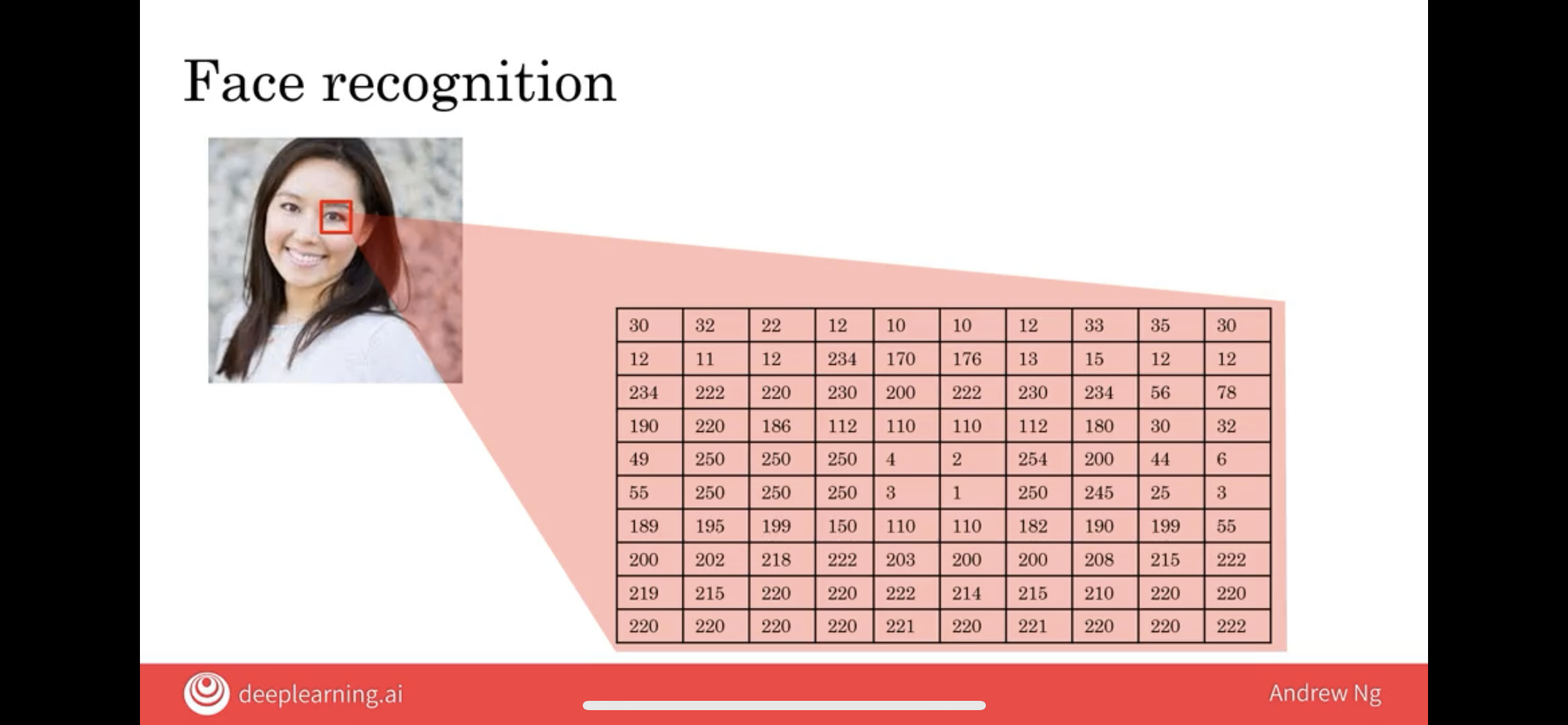
8.3 Face Recognition
- If it were a black and white or grayscale image, then each pixel would correspond to a single number telling you how bright is that pixel.
- If it’s a color image, then each pixel will actually have three numbers, corresponding to how bright are the red, green, and blue elements of that pixel.
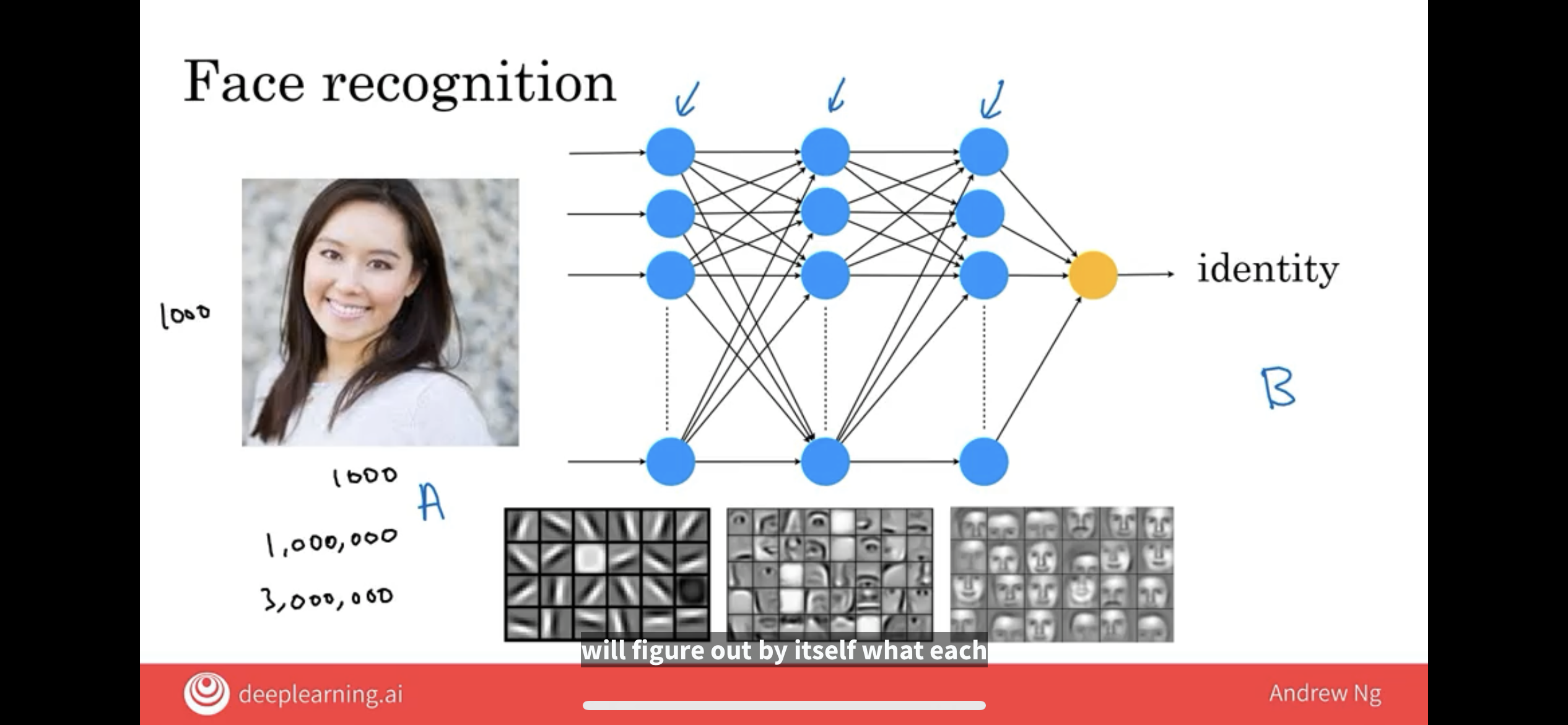
So, the neural networks job is to take as input a lot of numbers like these and tell you the name of the person in the picture.
Similar to before, you will have many many of these artificial neurons computing various values, and it’s not your job to figure out what these neurons should compute. The neural network will figured out by itself.
Typically, when you give it an image,
- the neurons in the earlier parts of the neural network will learn to detect edges in pictures,
- and then a little bit later learn to detect parts of objects.
- So, they learn to detect eyes and noses and the shape of cheeks and the shape of mouths
- and then the later neurons, further to the right, will learn to detect different shapes of faces
- and it will finally, put all this together to output the identity of the person in the image.
- Again, part of the magic of neural networks is that you don’t really need to worry about what it is doing in the middle.
- All you need to do is give it a lot of data of pictures like this, A, as well as the correct identity B, and the learning algorithm will figure out by itself what each of these neurons in the middle should be computing.
100 Some Terminologies
| English | Chinese | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ANI: artificial narrow intelligence | 人工狭义智能 | AI designed to perform a specific task, such as smart speakers, self-driving cars, or AI applications in various industries. |
| AGI: Artificial General Intelligence | 人工通用智能 | The goal of building AI that can perform any intellectual task that a human can, and possibly surpass human abilities. |
| generative AI | 生成式 AI | A new type of AI that can create new content such as text, images, and music. |
| machine learning | 机器学习 | A type of AI that allows computers to learn from data and make decisions. |
| supervised learning | 监督学习 | A mature type of machine learning where the model is trained on labeled data. |
| deep learning | 深度学习 | A subset of machine learning involving neural networks with many layers. |
| neural networks | 神经网络 | Computational models inspired by the human brain, used in machine learning. |
| spam filter | 垃圾邮件过滤器 | A tool used to block unwanted emails |
| speech recognition | 语音识别 | Technology that can recognize spoken language and convert it to text |
| machine translation | 机器翻译 | Automated translation of text from one language to another |
| online advertising | 在线广告 | Marketing efforts conducted over the internet |
| self-driving car | 自动驾驶汽车 | A vehicle capable of navigating without human intervention |
| LLM: large language models | 大语言模型 | Advanced AI models that understand and generate human language |
| acquire data | 获取数据 | To obtain or collect information |
| e-commerce | 电子商务 | Commercial transactions conducted electronically on the internet |
| unstructured data | 非结构化数据 | Information that does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a predefined manner |
| structured data | 结构化数据 | Information that is organized according to a data model, making it easier to analyze |
| manual labeling | 手动标注 | The process of manually tagging data with labels |
| unsupervised learning | 无监督学习 | A type of machine learning that infers patterns from a dataset without labeled responses |
| reinforcement learning | 强化学习 | A type of machine learning where an agent learns to make decisions by taking actions in an environment to maximize some notion of cumulative reward |
| data science | 数据科学 | An interdisciplinary field that uses scientific methods to extract insights from data |
| graphical models | 图形模型 | Statistical models that use graphs to represent variables and their conditional dependencies |
| planning knowledge graphs | 规划知识图谱 | Creating and organizing knowledge in a structured format using graphs |