【Meachine Learning】10 Transfer Learning
0 intuition
For an application where you don’t have that much data, transfer learning is a wonderful technique that lets you use data from a different task to help on your application.
1 supervised pre-training
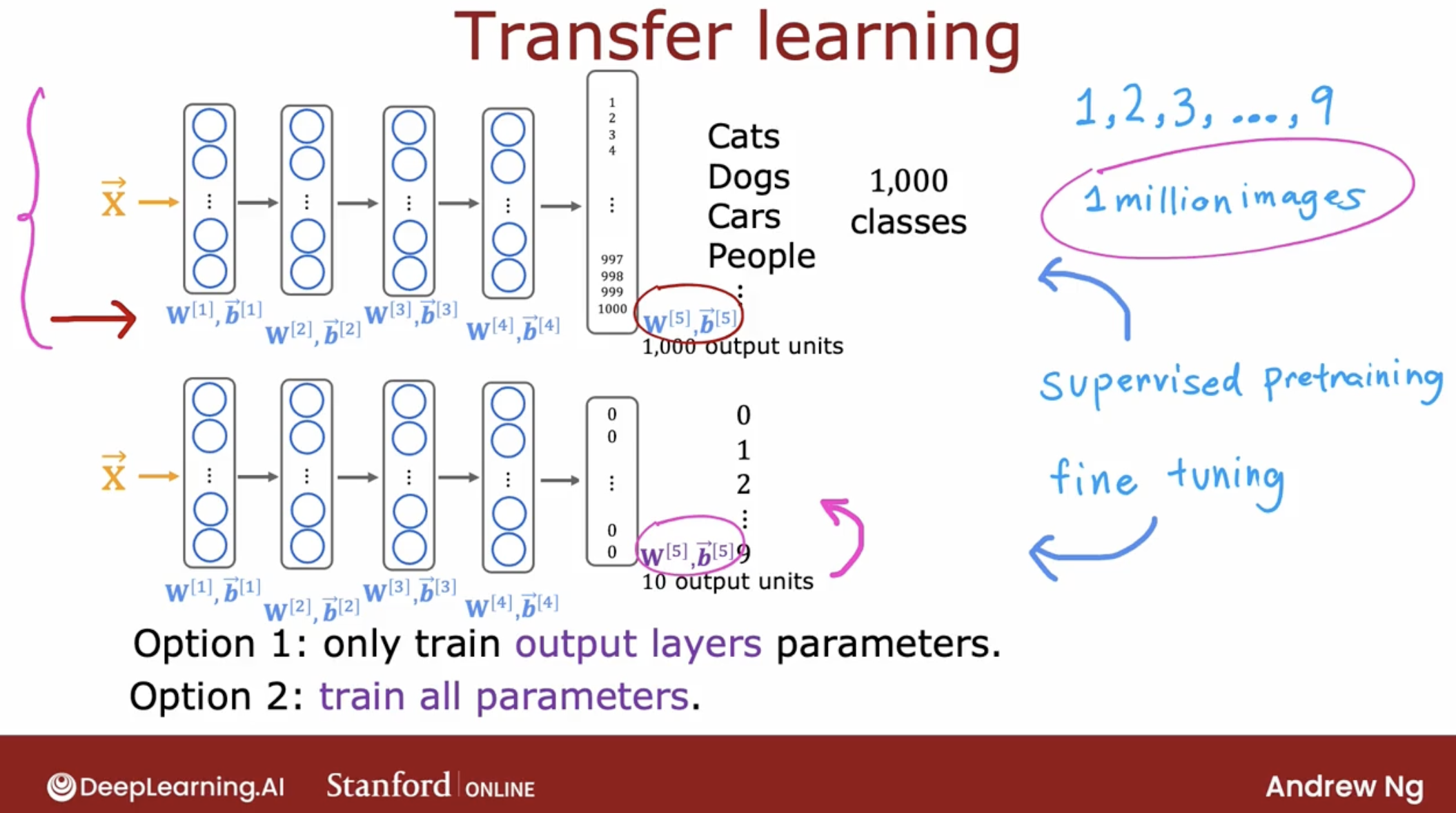
In transfer learning, what you can do is use the parameters from the first four layers, really all the layers except the final output layer as a starting point for the parameters and then run an optimization algorithm such as gradient descent or the Adam optimization algorithm with the parameters initialized using the values from this neural network up on top.
2 how to use it
2 options you can select
If you have a very small training set then Option 1 might work a little bit better, but if you have a training set that’s a little bit larger then Option 2 might work a little bit better.
so, to recap, One nice thing about transfer learning as well is maybe you don’t need to be the one to carry out supervised pre-training.
3 why it worked?
For a lot of neural networks, there will already be researchers they have already trained a neural network on a large image and will have posted a trained neural networks on the Internet, freely licensed for anyone to download and use.
What that means is rather than carrying out the first step yourself, you can just download the neural network that someone else may have spent weeks training and then replace the output layer with your own output layer and carry out either Option 1 or Option 2 to fine tune a neural network that someone else has already carried out supervised pre-training on, and just do a little bit of fine tuning to quickly be able to get a neural network that performs well on your task.
why it work?
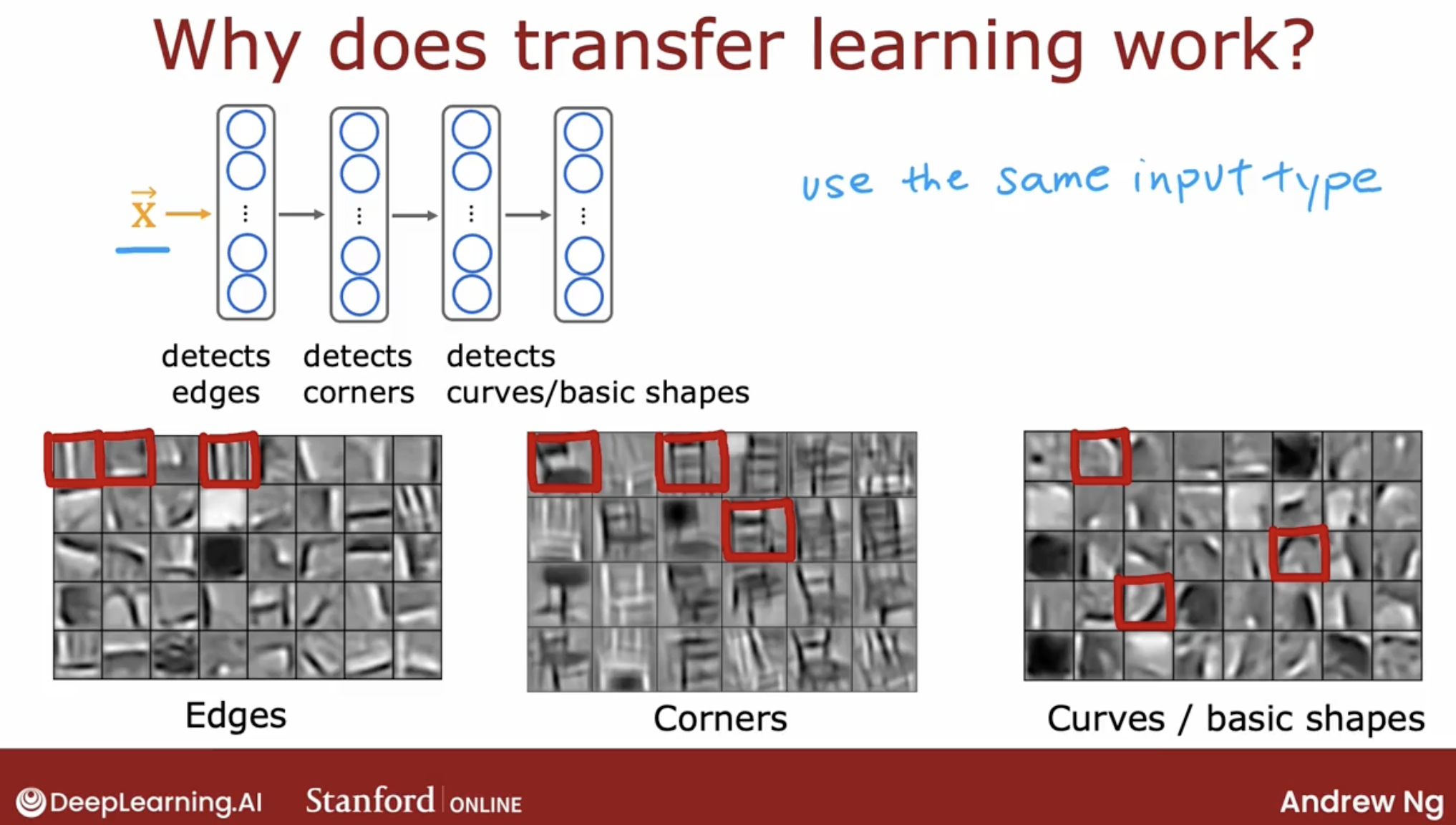
low-level features is same for same type of dataset. like computer vision.
- finding cats, dogs, cars, people
- finding handwritten digit
Conversely, if your goal is to build a speech recognition system to process audio, then a neural network pre-trained on images probably won’t do much good on audio. Instead, you want a neural network pre-trained on audio data, there you then fine tune on your own audio dataset and the same for other types of applications.
You can pre-train a neural network on text data and If your application has a save feature input x of text data, then you can fine tune that neural network on your own data.
4 summary
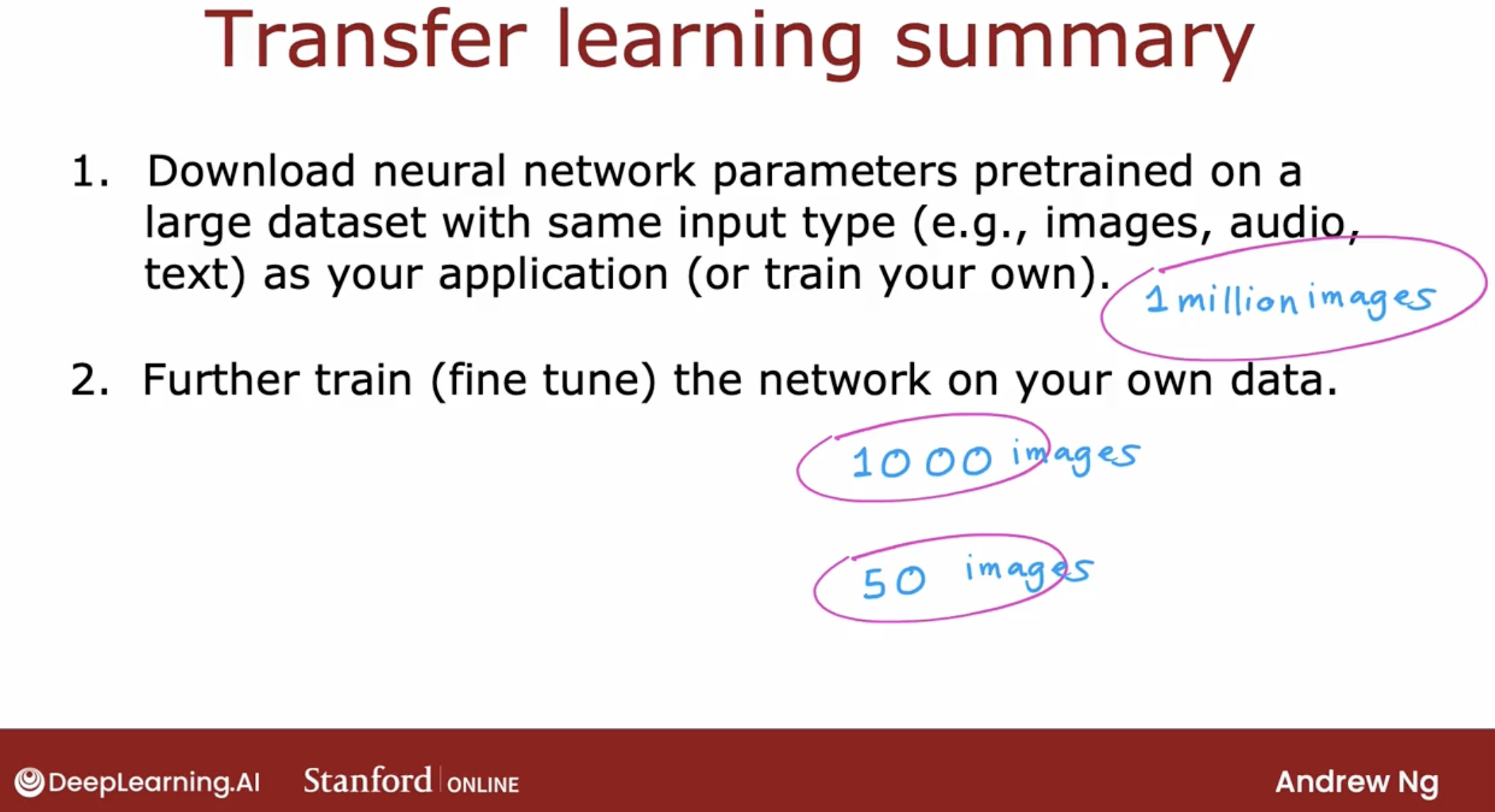
I’d sometimes train neural networks on as few as 50 images that were quite well using this technique, when it has already been pre-trained on a much larger dataset.
This technique isn’t panacea, you can’t get every application to work just on 50 images, but it does help a lot when the dataset you have for your application isn’t that large.