【Generative AI】02 Generative AI Project
1 project intuition
let’s see the step from all human to all chatbot in a customer service center.
Advice for deploying chatbots
- Start with an internal-facing chatbot
- Work with staff to assess behavior of chatbot
- Avoid public mistakes
- Deploy with human-in-the-loop to check for mistakes
- Onlv after deemed safe, allow bot to communicate directlwith customers
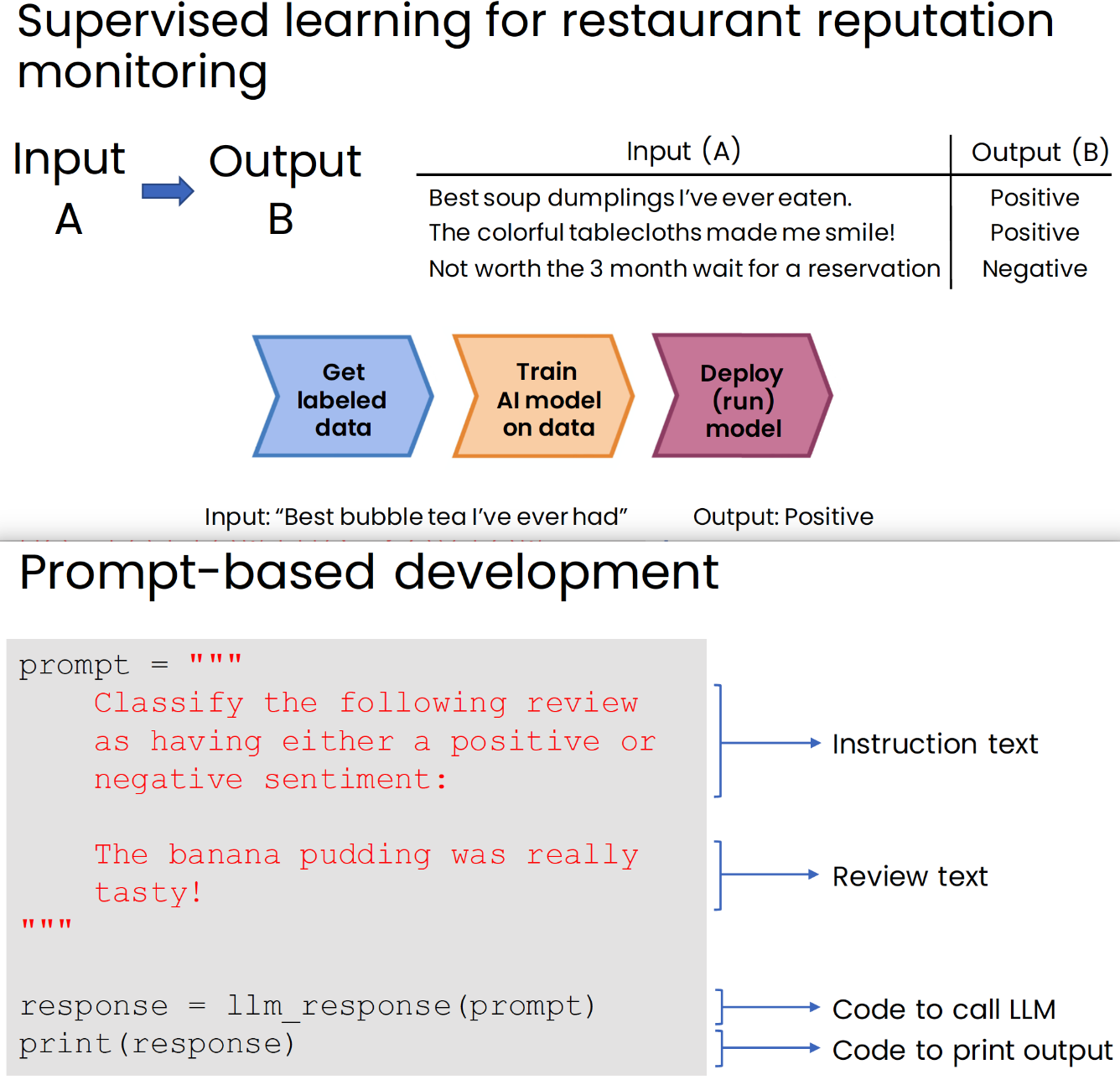
2 compare with supervised learning
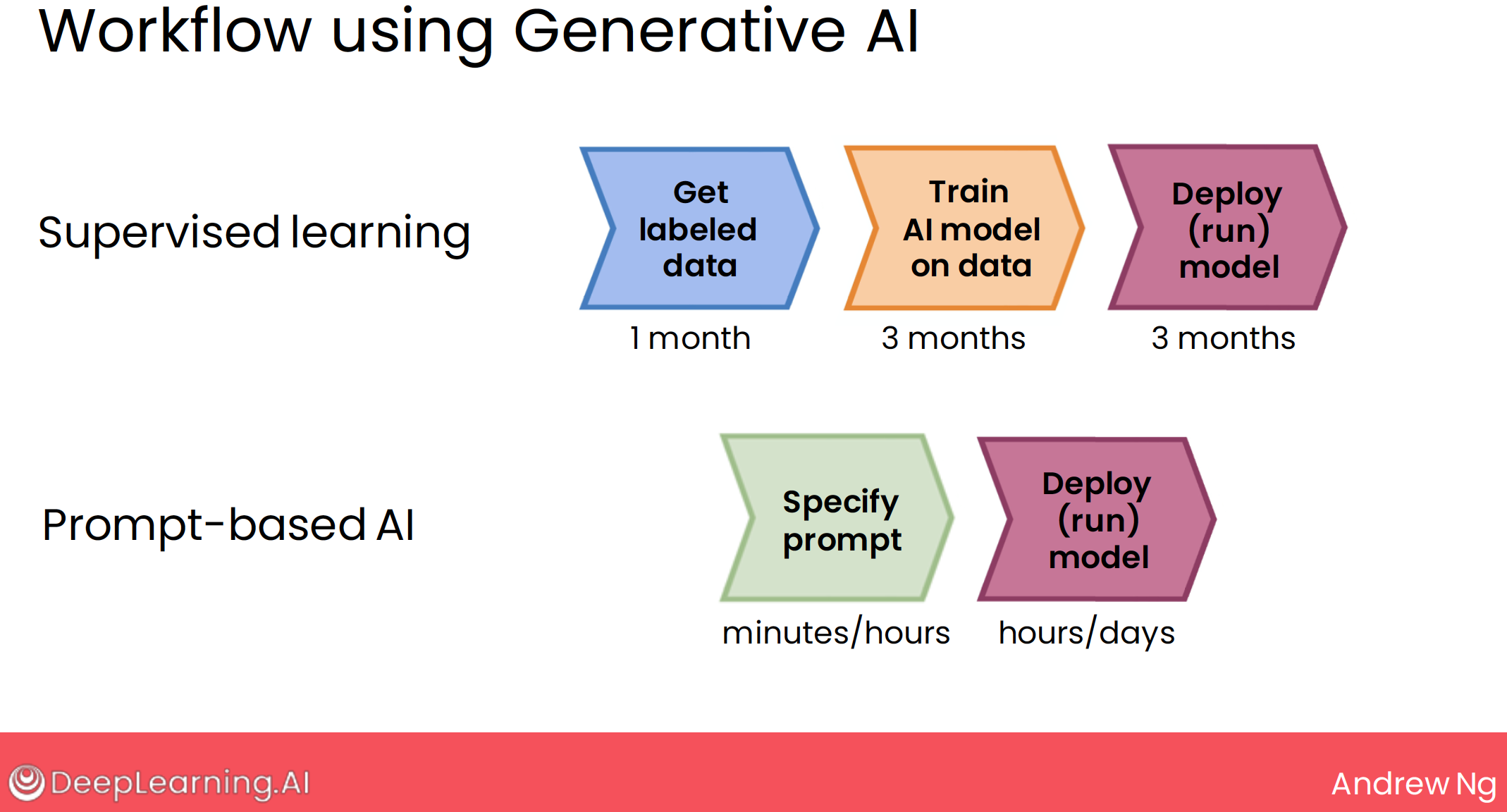
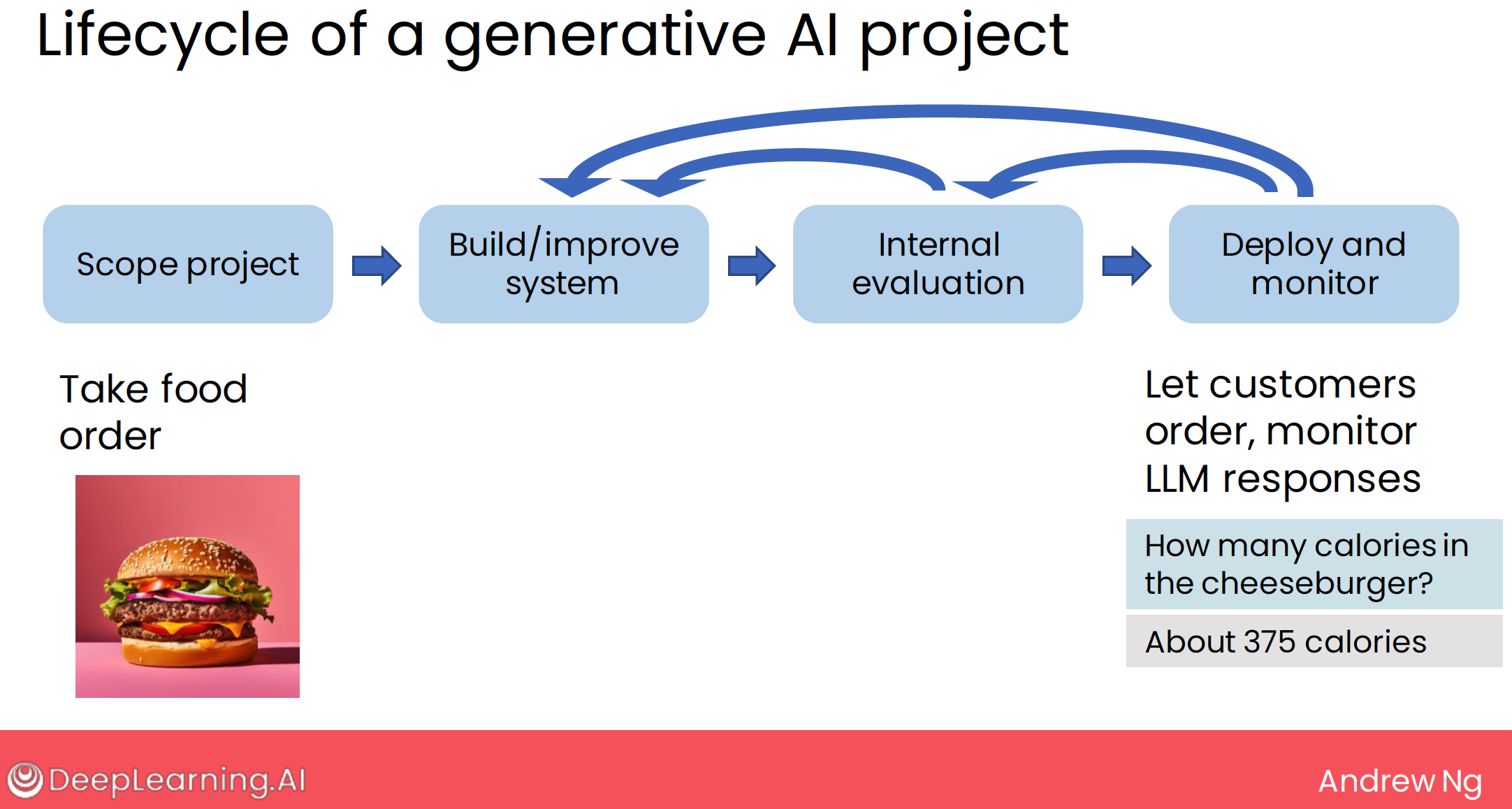
3 lifecycle of a GenAI project
4 tools to improve performance
Building Generative Al is a highly empirical or experimental process - we repeatedly find and fix mistakes.
4.1 prompting
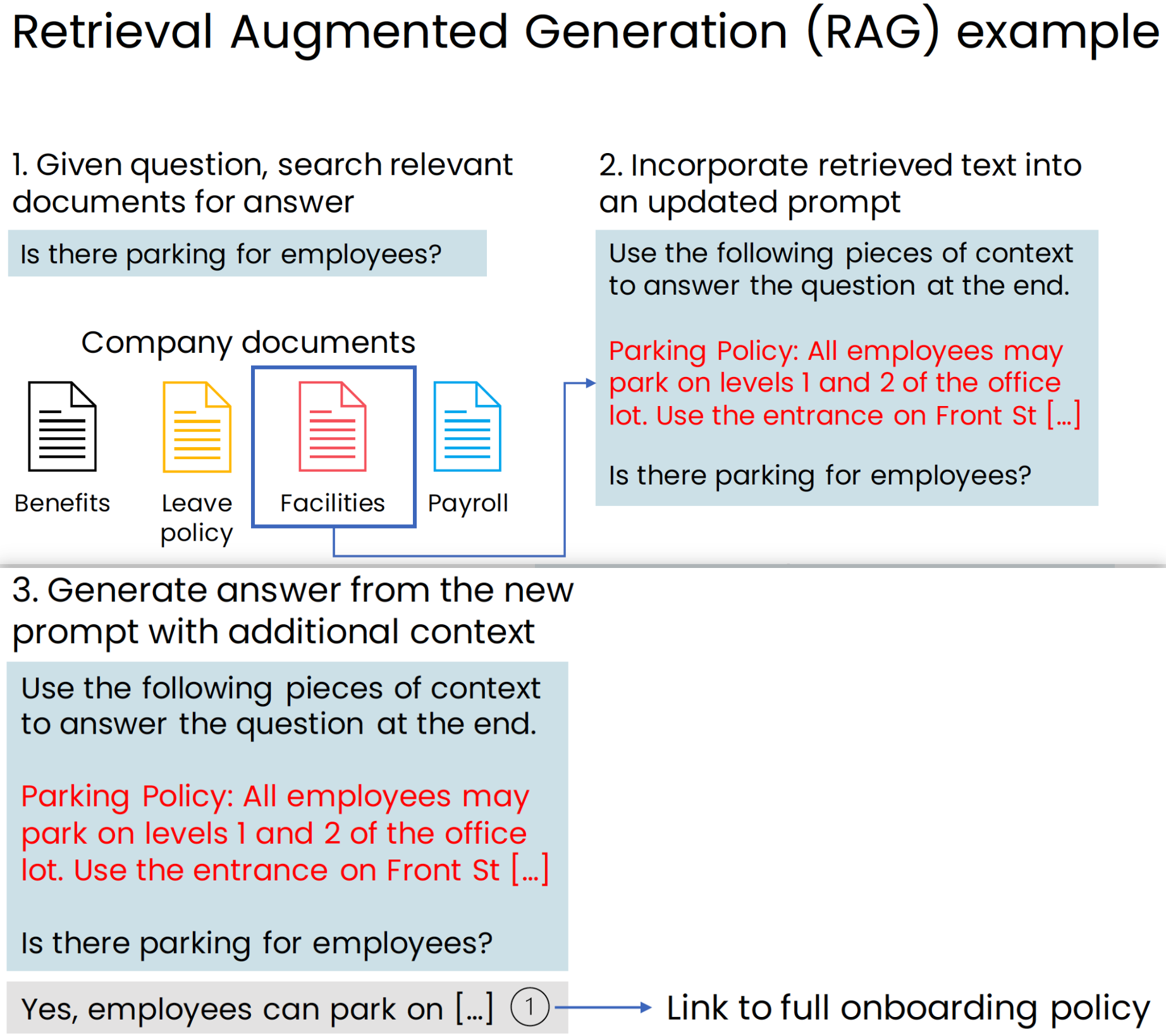
4.2 RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation)
summary: Give LLM access to external data sources
If you were to ask a general purpose chat system, such as one of the ones on the internet, a question like, is there parking for employees? It might answer something like, I need more specific information about your workplace because it doesn’t know what is the parking policy for your company.
But RAG or Retrieval Augmented Generation will see, is a technique that can give the LLM additional information so that if you ask it if there’s parking, it can refer to policies specific to your company.
RAG Retrieval Augmented Generation is an important technique that is enabling many LLMs to have context or to have information beyond what it may have learned on the open Internet.
RAG is used in many applications today:
- chat with pdf, excel, … file
- answer questions based on a website’s articles
- and excitingly, it seems to be transforming even web search.
Sometimes I would take a piece of text and just copy it into the prompt of an online web UI of an LLM and then tell it to use that context to generate an answer for me and that too can be an application of RAG.
4.3 Fine-tune models
summary: Adapt LLM to your task
why fine-tune?
4.3.1 input or context window length of the LLM is too small for your task
In particular, if you have context that is bigger, that can fit into the input length or the context window length of the LLM, then fine-tuning gives you another way to get LLM to absorb this information.
4.3.2 to carry out a task isn’t easy to define in a prompt.
- EX1: summarize in a specific style
- a well-done good LLM + about hundreds of carefully handwritten summaryies
- But if you additionally fine-tune it on maybe just hundreds of carefully handwritten summaries of the specific style, then that would shift the LLM’s ability to write summaries in the style that you want. The specific style summary is actually not that easy to define in a text prompt.
- EX2: Mimicking a write or speaking style
So if you were to prompt a general-purpose LLM and ask it to sound like me, you’d get texts like this, which I don’t think it sounds that much like me.
But if you were to take a lot of transcripts of the way I actually talk and have an LLM be fine-tuned to train it to really sound exactly like me by learning on my actual words, then asking it to write something that sounds like me results in texts like this, which I don’t know, that sounds more like how I would talk.
- EX3: let LLM response always positive or negative or even poetic
4.3.3 to help LLM gain specific knowledge
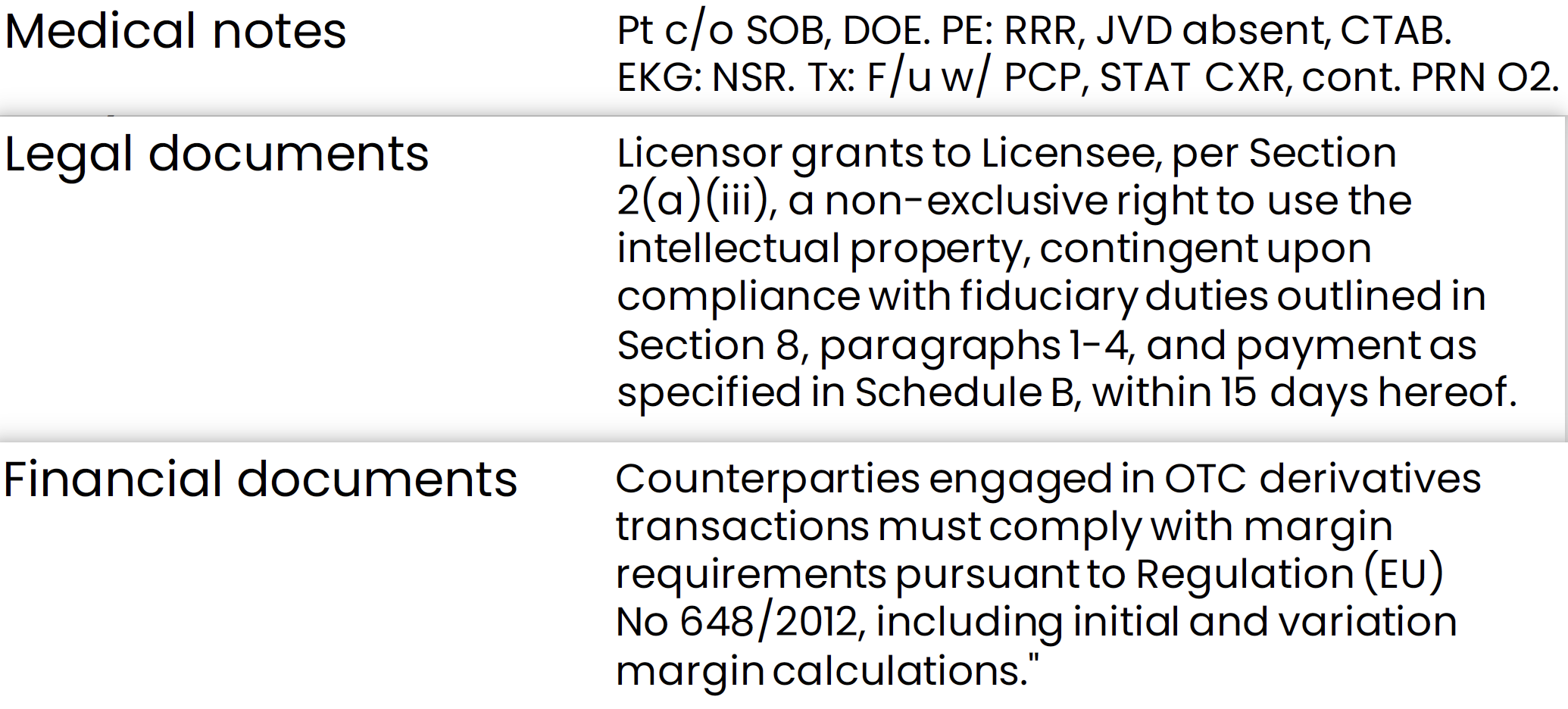
- medical notes
- legal documents
- financial documents
4.3.4 to get a smaller model to perform task
- large model: maybe 100B+ parameters, need gpu server
- small model: maybe 1B parameters, mobile/laptop/edge service
我们已经知道了:模型越大,结果越好。
所以我们需要根据我们的任务来选择合适的模型。这个稍后会说。
另一点,当我们要用模型来进行微调的时候,我们需要准备大约 500~1000 条数据。
4.4 Pretrain models
summary: Train LLM from scratch
- There’s another technique, pre-training your own model that turns out to be very expensive.
- today, almost no one other than reasonably large companies, usually tech companies are attempting this.
Many of the LLMs we’ve been using have been previously trained, or we say pretrained by some company, often by a big tech company.
But for building a specific application, given the time and expense of pretraining a model from scratch, I think of this as often an option of last resort. It could help if you have a highly specialized domain and a lot of data.
So, for many practical applications, unless you have a huge amount of resources and a huge amount of data, it may be more practical to start with an LLM that someone else had pretrained.
Say, a general purpose LLM that’s learned from a lot of internet data and that someone has open source, and then to fine tune that to your own data. And that will often give pretty decent performance, but in a much more economic way.
4.5 tools summary
It turns out that RAG and fine-tuning are both relatively cheap to implement.
RAG just is modifications of your prompt, fine-tuning, you might be able to get started with tens of dollars or maybe even hundreds of dollars depending on how much data you want to fine-tune on.
5 how to choose a model
5.1 model size
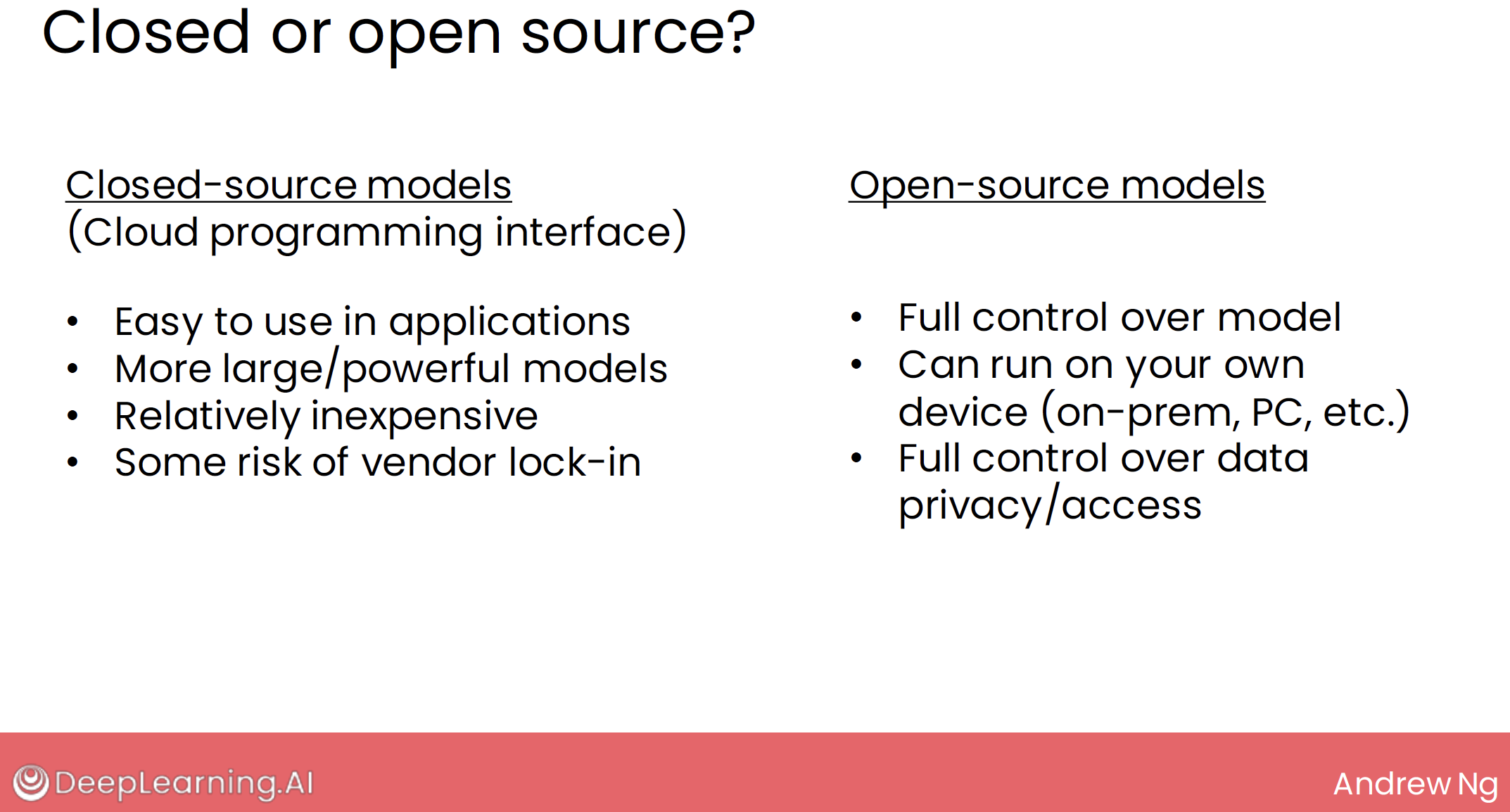
5.1 closed or open source
6 how LLM follow instructions
We’ve been thinking of LLMs as having learned from a lot of texts on the Internet to predict the next word.
But when you prompt an LLM, it doesn’t just predict the next word on the Internet, it actually follows your instructions. How does it do that?
6.1 instruction tuning
Let’s say if only study from internet, the next word or sentence of What is the capital of France?, may be the other question. like this pic. well, maybe it study from some questions database.
So how to solve it? Let’s see what the result will be.
How to carry out it?
it is a technique called instruction tuning.
In order to get an LLM to follow instructions and not just predict the next word, there’s a technique called instruction tuning, which is basically to take a pre-trained LLM and to fine tune it on examples of good answers to questions or good examples of the LLM following your instructions.
When you fine tune an LLM on a dataset of prompts and good responses that LLM will learn to not just predict the next word on the Internet, but to answer your questions and to follow your instructions.
6.2 RLHF (reinforcement learning from human feedback)
it turns out that there’s a technique called reinforcement learning from human feedback or RLHF, that can improve the quality of answers further.
the 3H response is the best answer.
3H: Helpful, Honest, Harmless
The reason this technique is called reinforcement learning from human feedback is because the scores correspond to the reinforcement or the reward that we’re giving the LLM for generating different answers.
By having the LLM learn to generate answers that merit higher scores or higher rewards or higher reinforcements, the LLM automatically learns to generate responses that are more helpful, honest, and harmless.
6.3 summary
So that’s how an LLM learns to follow instructions.
The first step is basically fine tuning, where you fine tune it to follow instructions and to answer questions, and then second is RLHF, reinforcement learning from human feedback to further train it to generate better answers.
7 LLM use tools and AI Agents
7.1 LLM use tools
LLM use tools, based on fine tune to format the output.
7.1.1 tools for taking actions
do the thing by fine tune LLM, and let the output be a standard format, then some content is for software, some content is for user response
And clearly, given that LLM’s outputs are not completely reliable for any safety critical or mission critical action, it would be a good idea to let a user confirm the desire action before letting the LLM trigger some potentially costly mistake by itself.
7.1.2 tools for taking reasoning
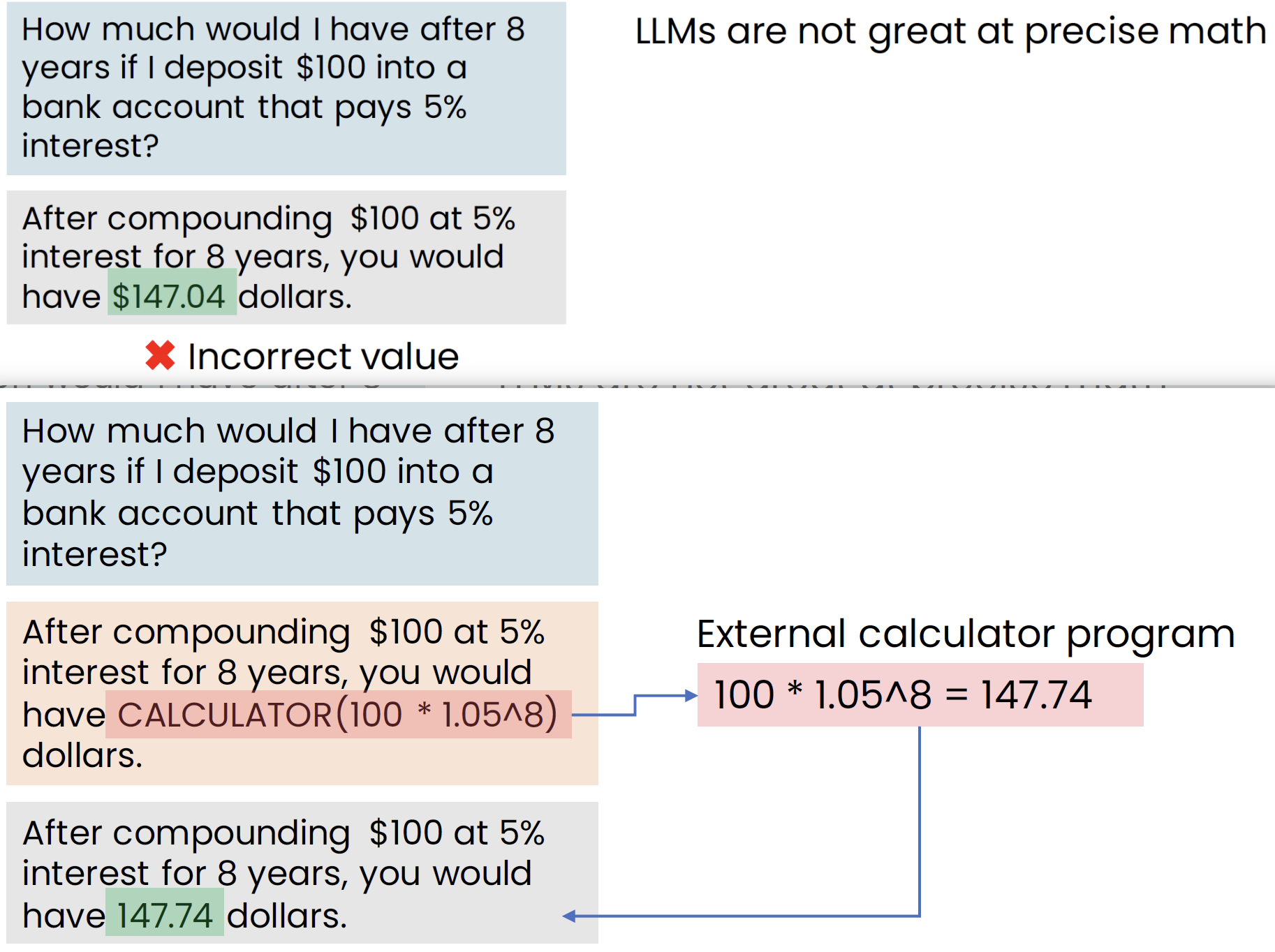
demo: tools to solve LLM not great at precise math
So by giving LLMs the ability to call tools in its output, we can significantly extend the reasoning or the action taking capabilities of LLMs.
Tool used today is an important part of many LLM applications and of course, designers of these applications should be careful to make sure that tools aren’t triggered in a way that causes harm or causes irreversible damage.
7.2 AI Agents
Agent的核心思想是使用语言模型来选择要采取的一系列操作。在Agent中,语言模型被用作推理引擎来确定要采取哪些操作以及按什么顺序。相比于传统机械或软件被动的“给予输入——>做出输出”的模式,Agent 由于更加强调自主的发现问题、确定目标、构想方案、选择方案、执行方案、检查更新的特性,因此可以被认为是一类拥有“自主智能的实体”,而被广泛称之为智能体。